Undifferentiated Cells Vs Differentiated - Our body is composed of over 200 specialised cell types, that can carry out specific functions, eg. To help counteract this loss, tissues maintain stem cells to serve as a reservoir of. There are two types of cell division. In fact, many differentiated cells lose this ability. Mitosis produces two identical diploid daughter cells. The main difference between differentiated and undifferentiated cells is that differentiated cells are specialized cells to perform a unique.
Our body is composed of over 200 specialised cell types, that can carry out specific functions, eg. To help counteract this loss, tissues maintain stem cells to serve as a reservoir of. There are two types of cell division. The main difference between differentiated and undifferentiated cells is that differentiated cells are specialized cells to perform a unique. In fact, many differentiated cells lose this ability. Mitosis produces two identical diploid daughter cells.
To help counteract this loss, tissues maintain stem cells to serve as a reservoir of. There are two types of cell division. Our body is composed of over 200 specialised cell types, that can carry out specific functions, eg. Mitosis produces two identical diploid daughter cells. In fact, many differentiated cells lose this ability. The main difference between differentiated and undifferentiated cells is that differentiated cells are specialized cells to perform a unique.
Undifferentiated vs. Differentiated Marketing Strategy Which is Right
To help counteract this loss, tissues maintain stem cells to serve as a reservoir of. The main difference between differentiated and undifferentiated cells is that differentiated cells are specialized cells to perform a unique. There are two types of cell division. Mitosis produces two identical diploid daughter cells. In fact, many differentiated cells lose this ability.
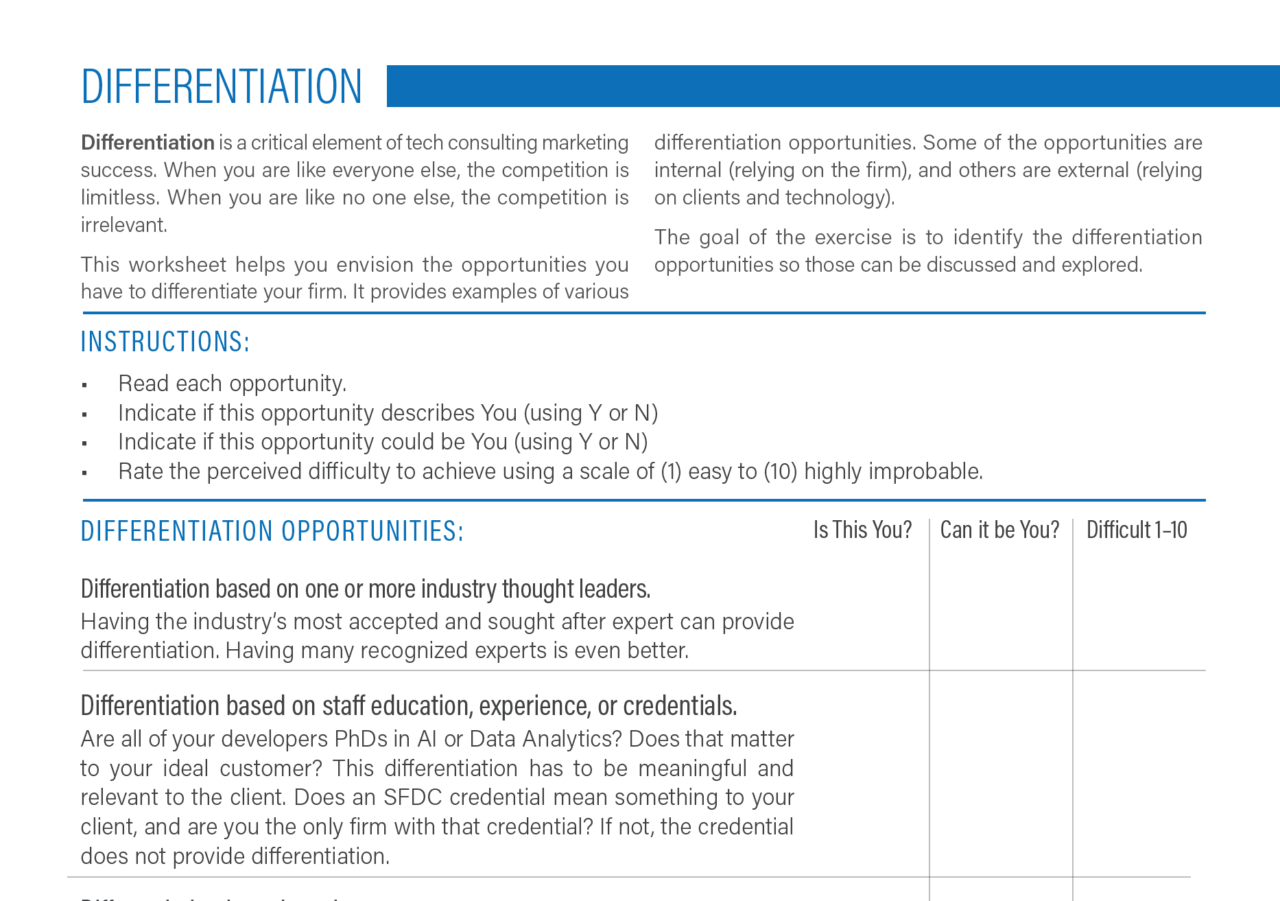
Difference Between Differentiated and Undifferentiated Marketing
Our body is composed of over 200 specialised cell types, that can carry out specific functions, eg. To help counteract this loss, tissues maintain stem cells to serve as a reservoir of. There are two types of cell division. In fact, many differentiated cells lose this ability. The main difference between differentiated and undifferentiated cells is that differentiated cells are.
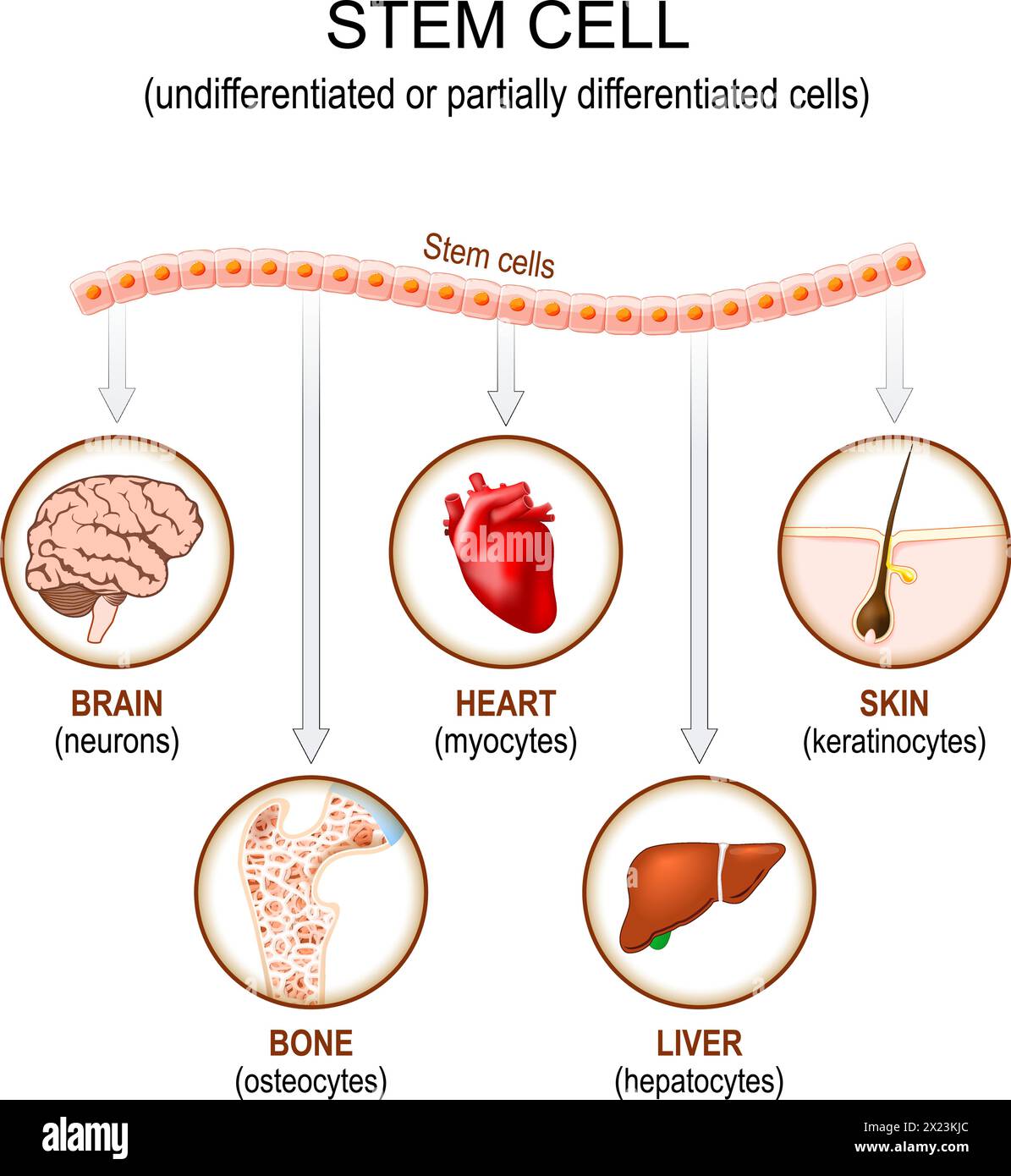
Undifferentiated Stem Cells Definition, Sources and Purpose
There are two types of cell division. To help counteract this loss, tissues maintain stem cells to serve as a reservoir of. The main difference between differentiated and undifferentiated cells is that differentiated cells are specialized cells to perform a unique. Mitosis produces two identical diploid daughter cells. In fact, many differentiated cells lose this ability.
Differentiated fold change vs undifferentiated Download Table
To help counteract this loss, tissues maintain stem cells to serve as a reservoir of. In fact, many differentiated cells lose this ability. Mitosis produces two identical diploid daughter cells. The main difference between differentiated and undifferentiated cells is that differentiated cells are specialized cells to perform a unique. There are two types of cell division.
Undifferentiated and differentiated cells. The morphology of the cells
Mitosis produces two identical diploid daughter cells. To help counteract this loss, tissues maintain stem cells to serve as a reservoir of. There are two types of cell division. Our body is composed of over 200 specialised cell types, that can carry out specific functions, eg. The main difference between differentiated and undifferentiated cells is that differentiated cells are specialized.
Morphometric analyses of undifferentiated Vs differentiated SHSY5Y
To help counteract this loss, tissues maintain stem cells to serve as a reservoir of. There are two types of cell division. Our body is composed of over 200 specialised cell types, that can carry out specific functions, eg. Mitosis produces two identical diploid daughter cells. In fact, many differentiated cells lose this ability.
Differentiated vs. Undifferentiated Marketing Key Differences
The main difference between differentiated and undifferentiated cells is that differentiated cells are specialized cells to perform a unique. Mitosis produces two identical diploid daughter cells. To help counteract this loss, tissues maintain stem cells to serve as a reservoir of. In fact, many differentiated cells lose this ability. There are two types of cell division.
Differentiated vs Undifferentiated Marketing Which is Superior? YCC
There are two types of cell division. The main difference between differentiated and undifferentiated cells is that differentiated cells are specialized cells to perform a unique. To help counteract this loss, tissues maintain stem cells to serve as a reservoir of. Our body is composed of over 200 specialised cell types, that can carry out specific functions, eg. In fact,.
What is the Difference Between Differentiated and Undifferentiated
To help counteract this loss, tissues maintain stem cells to serve as a reservoir of. There are two types of cell division. Mitosis produces two identical diploid daughter cells. In fact, many differentiated cells lose this ability. The main difference between differentiated and undifferentiated cells is that differentiated cells are specialized cells to perform a unique.
Stem cell application. Undifferentiated or partially differentiated
The main difference between differentiated and undifferentiated cells is that differentiated cells are specialized cells to perform a unique. To help counteract this loss, tissues maintain stem cells to serve as a reservoir of. There are two types of cell division. Mitosis produces two identical diploid daughter cells. Our body is composed of over 200 specialised cell types, that can.
In Fact, Many Differentiated Cells Lose This Ability.
To help counteract this loss, tissues maintain stem cells to serve as a reservoir of. Mitosis produces two identical diploid daughter cells. Our body is composed of over 200 specialised cell types, that can carry out specific functions, eg. There are two types of cell division.