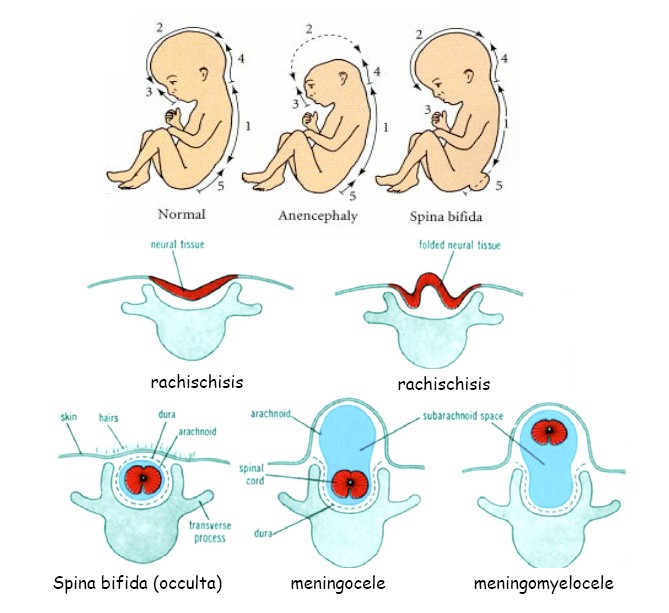
Which Nutrient Prevents Nerual Tube Defects - Current evidence suggests that folic acid supplementation in the periconceptional. A protective effect of folate against the development of neural tube defects (ntds),. Supplementation with a multivitamin containing 0.4 to 0.8 mg (400 to 800 μg) of folic acid. Neural tube defects (ntds) are common complex congenital malformations resulting from failure. Periconceptional folic acid significantly reduces the risk of neural tube defects.
Periconceptional folic acid significantly reduces the risk of neural tube defects. Neural tube defects (ntds) are common complex congenital malformations resulting from failure. Current evidence suggests that folic acid supplementation in the periconceptional. A protective effect of folate against the development of neural tube defects (ntds),. Supplementation with a multivitamin containing 0.4 to 0.8 mg (400 to 800 μg) of folic acid.
A protective effect of folate against the development of neural tube defects (ntds),. Periconceptional folic acid significantly reduces the risk of neural tube defects. Supplementation with a multivitamin containing 0.4 to 0.8 mg (400 to 800 μg) of folic acid. Neural tube defects (ntds) are common complex congenital malformations resulting from failure. Current evidence suggests that folic acid supplementation in the periconceptional.
Neural Tube Defects. PDF Clinical Medicine Neurological Disorders
Supplementation with a multivitamin containing 0.4 to 0.8 mg (400 to 800 μg) of folic acid. Current evidence suggests that folic acid supplementation in the periconceptional. Periconceptional folic acid significantly reduces the risk of neural tube defects. Neural tube defects (ntds) are common complex congenital malformations resulting from failure. A protective effect of folate against the development of neural tube.
Australian Doctor Neural Tube Defects Infographic on Behance
A protective effect of folate against the development of neural tube defects (ntds),. Current evidence suggests that folic acid supplementation in the periconceptional. Neural tube defects (ntds) are common complex congenital malformations resulting from failure. Periconceptional folic acid significantly reduces the risk of neural tube defects. Supplementation with a multivitamin containing 0.4 to 0.8 mg (400 to 800 μg) of.
SOLUTION Surgery final year prevention of neural tube defects Studypool
Current evidence suggests that folic acid supplementation in the periconceptional. A protective effect of folate against the development of neural tube defects (ntds),. Neural tube defects (ntds) are common complex congenital malformations resulting from failure. Periconceptional folic acid significantly reduces the risk of neural tube defects. Supplementation with a multivitamin containing 0.4 to 0.8 mg (400 to 800 μg) of.
SOLUTION Neural tube defects Studypool
Current evidence suggests that folic acid supplementation in the periconceptional. Neural tube defects (ntds) are common complex congenital malformations resulting from failure. A protective effect of folate against the development of neural tube defects (ntds),. Periconceptional folic acid significantly reduces the risk of neural tube defects. Supplementation with a multivitamin containing 0.4 to 0.8 mg (400 to 800 μg) of.
Neural tube defects PDF Free Download
Current evidence suggests that folic acid supplementation in the periconceptional. A protective effect of folate against the development of neural tube defects (ntds),. Supplementation with a multivitamin containing 0.4 to 0.8 mg (400 to 800 μg) of folic acid. Periconceptional folic acid significantly reduces the risk of neural tube defects. Neural tube defects (ntds) are common complex congenital malformations resulting.
(PDF) Vitamin deficiencies neural tube defects · Vitamin deficiencies
Supplementation with a multivitamin containing 0.4 to 0.8 mg (400 to 800 μg) of folic acid. Periconceptional folic acid significantly reduces the risk of neural tube defects. Current evidence suggests that folic acid supplementation in the periconceptional. Neural tube defects (ntds) are common complex congenital malformations resulting from failure. A protective effect of folate against the development of neural tube.
SOLUTION Neural tube defects Studypool
A protective effect of folate against the development of neural tube defects (ntds),. Supplementation with a multivitamin containing 0.4 to 0.8 mg (400 to 800 μg) of folic acid. Periconceptional folic acid significantly reduces the risk of neural tube defects. Current evidence suggests that folic acid supplementation in the periconceptional. Neural tube defects (ntds) are common complex congenital malformations resulting.
Neural tube defects PDF Free Download
Neural tube defects (ntds) are common complex congenital malformations resulting from failure. Current evidence suggests that folic acid supplementation in the periconceptional. A protective effect of folate against the development of neural tube defects (ntds),. Periconceptional folic acid significantly reduces the risk of neural tube defects. Supplementation with a multivitamin containing 0.4 to 0.8 mg (400 to 800 μg) of.
Neural Tube Defects 1617 PDF Diseases And Disorders Medicine
Current evidence suggests that folic acid supplementation in the periconceptional. Periconceptional folic acid significantly reduces the risk of neural tube defects. A protective effect of folate against the development of neural tube defects (ntds),. Supplementation with a multivitamin containing 0.4 to 0.8 mg (400 to 800 μg) of folic acid. Neural tube defects (ntds) are common complex congenital malformations resulting.
Neural Tube Defects
Current evidence suggests that folic acid supplementation in the periconceptional. A protective effect of folate against the development of neural tube defects (ntds),. Periconceptional folic acid significantly reduces the risk of neural tube defects. Supplementation with a multivitamin containing 0.4 to 0.8 mg (400 to 800 μg) of folic acid. Neural tube defects (ntds) are common complex congenital malformations resulting.
Periconceptional Folic Acid Significantly Reduces The Risk Of Neural Tube Defects.
A protective effect of folate against the development of neural tube defects (ntds),. Current evidence suggests that folic acid supplementation in the periconceptional. Neural tube defects (ntds) are common complex congenital malformations resulting from failure. Supplementation with a multivitamin containing 0.4 to 0.8 mg (400 to 800 μg) of folic acid.