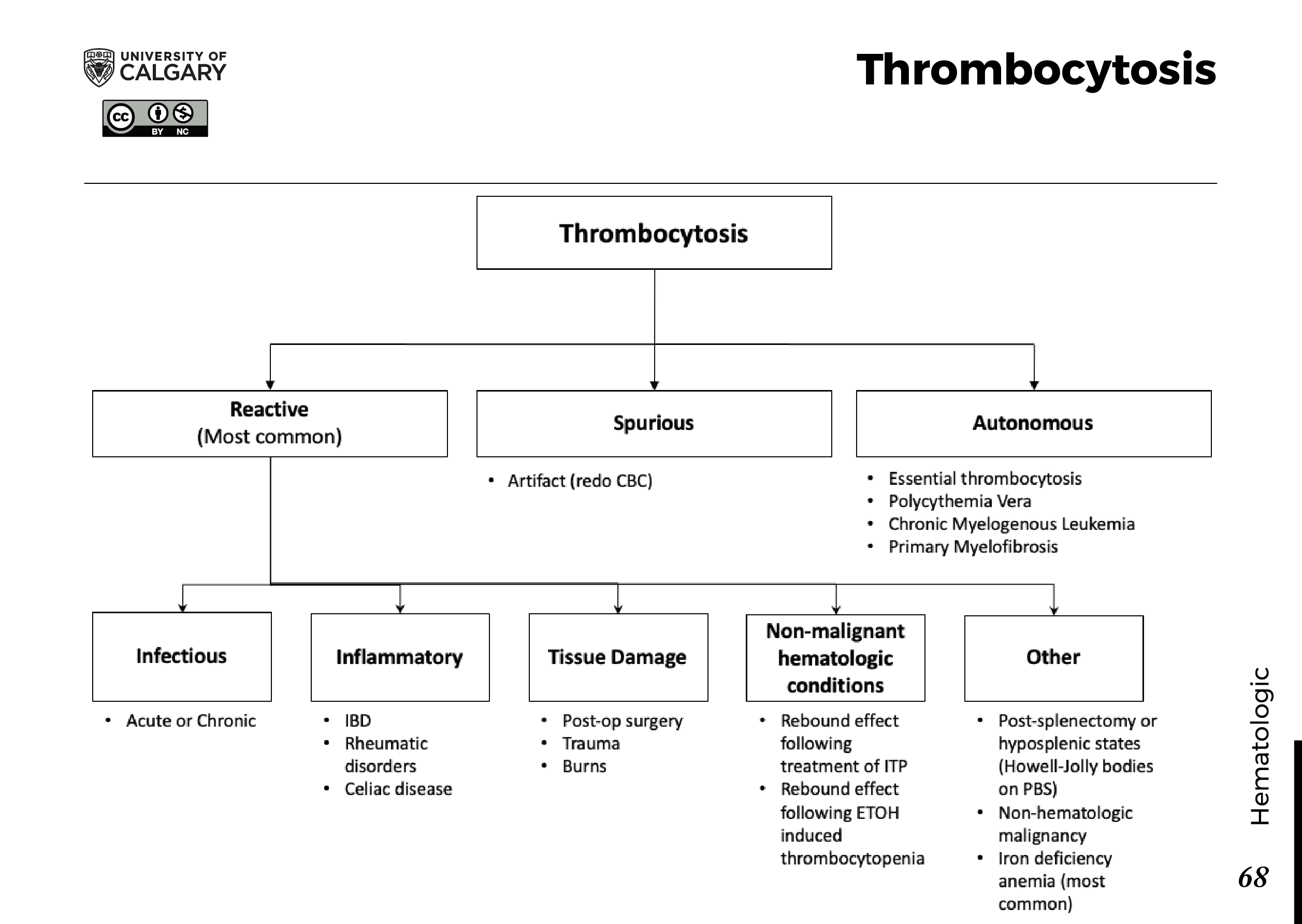
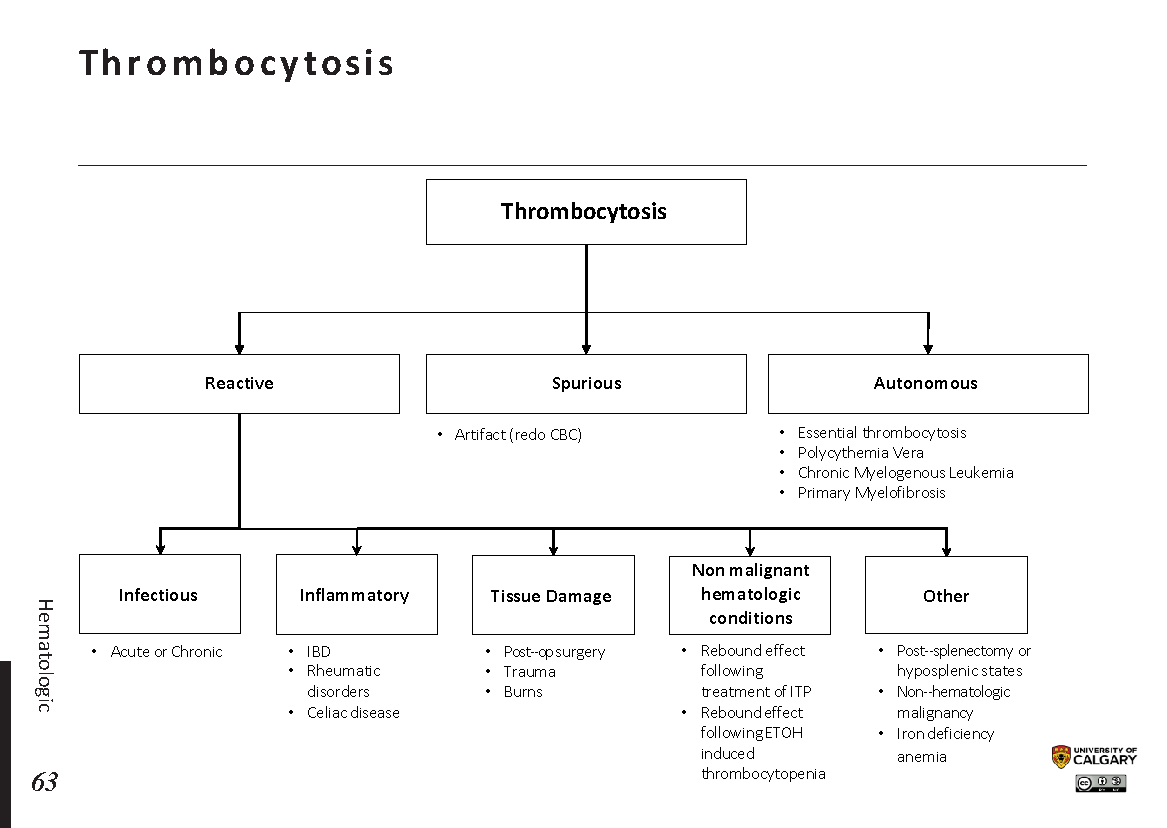
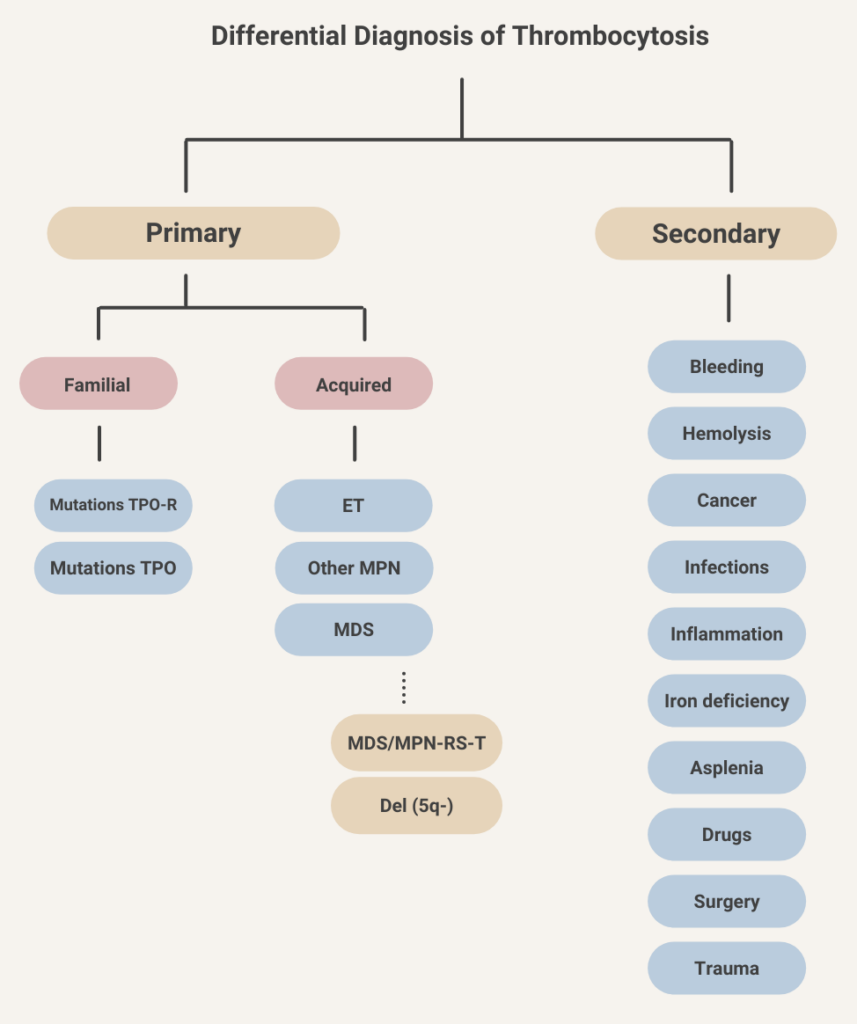
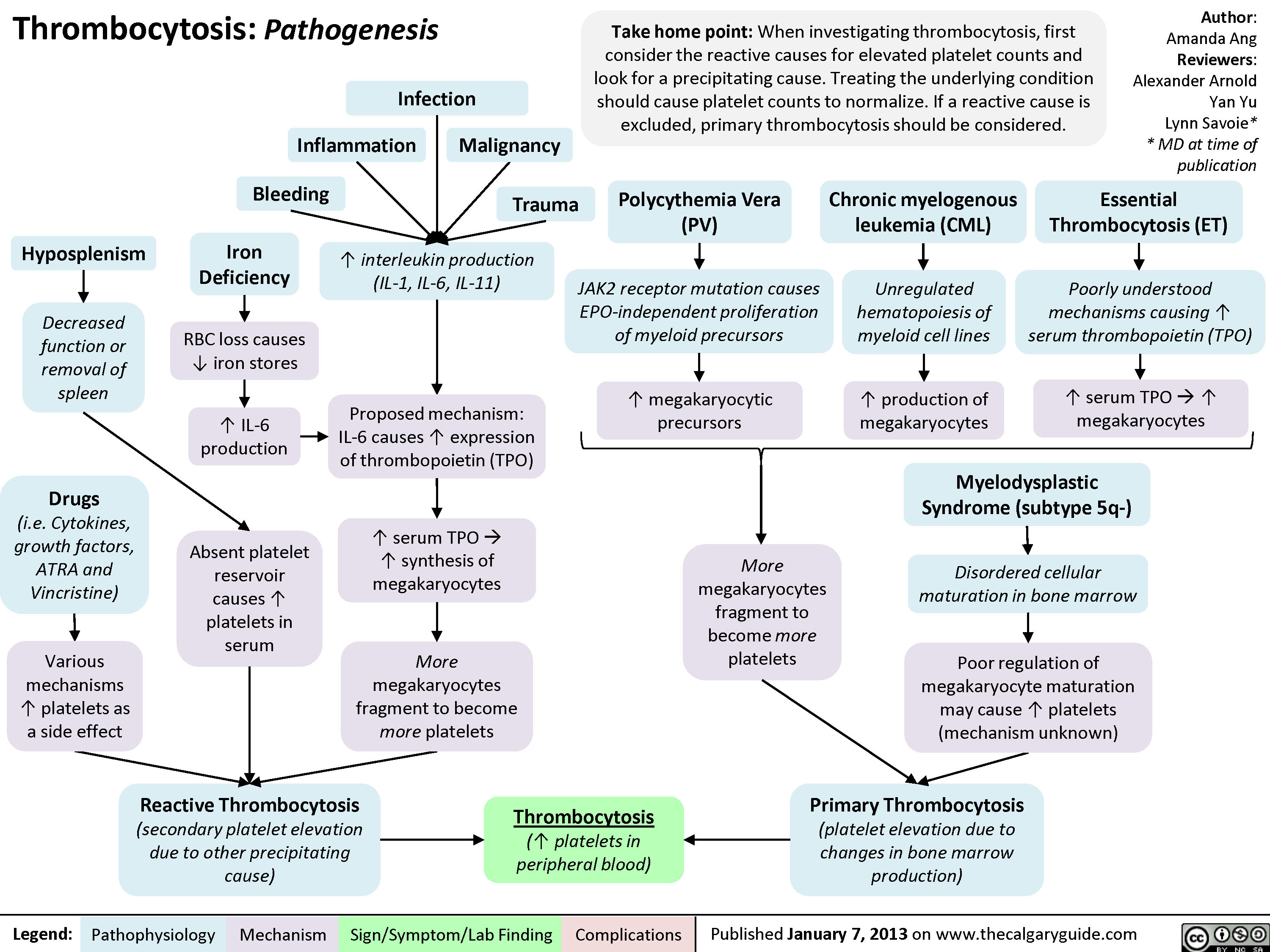
Thrombocytosis Differential - The differential diagnosis for thrombocytosis is broad and the diagnostic process can be challenging. Secondary thrombocytosis, also known as reactive thrombocytosis, is characterized by an abnormally high platelet. Complications, such as bleeding and/or thrombosis, are more likely with at than with rt so it is clinically important to. Differentiating between secondary causes of thrombocytosis and essential thrombocythemia (et) is often clinically challenging. Thrombocytosis refers to an increased platelet count which, in this review, is ≥450,000/microl (≥450 x 10 9 /l). Essential thrombocytosis must be differentiated from secondary thrombocytosis, which may be due to an inflammatory state,.
Complications, such as bleeding and/or thrombosis, are more likely with at than with rt so it is clinically important to. Thrombocytosis refers to an increased platelet count which, in this review, is ≥450,000/microl (≥450 x 10 9 /l). Secondary thrombocytosis, also known as reactive thrombocytosis, is characterized by an abnormally high platelet. Differentiating between secondary causes of thrombocytosis and essential thrombocythemia (et) is often clinically challenging. Essential thrombocytosis must be differentiated from secondary thrombocytosis, which may be due to an inflammatory state,. The differential diagnosis for thrombocytosis is broad and the diagnostic process can be challenging.
Differentiating between secondary causes of thrombocytosis and essential thrombocythemia (et) is often clinically challenging. Complications, such as bleeding and/or thrombosis, are more likely with at than with rt so it is clinically important to. Secondary thrombocytosis, also known as reactive thrombocytosis, is characterized by an abnormally high platelet. The differential diagnosis for thrombocytosis is broad and the diagnostic process can be challenging. Thrombocytosis refers to an increased platelet count which, in this review, is ≥450,000/microl (≥450 x 10 9 /l). Essential thrombocytosis must be differentiated from secondary thrombocytosis, which may be due to an inflammatory state,.
📗 Essay Sample on Thrombocytosis Differential Diagnosis
Secondary thrombocytosis, also known as reactive thrombocytosis, is characterized by an abnormally high platelet. Complications, such as bleeding and/or thrombosis, are more likely with at than with rt so it is clinically important to. Thrombocytosis refers to an increased platelet count which, in this review, is ≥450,000/microl (≥450 x 10 9 /l). Essential thrombocytosis must be differentiated from secondary thrombocytosis,.
Thrombocytosis in the ED emdocs
Differentiating between secondary causes of thrombocytosis and essential thrombocythemia (et) is often clinically challenging. Secondary thrombocytosis, also known as reactive thrombocytosis, is characterized by an abnormally high platelet. Complications, such as bleeding and/or thrombosis, are more likely with at than with rt so it is clinically important to. Thrombocytosis refers to an increased platelet count which, in this review, is.
Essential Thrombocytosis Diagnosis
Thrombocytosis refers to an increased platelet count which, in this review, is ≥450,000/microl (≥450 x 10 9 /l). Essential thrombocytosis must be differentiated from secondary thrombocytosis, which may be due to an inflammatory state,. Secondary thrombocytosis, also known as reactive thrombocytosis, is characterized by an abnormally high platelet. The differential diagnosis for thrombocytosis is broad and the diagnostic process can.
THROMBOCYTOSIS Blackbook Blackbook
Secondary thrombocytosis, also known as reactive thrombocytosis, is characterized by an abnormally high platelet. Essential thrombocytosis must be differentiated from secondary thrombocytosis, which may be due to an inflammatory state,. The differential diagnosis for thrombocytosis is broad and the diagnostic process can be challenging. Complications, such as bleeding and/or thrombosis, are more likely with at than with rt so it.
THROMBOCYTOSIS Blackbook Blackbook
Thrombocytosis refers to an increased platelet count which, in this review, is ≥450,000/microl (≥450 x 10 9 /l). Secondary thrombocytosis, also known as reactive thrombocytosis, is characterized by an abnormally high platelet. Differentiating between secondary causes of thrombocytosis and essential thrombocythemia (et) is often clinically challenging. Complications, such as bleeding and/or thrombosis, are more likely with at than with rt.
How is thrombocytosis classified? • The Blood Project
Secondary thrombocytosis, also known as reactive thrombocytosis, is characterized by an abnormally high platelet. Essential thrombocytosis must be differentiated from secondary thrombocytosis, which may be due to an inflammatory state,. The differential diagnosis for thrombocytosis is broad and the diagnostic process can be challenging. Complications, such as bleeding and/or thrombosis, are more likely with at than with rt so it.
Pathogenesis of thrombocytosis Calgary Guide
Thrombocytosis refers to an increased platelet count which, in this review, is ≥450,000/microl (≥450 x 10 9 /l). Essential thrombocytosis must be differentiated from secondary thrombocytosis, which may be due to an inflammatory state,. Differentiating between secondary causes of thrombocytosis and essential thrombocythemia (et) is often clinically challenging. Complications, such as bleeding and/or thrombosis, are more likely with at than.
Thrombocytosis — The Intern at Work
Essential thrombocytosis must be differentiated from secondary thrombocytosis, which may be due to an inflammatory state,. Complications, such as bleeding and/or thrombosis, are more likely with at than with rt so it is clinically important to. Secondary thrombocytosis, also known as reactive thrombocytosis, is characterized by an abnormally high platelet. Differentiating between secondary causes of thrombocytosis and essential thrombocythemia (et).
Thrombocytosis Differential Diagnosis • The Blood Project
The differential diagnosis for thrombocytosis is broad and the diagnostic process can be challenging. Complications, such as bleeding and/or thrombosis, are more likely with at than with rt so it is clinically important to. Essential thrombocytosis must be differentiated from secondary thrombocytosis, which may be due to an inflammatory state,. Thrombocytosis refers to an increased platelet count which, in this.
Thrombocytosis The Clinical Problem Solvers
The differential diagnosis for thrombocytosis is broad and the diagnostic process can be challenging. Secondary thrombocytosis, also known as reactive thrombocytosis, is characterized by an abnormally high platelet. Differentiating between secondary causes of thrombocytosis and essential thrombocythemia (et) is often clinically challenging. Complications, such as bleeding and/or thrombosis, are more likely with at than with rt so it is clinically.
The Differential Diagnosis For Thrombocytosis Is Broad And The Diagnostic Process Can Be Challenging.
Complications, such as bleeding and/or thrombosis, are more likely with at than with rt so it is clinically important to. Thrombocytosis refers to an increased platelet count which, in this review, is ≥450,000/microl (≥450 x 10 9 /l). Secondary thrombocytosis, also known as reactive thrombocytosis, is characterized by an abnormally high platelet. Differentiating between secondary causes of thrombocytosis and essential thrombocythemia (et) is often clinically challenging.