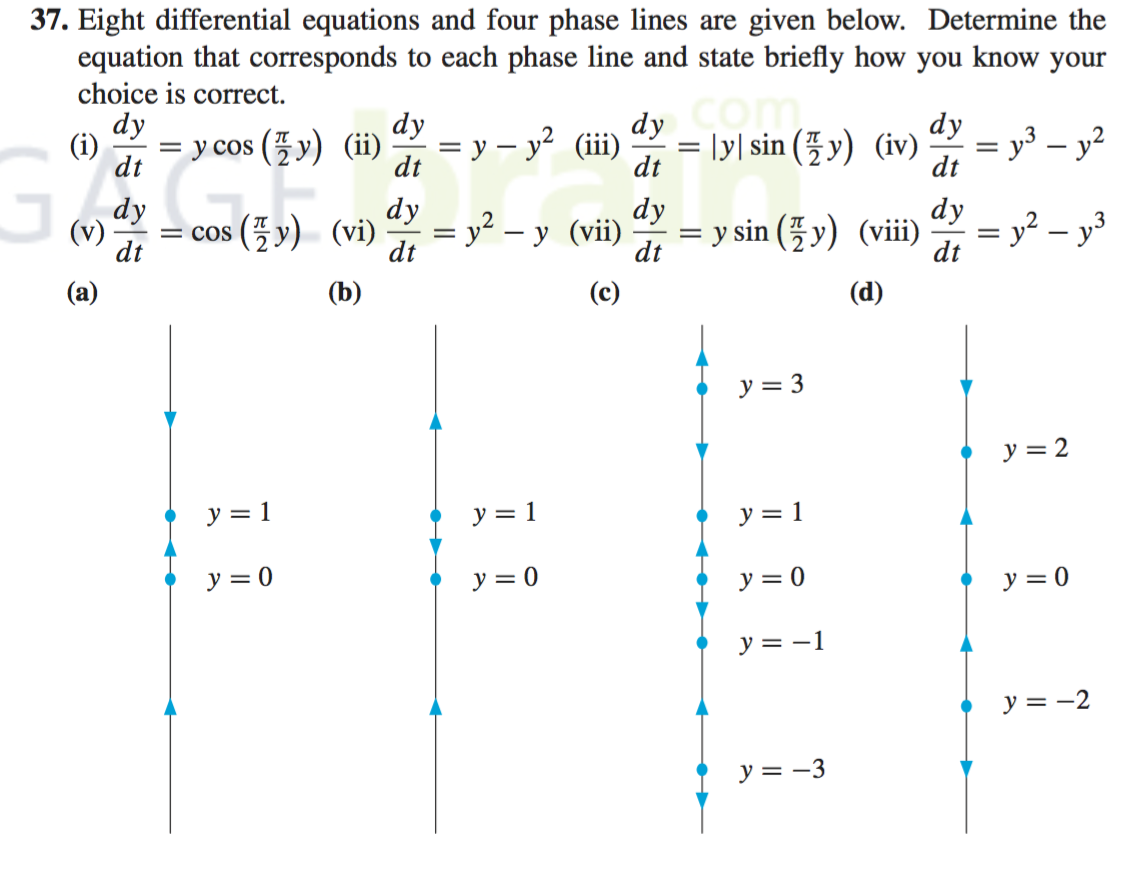
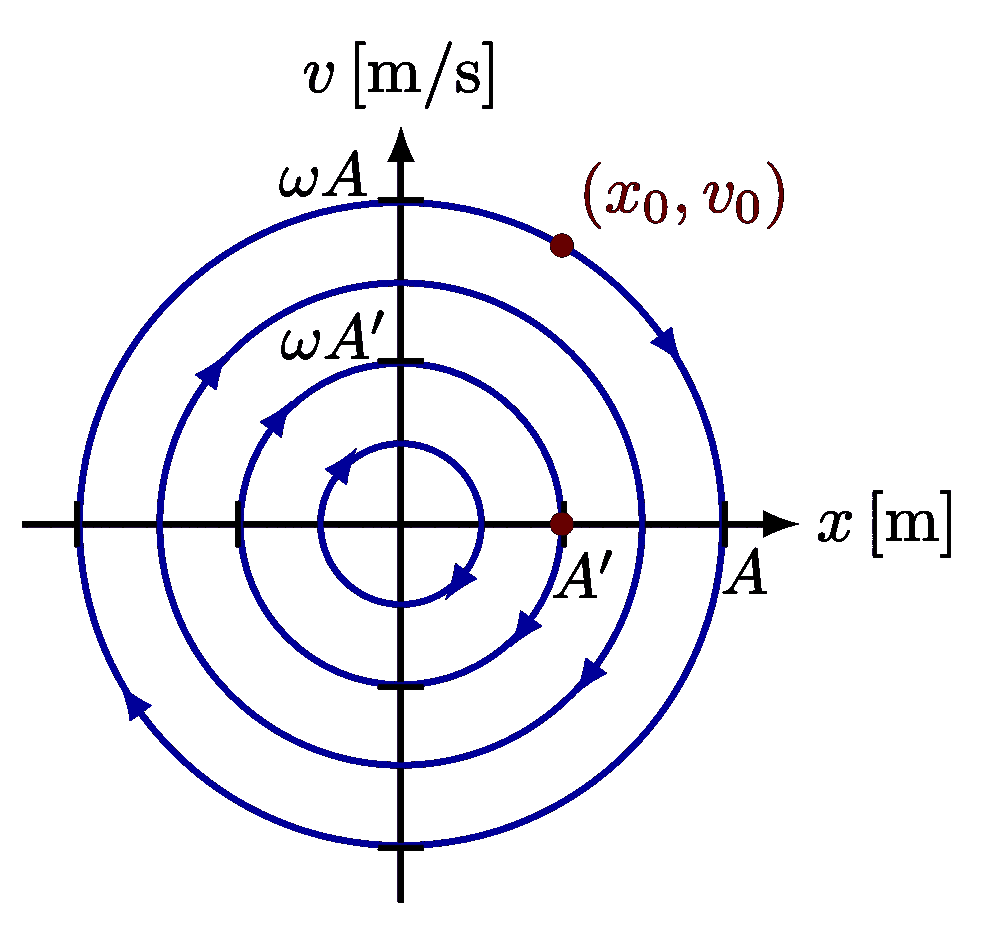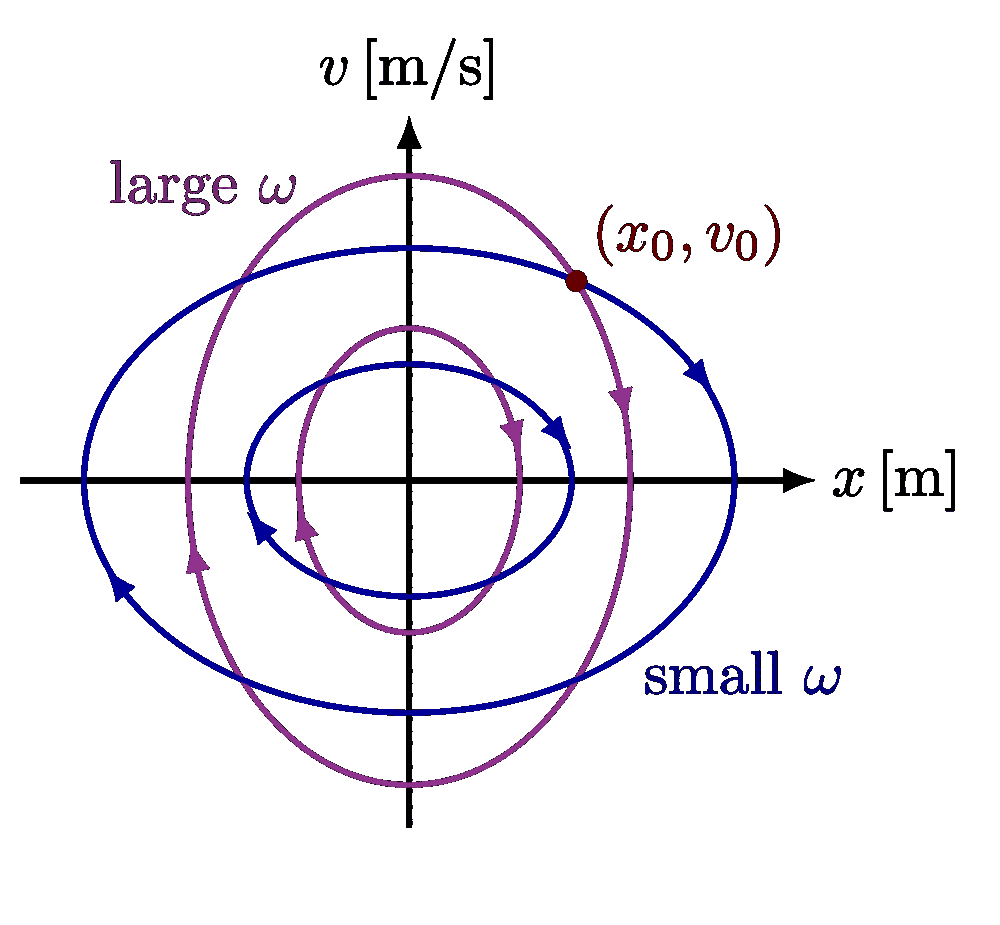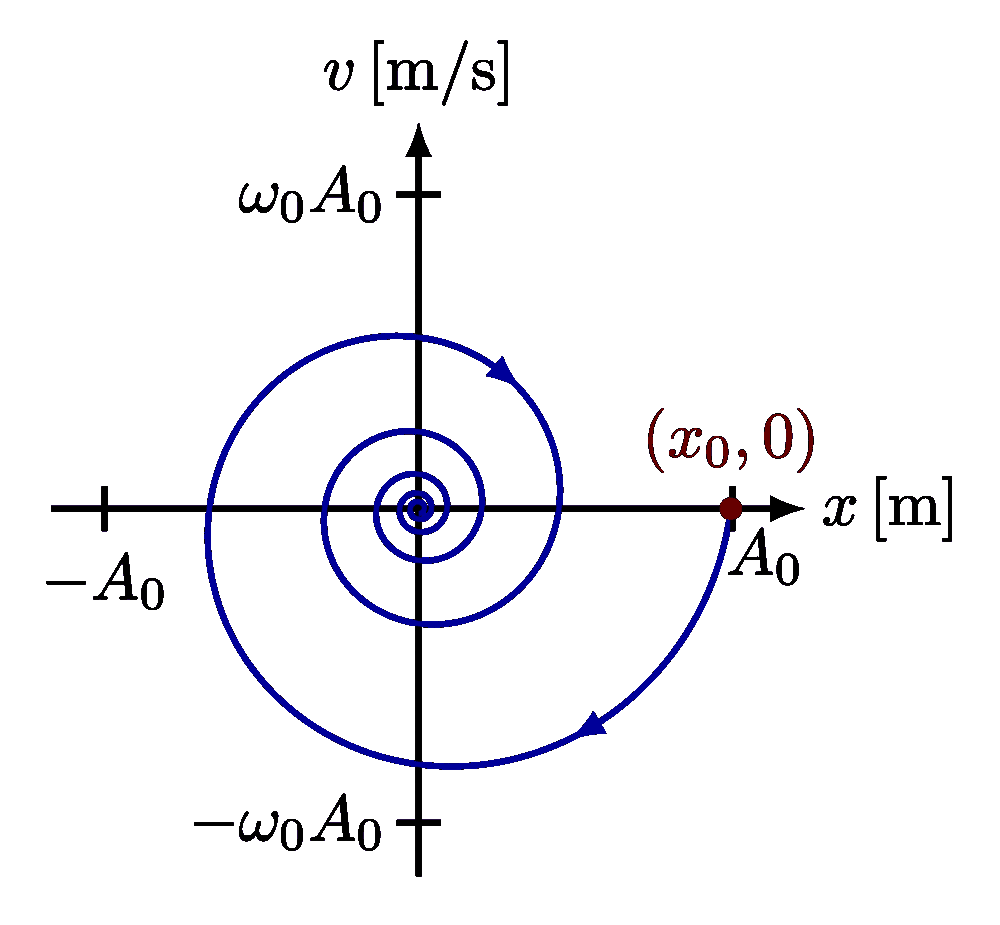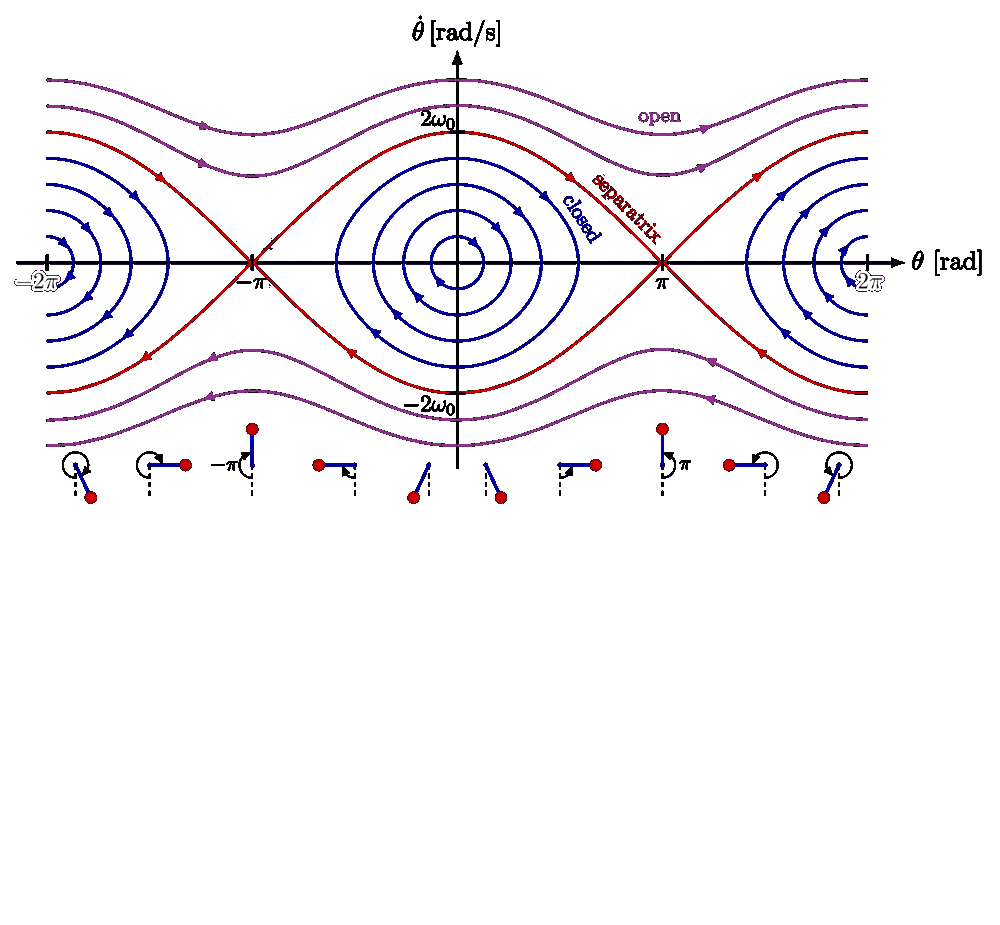
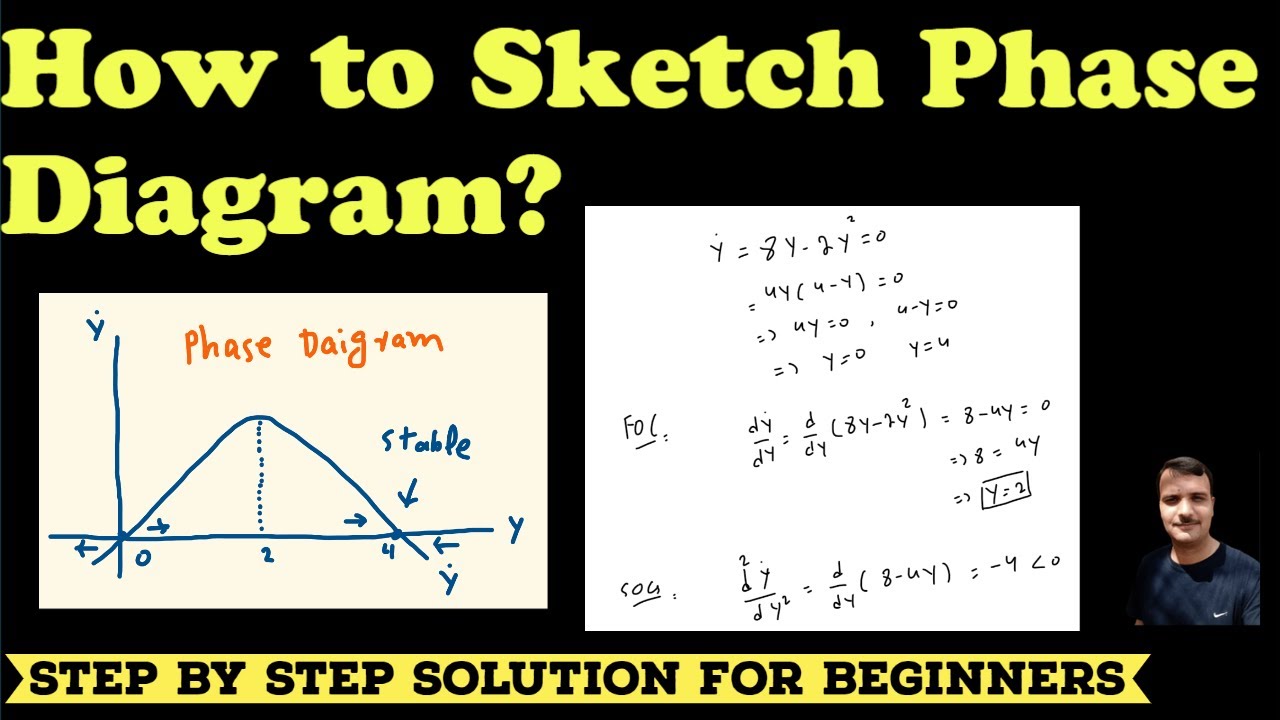
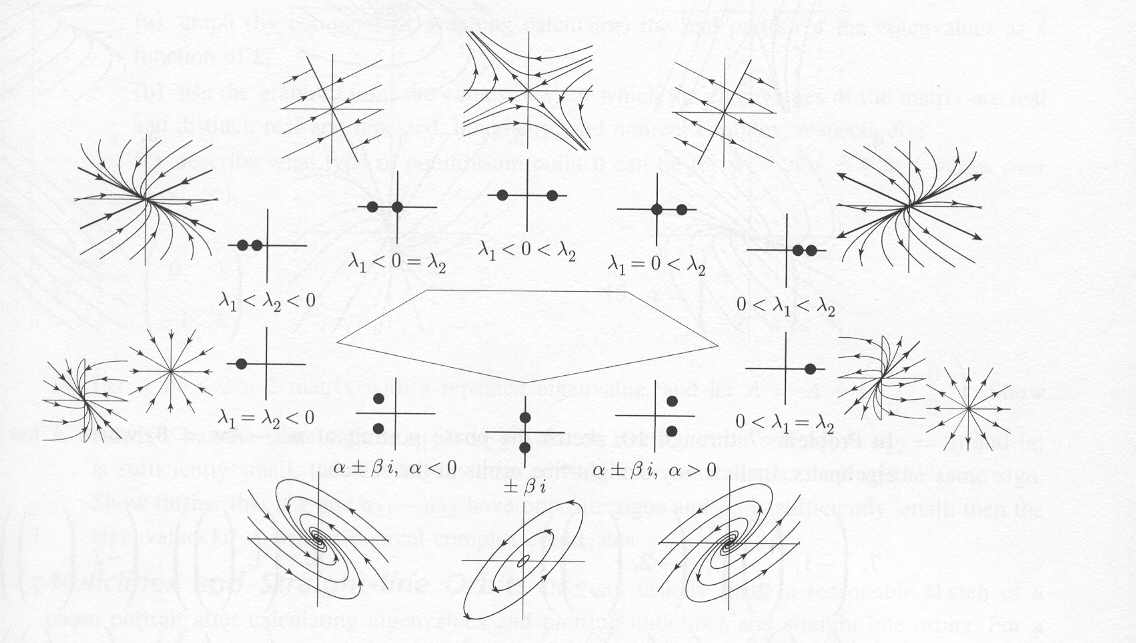
Phase Line Differential Equations - In each of the intervals delimited by the equilibria draw an upward pointing arrow if f (y) > 0 and a downward pointing arrow if f (y) < 0. A plot of (x(t);y(t)) is a solution of (2) is a curve in the plane,. In this section we will give a brief introduction to the phase plane and phase portraits. Draw the phase line for the following equations for several values of the parameter a. Choose one value of a for every possible qualitatively. Let us review what the phase plane equation tells us and what it does not tell us.
Draw the phase line for the following equations for several values of the parameter a. In this section we will give a brief introduction to the phase plane and phase portraits. Let us review what the phase plane equation tells us and what it does not tell us. Choose one value of a for every possible qualitatively. In each of the intervals delimited by the equilibria draw an upward pointing arrow if f (y) > 0 and a downward pointing arrow if f (y) < 0. A plot of (x(t);y(t)) is a solution of (2) is a curve in the plane,.
Let us review what the phase plane equation tells us and what it does not tell us. In each of the intervals delimited by the equilibria draw an upward pointing arrow if f (y) > 0 and a downward pointing arrow if f (y) < 0. Choose one value of a for every possible qualitatively. In this section we will give a brief introduction to the phase plane and phase portraits. A plot of (x(t);y(t)) is a solution of (2) is a curve in the plane,. Draw the phase line for the following equations for several values of the parameter a.
Differential Equations Phase Diagrams Differential Equation
Draw the phase line for the following equations for several values of the parameter a. Choose one value of a for every possible qualitatively. Let us review what the phase plane equation tells us and what it does not tell us. In each of the intervals delimited by the equilibria draw an upward pointing arrow if f (y) > 0.
Understanding Phase Diagrams A Comprehensive Calculator for
In each of the intervals delimited by the equilibria draw an upward pointing arrow if f (y) > 0 and a downward pointing arrow if f (y) < 0. A plot of (x(t);y(t)) is a solution of (2) is a curve in the plane,. Draw the phase line for the following equations for several values of the parameter a. Choose.
differential equations
In each of the intervals delimited by the equilibria draw an upward pointing arrow if f (y) > 0 and a downward pointing arrow if f (y) < 0. A plot of (x(t);y(t)) is a solution of (2) is a curve in the plane,. In this section we will give a brief introduction to the phase plane and phase portraits..
Differential Equations Phase Diagram
Let us review what the phase plane equation tells us and what it does not tell us. Choose one value of a for every possible qualitatively. In this section we will give a brief introduction to the phase plane and phase portraits. Draw the phase line for the following equations for several values of the parameter a. A plot of.
Phase Diagram Calculator Differential Equations
Choose one value of a for every possible qualitatively. In each of the intervals delimited by the equilibria draw an upward pointing arrow if f (y) > 0 and a downward pointing arrow if f (y) < 0. In this section we will give a brief introduction to the phase plane and phase portraits. Draw the phase line for the.
Plotting Differential Equation Phase Diagrams Mathematics Stack
In each of the intervals delimited by the equilibria draw an upward pointing arrow if f (y) > 0 and a downward pointing arrow if f (y) < 0. Choose one value of a for every possible qualitatively. A plot of (x(t);y(t)) is a solution of (2) is a curve in the plane,. In this section we will give a.
phase diagram differential equations Earth Shack
A plot of (x(t);y(t)) is a solution of (2) is a curve in the plane,. Choose one value of a for every possible qualitatively. In each of the intervals delimited by the equilibria draw an upward pointing arrow if f (y) > 0 and a downward pointing arrow if f (y) < 0. In this section we will give a.
Phase Diagram Straight Line Solutions Differential Equations
A plot of (x(t);y(t)) is a solution of (2) is a curve in the plane,. Draw the phase line for the following equations for several values of the parameter a. Let us review what the phase plane equation tells us and what it does not tell us. In this section we will give a brief introduction to the phase plane.
Differential Equations Phase Diagram
In this section we will give a brief introduction to the phase plane and phase portraits. In each of the intervals delimited by the equilibria draw an upward pointing arrow if f (y) > 0 and a downward pointing arrow if f (y) < 0. Draw the phase line for the following equations for several values of the parameter a..
SOLUTION Differential Equations Phase Planes and Stability Studypool
Let us review what the phase plane equation tells us and what it does not tell us. Choose one value of a for every possible qualitatively. A plot of (x(t);y(t)) is a solution of (2) is a curve in the plane,. In each of the intervals delimited by the equilibria draw an upward pointing arrow if f (y) > 0.
Draw The Phase Line For The Following Equations For Several Values Of The Parameter A.
In this section we will give a brief introduction to the phase plane and phase portraits. A plot of (x(t);y(t)) is a solution of (2) is a curve in the plane,. Choose one value of a for every possible qualitatively. Let us review what the phase plane equation tells us and what it does not tell us.