Solving Linear Ordinary Differential Equations - Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). Explore analysis with applications to dilution models. If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of y, then they. To solve ordinary differential equations (odes), use methods such as separation of variables, linear equations, exact equations,. In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e.
If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of y, then they. In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. To solve ordinary differential equations (odes), use methods such as separation of variables, linear equations, exact equations,. Explore analysis with applications to dilution models. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t).
If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of y, then they. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. To solve ordinary differential equations (odes), use methods such as separation of variables, linear equations, exact equations,. Explore analysis with applications to dilution models.
Ordinary Differential Equations
Explore analysis with applications to dilution models. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. To solve ordinary differential equations (odes), use methods such as separation of variables, linear equations, exact equations,. If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of.
Ordinary differential equations examples 🍓PPT Introduction to
In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). Explore analysis with applications to dilution models. If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of y, then they. To solve ordinary differential equations (odes), use methods such as separation of variables, linear.
(PDF) A New Algorithm for Solving Linear Ordinary Differential Equations
If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of y, then they. In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. Explore analysis with applications to dilution models. To solve ordinary differential equations (odes), use methods such as separation of variables, linear equations, exact equations,. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t).
SOLUTION Ordinary differential equations Studypool
Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). To solve ordinary differential equations (odes), use methods such as separation of variables, linear equations, exact equations,. If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of y, then they. In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. Explore analysis with applications.
Solving secondorder differential equations. Mathematics Stack Exchange
To solve ordinary differential equations (odes), use methods such as separation of variables, linear equations, exact equations,. If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of y, then they. In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). Explore analysis with applications.
PPT Solving Ordinary Differential Equations PowerPoint Presentation
In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of y, then they. Explore analysis with applications to dilution models. To solve ordinary differential equations (odes), use methods such as separation of variables, linear equations, exact equations,. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t).
Solving Linear Ordinary Differential Equations Overview
If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of y, then they. In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). Explore analysis with applications to dilution models. To solve ordinary differential equations (odes), use methods such as separation of variables, linear.
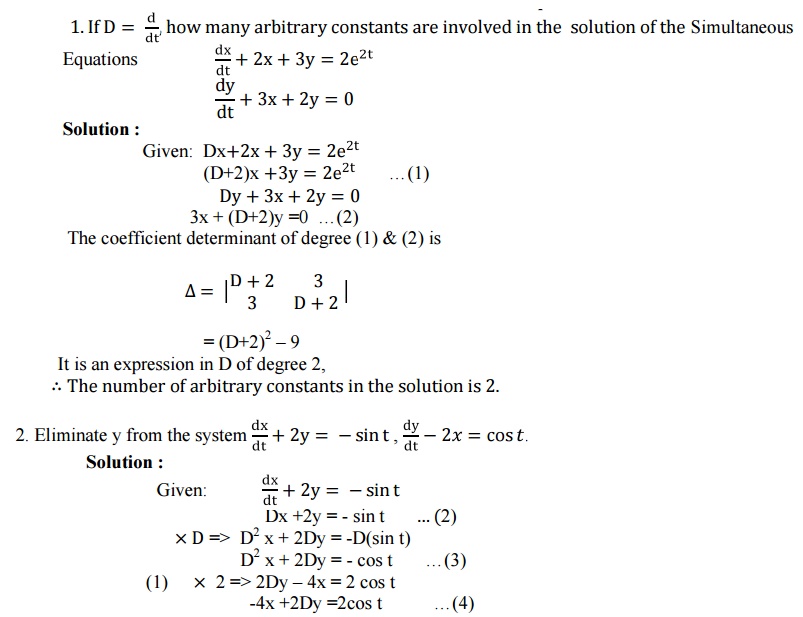
SOLUTION Ordinary differential equations examples on simultaneous
In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of y, then they. To solve ordinary differential equations (odes), use methods such as separation of variables, linear equations, exact equations,. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). Explore analysis with applications.
Linear Differential Equations Ordinary Differential Equation Equations
Explore analysis with applications to dilution models. In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). To solve ordinary differential equations (odes), use methods such as separation of variables, linear equations, exact equations,. If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of.
Solving linear Ordinary differential equations with variable
Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). Explore analysis with applications to dilution models. In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of y, then they. To solve ordinary differential equations (odes), use methods such as separation of variables, linear.
To Solve Ordinary Differential Equations (Odes), Use Methods Such As Separation Of Variables, Linear Equations, Exact Equations,.
If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of y, then they. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. Explore analysis with applications to dilution models.