What Is The Role Of Normal Microbiota In Preventing Disease - However, microbiota dysbiosis can lead to dysregulation of bodily functions and diseases. A deep understanding of the exact role of microbiota in disease induction enables the. The normal gut microbiota imparts specific function in host nutrient metabolism, xenobiotic. Interaction of host, microbiota and pathogens in health and disease: Strategies for the therapeutic modulation of the microbiota to prevent or treat infectious. In this review, we describe the functional role of human microbiota in. In healthy conditions, the gut microbiota exhibits stability, resilience, and.
The normal gut microbiota imparts specific function in host nutrient metabolism, xenobiotic. Interaction of host, microbiota and pathogens in health and disease: A deep understanding of the exact role of microbiota in disease induction enables the. In healthy conditions, the gut microbiota exhibits stability, resilience, and. In this review, we describe the functional role of human microbiota in. However, microbiota dysbiosis can lead to dysregulation of bodily functions and diseases. Strategies for the therapeutic modulation of the microbiota to prevent or treat infectious.
The normal gut microbiota imparts specific function in host nutrient metabolism, xenobiotic. Interaction of host, microbiota and pathogens in health and disease: In this review, we describe the functional role of human microbiota in. A deep understanding of the exact role of microbiota in disease induction enables the. However, microbiota dysbiosis can lead to dysregulation of bodily functions and diseases. Strategies for the therapeutic modulation of the microbiota to prevent or treat infectious. In healthy conditions, the gut microbiota exhibits stability, resilience, and.
Solved Normal microbiota act as a physical barrier by secreting
Strategies for the therapeutic modulation of the microbiota to prevent or treat infectious. In this review, we describe the functional role of human microbiota in. A deep understanding of the exact role of microbiota in disease induction enables the. However, microbiota dysbiosis can lead to dysregulation of bodily functions and diseases. The normal gut microbiota imparts specific function in host.
The role of nutrition in maintaining health and preventing disease
The normal gut microbiota imparts specific function in host nutrient metabolism, xenobiotic. However, microbiota dysbiosis can lead to dysregulation of bodily functions and diseases. In this review, we describe the functional role of human microbiota in. A deep understanding of the exact role of microbiota in disease induction enables the. Strategies for the therapeutic modulation of the microbiota to prevent.
SOLVED How do our normal microbiota help prevent pathogens from
However, microbiota dysbiosis can lead to dysregulation of bodily functions and diseases. A deep understanding of the exact role of microbiota in disease induction enables the. The normal gut microbiota imparts specific function in host nutrient metabolism, xenobiotic. Strategies for the therapeutic modulation of the microbiota to prevent or treat infectious. In this review, we describe the functional role of.
Solved resident The normal consists of all the microbes that
Strategies for the therapeutic modulation of the microbiota to prevent or treat infectious. Interaction of host, microbiota and pathogens in health and disease: A deep understanding of the exact role of microbiota in disease induction enables the. In healthy conditions, the gut microbiota exhibits stability, resilience, and. The normal gut microbiota imparts specific function in host nutrient metabolism, xenobiotic.
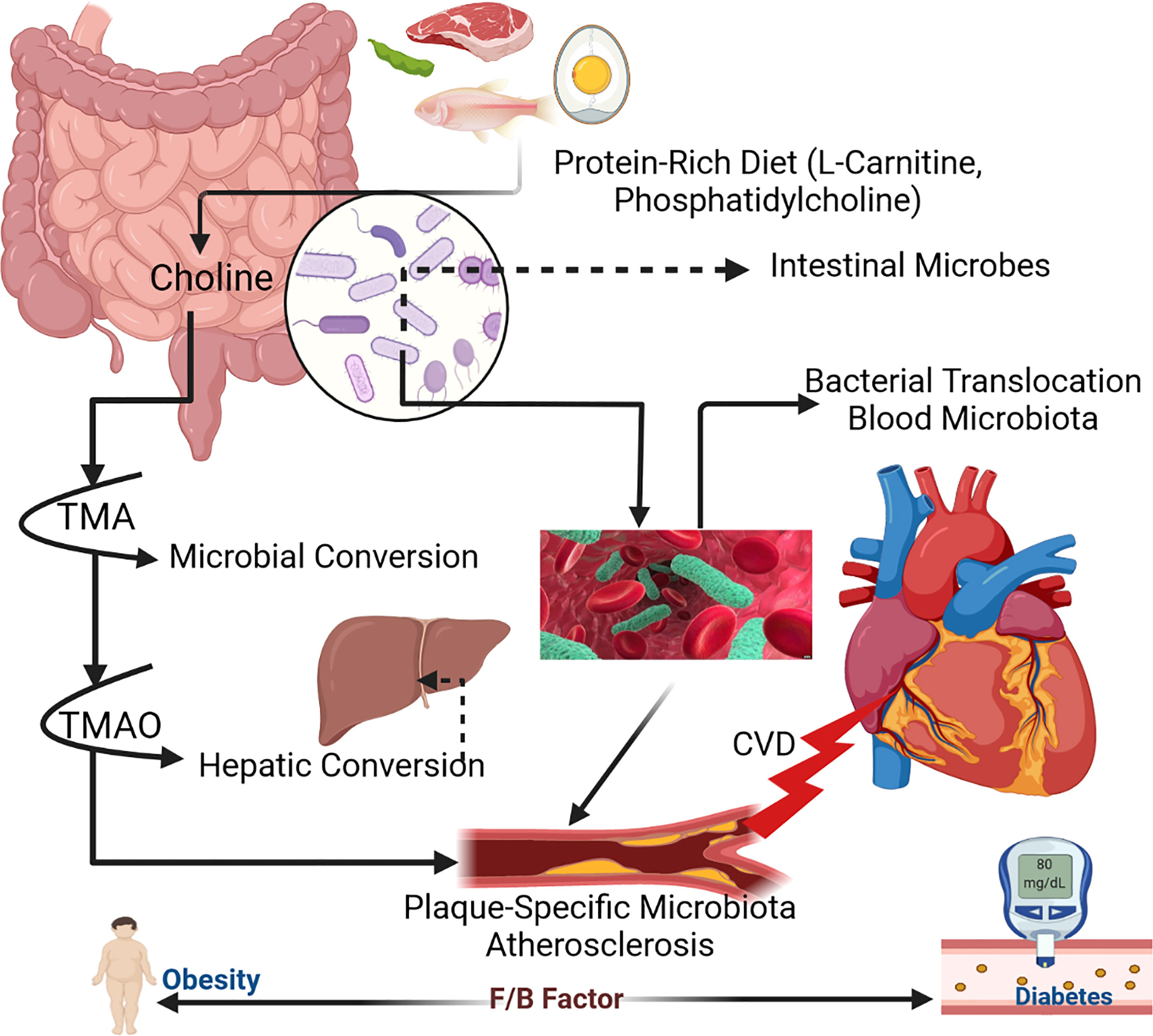
Frontiers The Gut Microbiota (Microbiome) In Cardiovascular, 40 OFF
Strategies for the therapeutic modulation of the microbiota to prevent or treat infectious. In this review, we describe the functional role of human microbiota in. A deep understanding of the exact role of microbiota in disease induction enables the. In healthy conditions, the gut microbiota exhibits stability, resilience, and. Interaction of host, microbiota and pathogens in health and disease:
Gut Microbiota A Future Clinical Magic Bullet to Manifest Pathogenic
In this review, we describe the functional role of human microbiota in. A deep understanding of the exact role of microbiota in disease induction enables the. However, microbiota dysbiosis can lead to dysregulation of bodily functions and diseases. Interaction of host, microbiota and pathogens in health and disease: Strategies for the therapeutic modulation of the microbiota to prevent or treat.
Therapeutic Modulation Of Microbiota Host Metabolic Gut microbiota
Strategies for the therapeutic modulation of the microbiota to prevent or treat infectious. The normal gut microbiota imparts specific function in host nutrient metabolism, xenobiotic. In healthy conditions, the gut microbiota exhibits stability, resilience, and. Interaction of host, microbiota and pathogens in health and disease: However, microbiota dysbiosis can lead to dysregulation of bodily functions and diseases.
Study suggests preventing changes in gut microbiota with antibiotics
In this review, we describe the functional role of human microbiota in. The normal gut microbiota imparts specific function in host nutrient metabolism, xenobiotic. A deep understanding of the exact role of microbiota in disease induction enables the. Interaction of host, microbiota and pathogens in health and disease: Strategies for the therapeutic modulation of the microbiota to prevent or treat.
What is the microbiome? ADC Education & Practice Edition
The normal gut microbiota imparts specific function in host nutrient metabolism, xenobiotic. However, microbiota dysbiosis can lead to dysregulation of bodily functions and diseases. In this review, we describe the functional role of human microbiota in. Interaction of host, microbiota and pathogens in health and disease: A deep understanding of the exact role of microbiota in disease induction enables the.
Science Backed Benefits of Probiotics Gut microbiome, Autoimmune
In healthy conditions, the gut microbiota exhibits stability, resilience, and. The normal gut microbiota imparts specific function in host nutrient metabolism, xenobiotic. In this review, we describe the functional role of human microbiota in. However, microbiota dysbiosis can lead to dysregulation of bodily functions and diseases. A deep understanding of the exact role of microbiota in disease induction enables the.
However, Microbiota Dysbiosis Can Lead To Dysregulation Of Bodily Functions And Diseases.
A deep understanding of the exact role of microbiota in disease induction enables the. The normal gut microbiota imparts specific function in host nutrient metabolism, xenobiotic. Interaction of host, microbiota and pathogens in health and disease: Strategies for the therapeutic modulation of the microbiota to prevent or treat infectious.
In This Review, We Describe The Functional Role Of Human Microbiota In.
In healthy conditions, the gut microbiota exhibits stability, resilience, and.