Wronskian Of A Differential Equation - We’ll start by noticing that if the original equation is true, then if we differentiate. To demonstrate that the wronskian either vanishes for all values of x or it is never equal. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to. If the wronskian of f f and g g is tcos(t)+ sin(t) t cos (t) + sin (t), and if u = f − 3g u = f − 3 g and v.
We’ll start by noticing that if the original equation is true, then if we differentiate. To demonstrate that the wronskian either vanishes for all values of x or it is never equal. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to. If the wronskian of f f and g g is tcos(t)+ sin(t) t cos (t) + sin (t), and if u = f − 3g u = f − 3 g and v.
To demonstrate that the wronskian either vanishes for all values of x or it is never equal. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to. If the wronskian of f f and g g is tcos(t)+ sin(t) t cos (t) + sin (t), and if u = f − 3g u = f − 3 g and v. We’ll start by noticing that if the original equation is true, then if we differentiate.
Solving 2nd Order non homogeneous differential equation using Wronskian
We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to. We’ll start by noticing that if the original equation is true, then if we differentiate. If the wronskian of f f and g g is tcos(t)+ sin(t) t cos (t) + sin (t), and if u = f − 3g u = f − 3 g.
Wronskian, differential, determinant
We’ll start by noticing that if the original equation is true, then if we differentiate. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to. To demonstrate that the wronskian either vanishes for all values of x or it is never equal. If the wronskian of f f and g g is tcos(t)+ sin(t) t cos.
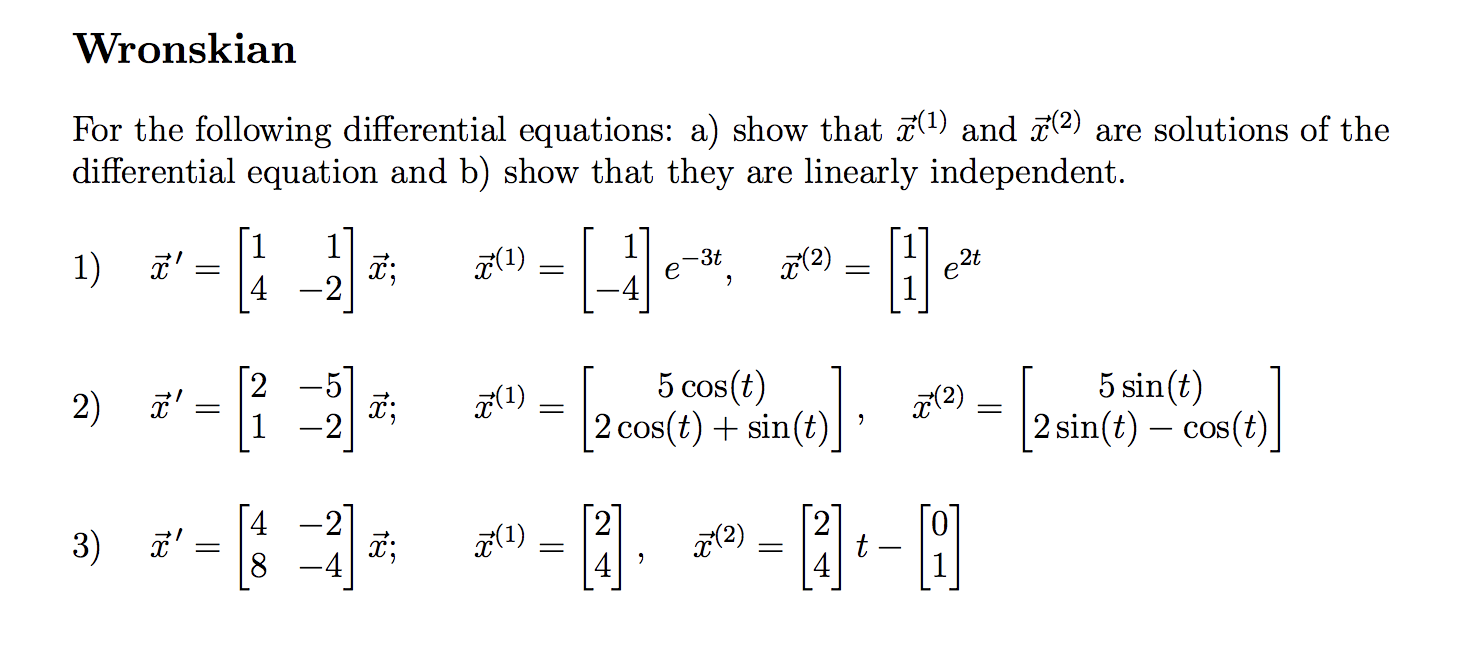
Solved Wronskian For the following differential equations
We’ll start by noticing that if the original equation is true, then if we differentiate. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to. If the wronskian of f f and g g is tcos(t)+ sin(t) t cos (t) + sin (t), and if u = f − 3g u = f − 3 g.
Wronskian StudyPug
We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to. We’ll start by noticing that if the original equation is true, then if we differentiate. If the wronskian of f f and g g is tcos(t)+ sin(t) t cos (t) + sin (t), and if u = f − 3g u = f − 3 g.
Solving 2nd Order non homogeneous differential equation using Wronskian
To demonstrate that the wronskian either vanishes for all values of x or it is never equal. We’ll start by noticing that if the original equation is true, then if we differentiate. If the wronskian of f f and g g is tcos(t)+ sin(t) t cos (t) + sin (t), and if u = f − 3g u = f.
SOLVEDThe Wronskian determinant (or simply, the Wronskian) of a linear
We’ll start by noticing that if the original equation is true, then if we differentiate. To demonstrate that the wronskian either vanishes for all values of x or it is never equal. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to. If the wronskian of f f and g g is tcos(t)+ sin(t) t cos.
Solved Compute the Wronskian for the following solutions to
If the wronskian of f f and g g is tcos(t)+ sin(t) t cos (t) + sin (t), and if u = f − 3g u = f − 3 g and v. To demonstrate that the wronskian either vanishes for all values of x or it is never equal. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they.
Wronskian equation WAR Herb Zinser's Atomic Social Science Reports
If the wronskian of f f and g g is tcos(t)+ sin(t) t cos (t) + sin (t), and if u = f − 3g u = f − 3 g and v. We’ll start by noticing that if the original equation is true, then if we differentiate. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be.
Solved Second order differential equation Wronskian and
We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to. To demonstrate that the wronskian either vanishes for all values of x or it is never equal. If the wronskian of f f and g g is tcos(t)+ sin(t) t cos (t) + sin (t), and if u = f − 3g u = f −.
⏩SOLVEDThe Wronskian formed from a solution set of the given… Numerade
If the wronskian of f f and g g is tcos(t)+ sin(t) t cos (t) + sin (t), and if u = f − 3g u = f − 3 g and v. We’ll start by noticing that if the original equation is true, then if we differentiate. To demonstrate that the wronskian either vanishes for all values of x.
We’ll Start By Noticing That If The Original Equation Is True, Then If We Differentiate.
We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to. If the wronskian of f f and g g is tcos(t)+ sin(t) t cos (t) + sin (t), and if u = f − 3g u = f − 3 g and v. To demonstrate that the wronskian either vanishes for all values of x or it is never equal.