Implicit Vs Explicit Solution Differential Equations - Math 2233 (differential equations) lecture 2 section 1.2 solutions and initial value problems. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; • it describes the relation between an. Then an equation of the form. Differential equations • what is a differential equation? A function f(x) that when substituted for y in f(x, y, dy/dx,. Let f be a given function of x, y, and derivatives of y. Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an.
Let f be a given function of x, y, and derivatives of y. A function f(x) that when substituted for y in f(x, y, dy/dx,. Math 2233 (differential equations) lecture 2 section 1.2 solutions and initial value problems. • it describes the relation between an. Differential equations • what is a differential equation? The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an. Then an equation of the form.
Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an. • it describes the relation between an. Then an equation of the form. Let f be a given function of x, y, and derivatives of y. A function f(x) that when substituted for y in f(x, y, dy/dx,. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Differential equations • what is a differential equation? Math 2233 (differential equations) lecture 2 section 1.2 solutions and initial value problems.
(PDF) An explicit solution to a system of implicit differential equations
Let f be a given function of x, y, and derivatives of y. Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; A function f(x) that when substituted for y in f(x, y, dy/dx,. Math 2233 (differential equations).
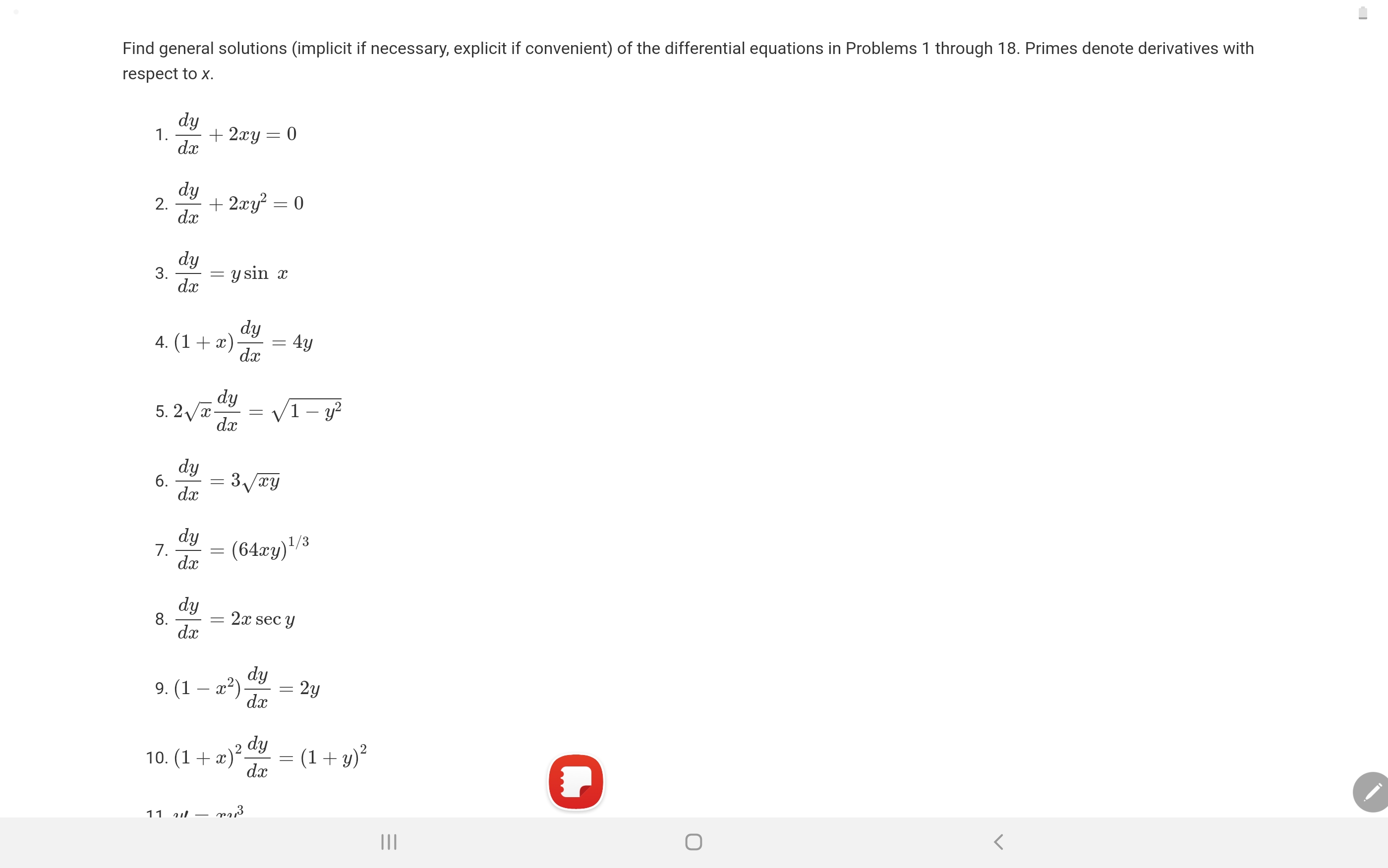
Solved Find general solutions (implicit if necessary,
Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an. A function f(x) that when substituted for y in f(x, y, dy/dx,. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Math 2233 (differential equations) lecture 2 section 1.2 solutions and initial value problems. Let f be a.
PPT Explicit vs Implicit Functions PowerPoint Presentation ID2752802
Math 2233 (differential equations) lecture 2 section 1.2 solutions and initial value problems. • it describes the relation between an. Then an equation of the form. Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an. A function f(x) that when substituted for y in f(x, y, dy/dx,.
Ordinary Differential Equations (A Comprehensive Resource)
A function f(x) that when substituted for y in f(x, y, dy/dx,. Then an equation of the form. Differential equations • what is a differential equation? • it describes the relation between an. Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an.
Explicit vs. Implicit Reading Between the Lines ESLBUZZ
• it describes the relation between an. Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an. A function f(x) that when substituted for y in f(x, y, dy/dx,. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Math 2233 (differential equations) lecture 2 section 1.2 solutions and.
Solved Find general solutions (implicit if necessary,
The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an. Math 2233 (differential equations) lecture 2 section 1.2 solutions and initial value problems. Then an equation of the form. Let f be a given function of x, y, and.
Implicit vs Explicit Analysis What is the difference? FEA Tips
• it describes the relation between an. Differential equations • what is a differential equation? Math 2233 (differential equations) lecture 2 section 1.2 solutions and initial value problems. Then an equation of the form. Let f be a given function of x, y, and derivatives of y.
ordinary differential equations Implicit solution of ODE to explicit
• it describes the relation between an. Math 2233 (differential equations) lecture 2 section 1.2 solutions and initial value problems. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Then an equation of the form. Let f be a given function of x, y, and derivatives of y.
Differential Equations Ordinary differential equation ODE Partial
Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an. Then an equation of the form. A function f(x) that when substituted for y in f(x, y, dy/dx,. Math 2233 (differential equations) lecture 2 section 1.2 solutions and initial value problems. Differential equations • what is a differential.
Solved A) Determine the implicit and explicit form of
Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an. Then an equation of the form. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Math 2233 (differential equations) lecture 2 section 1.2 solutions and initial value problems. • it describes the relation between an.
Thus, If A Differential Equation Of Order N Has The Form F(X, Y', Y'',.Y (N)) = 0, Then It Is Called An.
The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Differential equations • what is a differential equation? Then an equation of the form. • it describes the relation between an.
Math 2233 (Differential Equations) Lecture 2 Section 1.2 Solutions And Initial Value Problems.
A function f(x) that when substituted for y in f(x, y, dy/dx,. Let f be a given function of x, y, and derivatives of y.