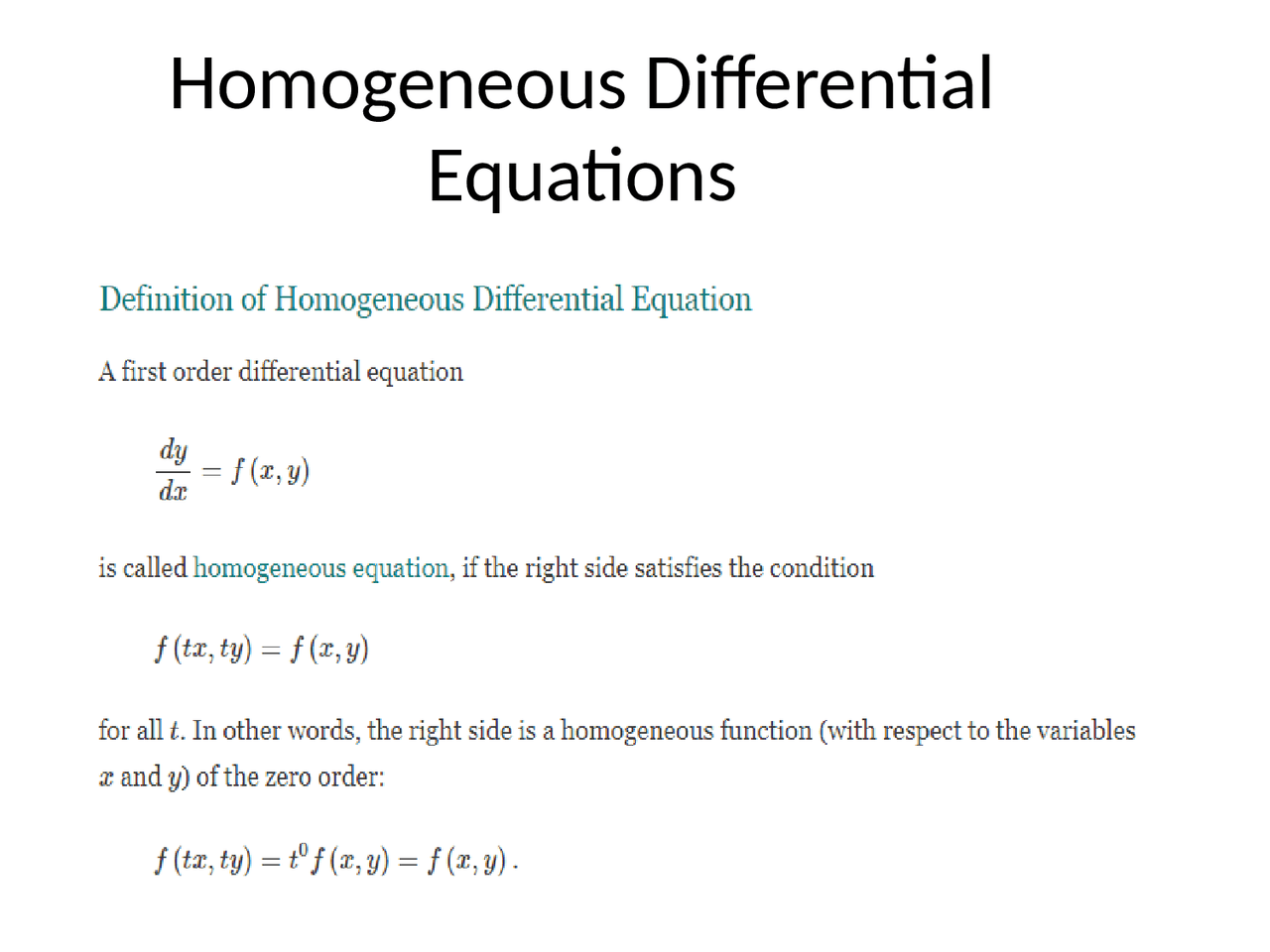
Examples Of Homogeneous Differential Equations - An equation with the function y and its derivative dy dx. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g (x, y) is called homogeneous differential equation if f (x,. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the function f(x, y) is a homogeneous function of. A first‐order differential equation is said to be homogeneous if m( x,y) and n( x,y) are both homogeneous functions of the same degree. Let us show you two examples to demonstrate how a differential equation looks when it is homogeneous and when it is non. Learn to solve the homogeneous equation of. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential.
A first‐order differential equation is said to be homogeneous if m( x,y) and n( x,y) are both homogeneous functions of the same degree. Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential. A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g (x, y) is called homogeneous differential equation if f (x,. Let us show you two examples to demonstrate how a differential equation looks when it is homogeneous and when it is non. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. An equation with the function y and its derivative dy dx. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the function f(x, y) is a homogeneous function of. Learn to solve the homogeneous equation of. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree.
A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g (x, y) is called homogeneous differential equation if f (x,. Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential. Learn to solve the homogeneous equation of. Let us show you two examples to demonstrate how a differential equation looks when it is homogeneous and when it is non. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the function f(x, y) is a homogeneous function of. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. A first‐order differential equation is said to be homogeneous if m( x,y) and n( x,y) are both homogeneous functions of the same degree. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. An equation with the function y and its derivative dy dx.
2nd Order Homogeneous Equations
A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g (x, y) is called homogeneous differential equation if f (x,. Learn to solve the homogeneous equation of. Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. In this section we will extend the ideas.
Solved 1. Solve the homogeneous differential equations
In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. Let us show you two examples to demonstrate how a differential equation looks when it is homogeneous and when it is non. Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential. An equation with the function y and its derivative.
Homogeneous Differential Equations Docsity
Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential. Learn to solve the homogeneous equation of. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. An equation with the function y and its derivative dy dx. Let us show you two examples to demonstrate how a differential equation looks when it is homogeneous and when.
Homogeneous Differential Equation2 PDF Waves Applied And
A first‐order differential equation is said to be homogeneous if m( x,y) and n( x,y) are both homogeneous functions of the same degree. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. Learn to solve the homogeneous equation of. Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential. Let.
Particular Solution of NonHomogeneous Differential Equations Mr
Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. A first‐order differential equation is said to be homogeneous if m( x,y) and n( x,y) are both homogeneous functions of the same degree. Let us show you two examples to demonstrate.
[Solved] Solve the HOMOGENEOUS differential equation in step by step
Let us show you two examples to demonstrate how a differential equation looks when it is homogeneous and when it is non. A first‐order differential equation is said to be homogeneous if m( x,y) and n( x,y) are both homogeneous functions of the same degree. An equation with the function y and its derivative dy dx. A differential equation of.
[Solved] Determine whether the given differential equations are
Learn to solve the homogeneous equation of. Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the function f(x, y) is a homogeneous function.
[Solved] find the general solution of this homogeneous differential
Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g (x, y) is called homogeneous differential equation if f (x,. An equation with the function y and its derivative dy dx. Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential. Learn to solve the.
[Solved] find the general solution of this homogeneous differential
A first‐order differential equation is said to be homogeneous if m( x,y) and n( x,y) are both homogeneous functions of the same degree. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the function f(x, y) is a homogeneous function of. Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential. A.
Solved Solve the following homogeneous differential
Learn to solve the homogeneous equation of. An equation with the function y and its derivative dy dx. Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher.
Homogeneous Differential Equation Are The Equations Having Functions Of The Same Degree.
Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the function f(x, y) is a homogeneous function of. A first‐order differential equation is said to be homogeneous if m( x,y) and n( x,y) are both homogeneous functions of the same degree. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher.
An Equation With The Function Y And Its Derivative Dy Dx.
Learn to solve the homogeneous equation of. Let us show you two examples to demonstrate how a differential equation looks when it is homogeneous and when it is non. A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g (x, y) is called homogeneous differential equation if f (x,.