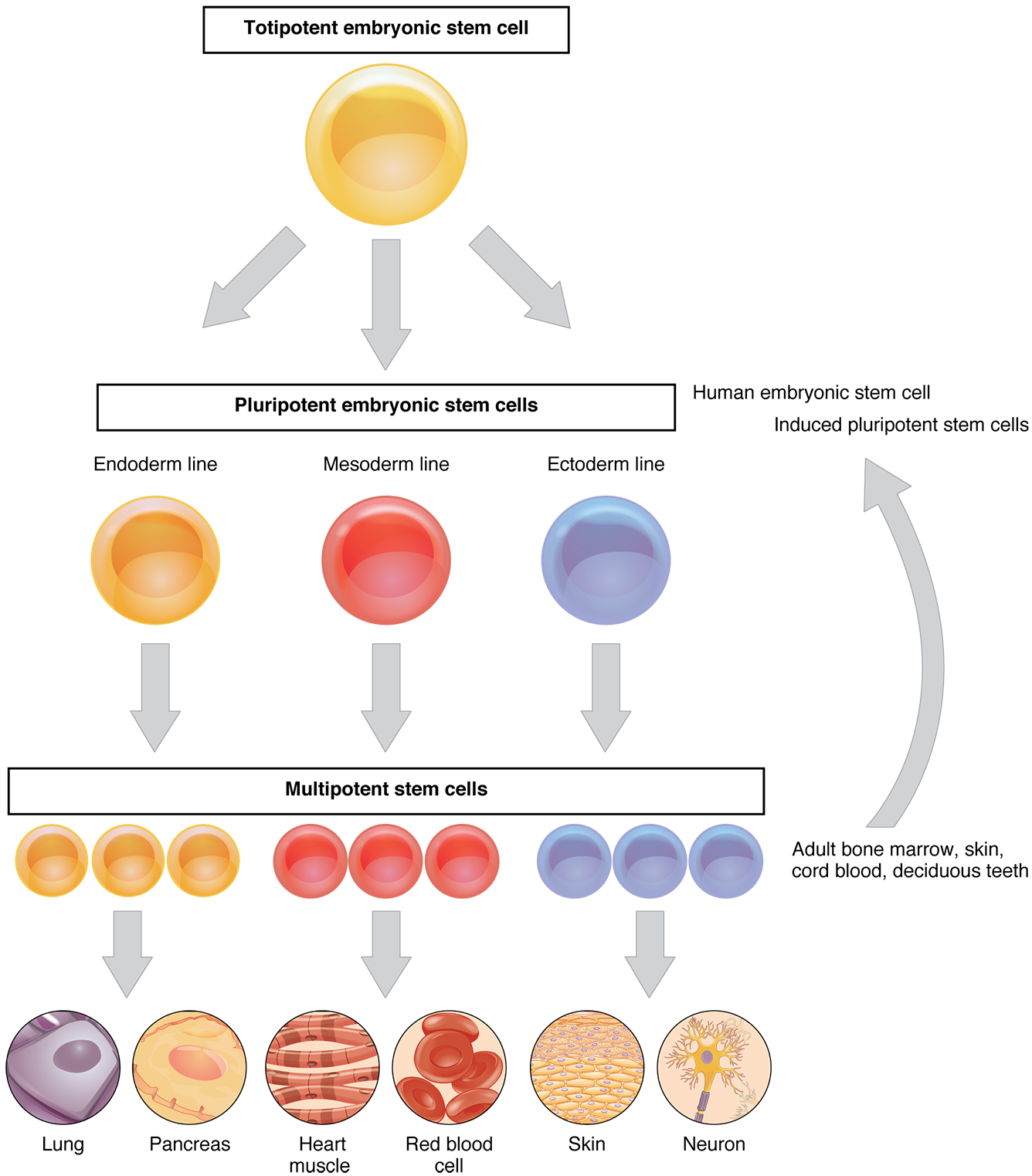
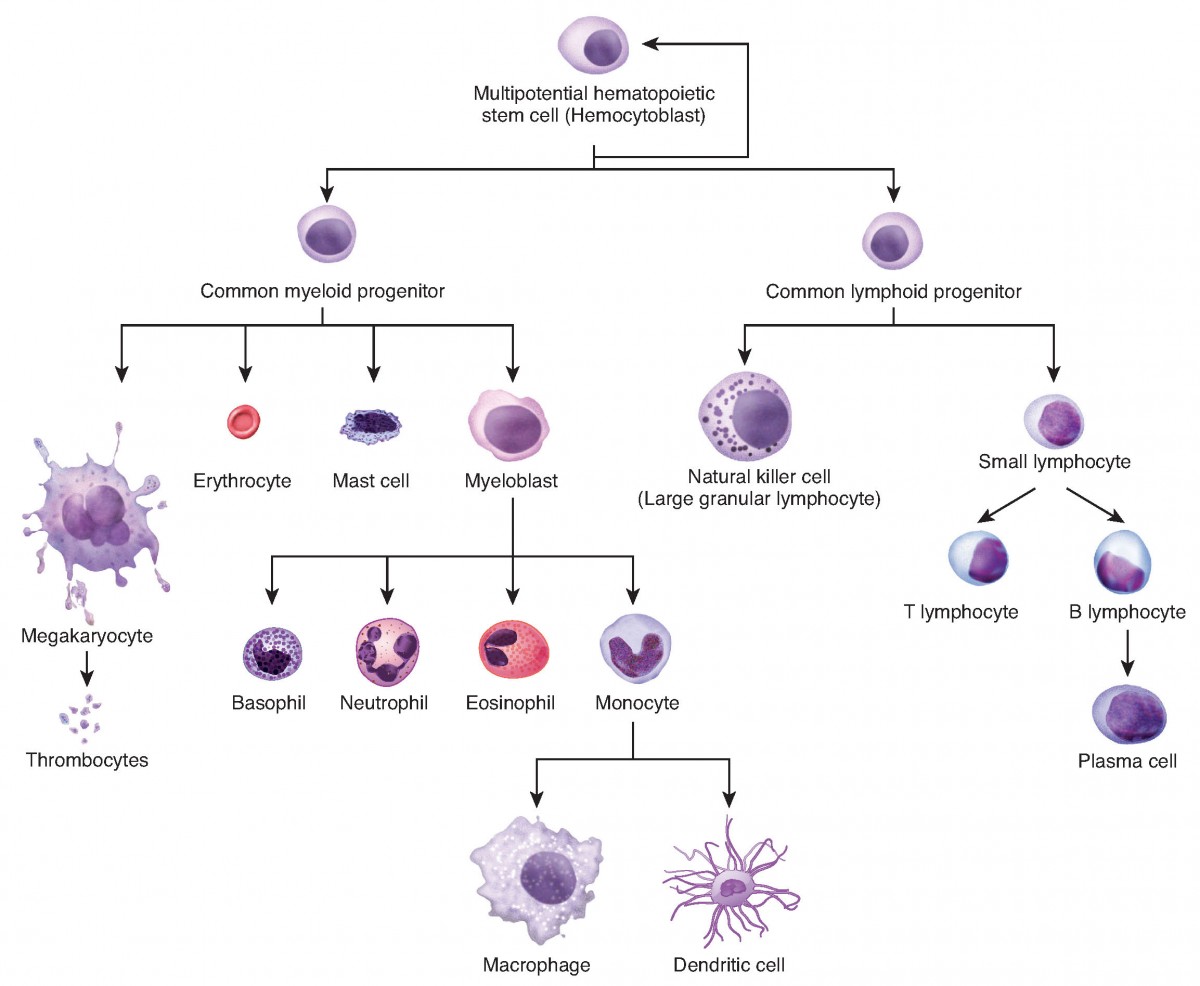
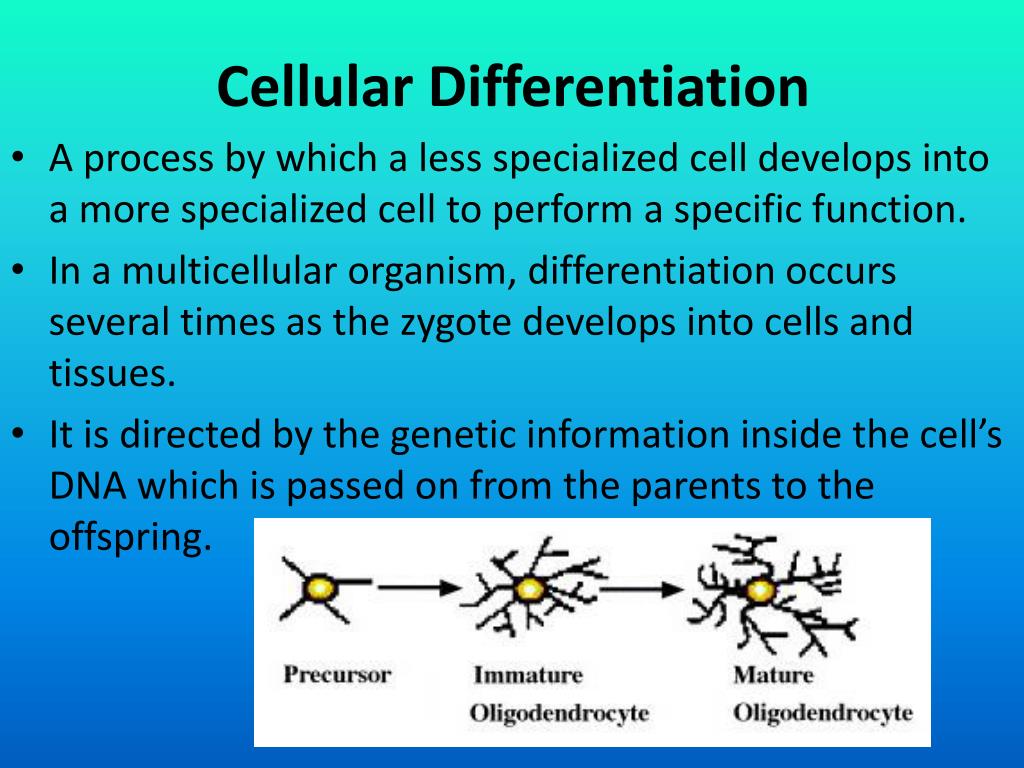
The Role Of Dna In Cellular Differentiation Is To - One purpose of dna is to replicate. Cellular differentiation is a complex process that involves the coordinated regulation of genes by a multitude of cellular pathways. This means that a strand of dna makes a copy of itself. Cellular differentiation refers to the complex process by which genes are regulated through various cellular pathways, specifically involving. Each step, from dna’s structural blueprint to the communication pathways within cells, contributes to the diversity of functions. The role of dna in cellular differentiation is to — a. It happens during cellular division, and it. Provide a series of genes that can be turned on or off.
Cellular differentiation refers to the complex process by which genes are regulated through various cellular pathways, specifically involving. This means that a strand of dna makes a copy of itself. Provide a series of genes that can be turned on or off. Each step, from dna’s structural blueprint to the communication pathways within cells, contributes to the diversity of functions. It happens during cellular division, and it. One purpose of dna is to replicate. Cellular differentiation is a complex process that involves the coordinated regulation of genes by a multitude of cellular pathways. The role of dna in cellular differentiation is to — a.
Each step, from dna’s structural blueprint to the communication pathways within cells, contributes to the diversity of functions. One purpose of dna is to replicate. Cellular differentiation is a complex process that involves the coordinated regulation of genes by a multitude of cellular pathways. The role of dna in cellular differentiation is to — a. This means that a strand of dna makes a copy of itself. It happens during cellular division, and it. Cellular differentiation refers to the complex process by which genes are regulated through various cellular pathways, specifically involving. Provide a series of genes that can be turned on or off.
DNA methylation plays a key role in the differentiation of CD8 + T
One purpose of dna is to replicate. Cellular differentiation refers to the complex process by which genes are regulated through various cellular pathways, specifically involving. This means that a strand of dna makes a copy of itself. The role of dna in cellular differentiation is to — a. It happens during cellular division, and it.
Cellular Differentiation From Embryo to Organism References http
The role of dna in cellular differentiation is to — a. It happens during cellular division, and it. Cellular differentiation refers to the complex process by which genes are regulated through various cellular pathways, specifically involving. This means that a strand of dna makes a copy of itself. Cellular differentiation is a complex process that involves the coordinated regulation of.
Solved Cellular differentiation is usually produced bySelect
One purpose of dna is to replicate. Each step, from dna’s structural blueprint to the communication pathways within cells, contributes to the diversity of functions. Provide a series of genes that can be turned on or off. The role of dna in cellular differentiation is to — a. Cellular differentiation refers to the complex process by which genes are regulated.
Rticle PDF Complementary Dna Cellular Differentiation
It happens during cellular division, and it. One purpose of dna is to replicate. Cellular differentiation is a complex process that involves the coordinated regulation of genes by a multitude of cellular pathways. This means that a strand of dna makes a copy of itself. The role of dna in cellular differentiation is to — a.
[LS14] Cellular Division and Differentiation Biology Dictionary
Cellular differentiation is a complex process that involves the coordinated regulation of genes by a multitude of cellular pathways. Each step, from dna’s structural blueprint to the communication pathways within cells, contributes to the diversity of functions. Cellular differentiation refers to the complex process by which genes are regulated through various cellular pathways, specifically involving. This means that a strand.
2.11 Cellular Differentiation Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology
Cellular differentiation refers to the complex process by which genes are regulated through various cellular pathways, specifically involving. Cellular differentiation is a complex process that involves the coordinated regulation of genes by a multitude of cellular pathways. It happens during cellular division, and it. The role of dna in cellular differentiation is to — a. This means that a strand.
Cellular Differentiation Anatomy and Physiology I
Cellular differentiation refers to the complex process by which genes are regulated through various cellular pathways, specifically involving. It happens during cellular division, and it. This means that a strand of dna makes a copy of itself. Cellular differentiation is a complex process that involves the coordinated regulation of genes by a multitude of cellular pathways. Each step, from dna’s.
Difference Between Cellular Differentiation and Cell Division Compare
One purpose of dna is to replicate. Cellular differentiation refers to the complex process by which genes are regulated through various cellular pathways, specifically involving. Cellular differentiation is a complex process that involves the coordinated regulation of genes by a multitude of cellular pathways. Each step, from dna’s structural blueprint to the communication pathways within cells, contributes to the diversity.
Cellular Differentiation Anatomy and Physiology I
One purpose of dna is to replicate. Each step, from dna’s structural blueprint to the communication pathways within cells, contributes to the diversity of functions. Provide a series of genes that can be turned on or off. The role of dna in cellular differentiation is to — a. This means that a strand of dna makes a copy of itself.
PPT Stem Cells and Cellular Differentiation PowerPoint Presentation
This means that a strand of dna makes a copy of itself. Provide a series of genes that can be turned on or off. Cellular differentiation refers to the complex process by which genes are regulated through various cellular pathways, specifically involving. Each step, from dna’s structural blueprint to the communication pathways within cells, contributes to the diversity of functions..
Cellular Differentiation Refers To The Complex Process By Which Genes Are Regulated Through Various Cellular Pathways, Specifically Involving.
One purpose of dna is to replicate. Cellular differentiation is a complex process that involves the coordinated regulation of genes by a multitude of cellular pathways. This means that a strand of dna makes a copy of itself. Each step, from dna’s structural blueprint to the communication pathways within cells, contributes to the diversity of functions.
The Role Of Dna In Cellular Differentiation Is To — A.
It happens during cellular division, and it. Provide a series of genes that can be turned on or off.




![[LS14] Cellular Division and Differentiation Biology Dictionary](https://biologydictionary.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/Cell-potency.jpg)