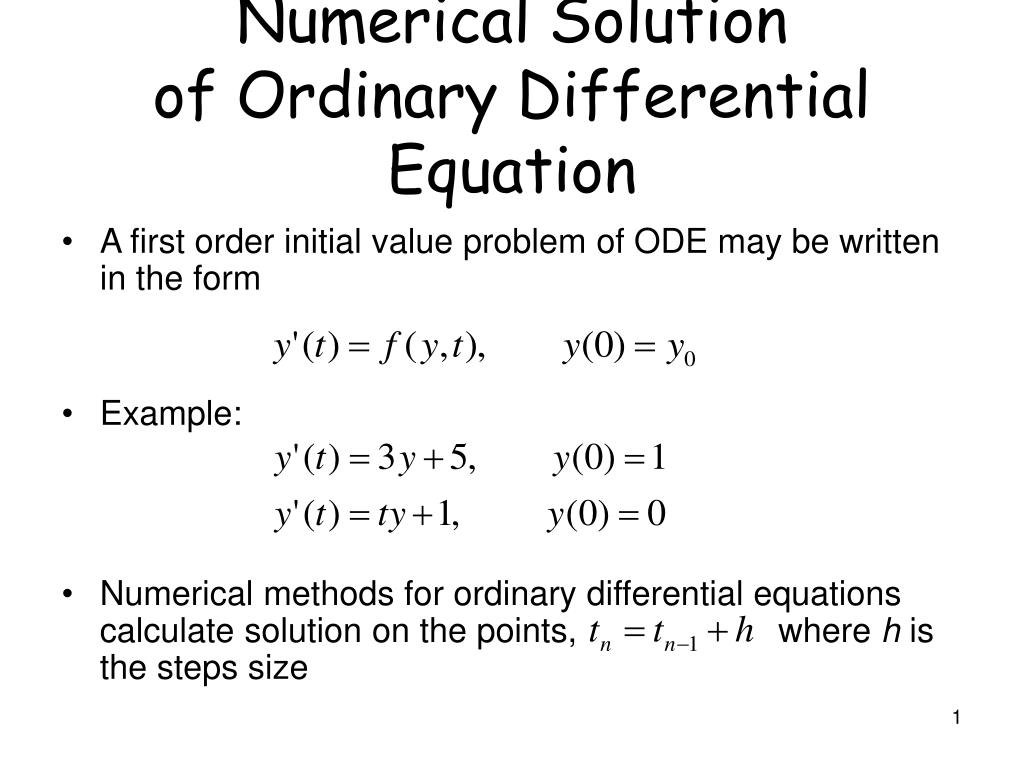
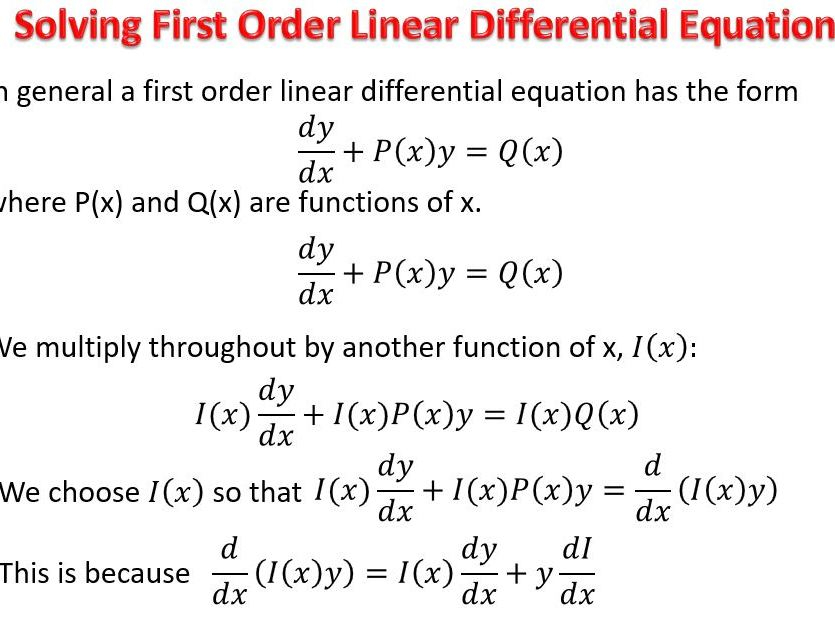
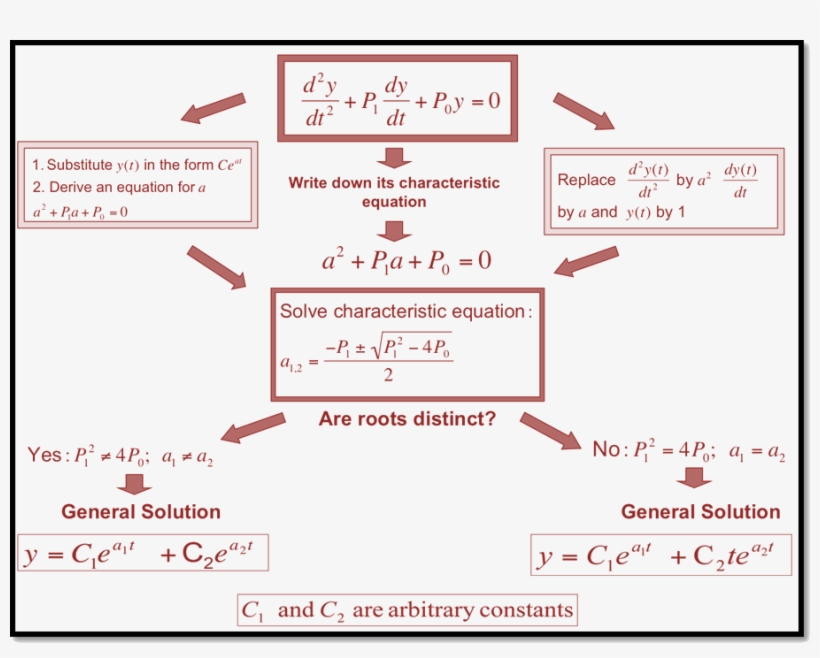
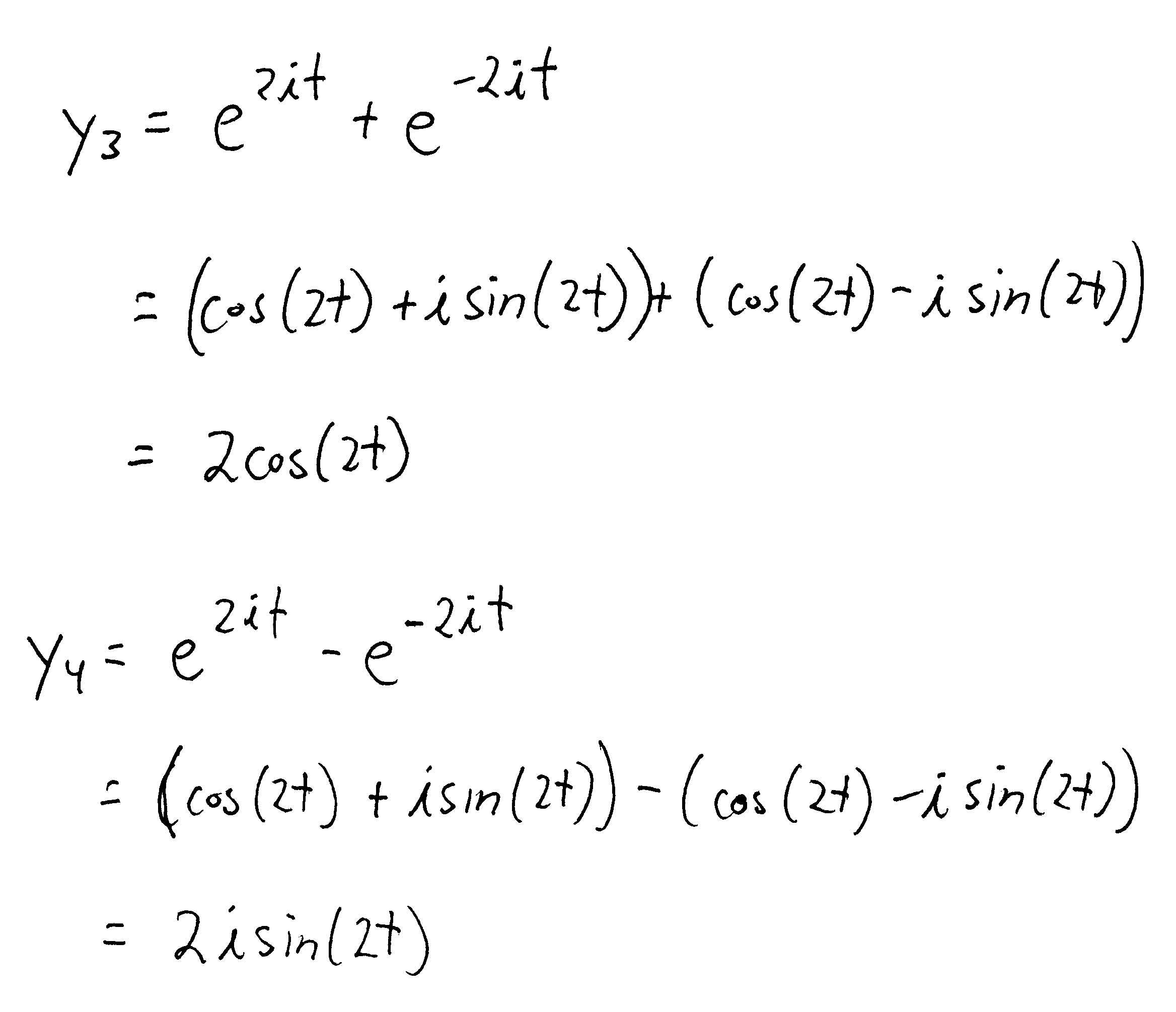Second Order Ordinary Differential Equation Solution - The solution of these equations is achieved in stages. Corresponding second order ode’s are obtained by taking another derivative, as x =tant, ⇒ x˙ =1+x2, ⇒ x¨ =2xx˙ =2x(1+x2), (1.3.17) and x =tanht, ⇒.
Corresponding second order ode’s are obtained by taking another derivative, as x =tant, ⇒ x˙ =1+x2, ⇒ x¨ =2xx˙ =2x(1+x2), (1.3.17) and x =tanht, ⇒. The solution of these equations is achieved in stages.
Corresponding second order ode’s are obtained by taking another derivative, as x =tant, ⇒ x˙ =1+x2, ⇒ x¨ =2xx˙ =2x(1+x2), (1.3.17) and x =tanht, ⇒. The solution of these equations is achieved in stages.
[Solved] The general solution to the secondorder differential equation
The solution of these equations is achieved in stages. Corresponding second order ode’s are obtained by taking another derivative, as x =tant, ⇒ x˙ =1+x2, ⇒ x¨ =2xx˙ =2x(1+x2), (1.3.17) and x =tanht, ⇒.
PPT Numerical Solution of Ordinary Differential Equation PowerPoint
Corresponding second order ode’s are obtained by taking another derivative, as x =tant, ⇒ x˙ =1+x2, ⇒ x¨ =2xx˙ =2x(1+x2), (1.3.17) and x =tanht, ⇒. The solution of these equations is achieved in stages.
First Order Differential Equation Worksheet Equations Worksheets
Corresponding second order ode’s are obtained by taking another derivative, as x =tant, ⇒ x˙ =1+x2, ⇒ x¨ =2xx˙ =2x(1+x2), (1.3.17) and x =tanht, ⇒. The solution of these equations is achieved in stages.
Solution Of Second Order Differential Equation Differential Equation
The solution of these equations is achieved in stages. Corresponding second order ode’s are obtained by taking another derivative, as x =tant, ⇒ x˙ =1+x2, ⇒ x¨ =2xx˙ =2x(1+x2), (1.3.17) and x =tanht, ⇒.
College Park Tutors Blog Differential Equations Solving a second
The solution of these equations is achieved in stages. Corresponding second order ode’s are obtained by taking another derivative, as x =tant, ⇒ x˙ =1+x2, ⇒ x¨ =2xx˙ =2x(1+x2), (1.3.17) and x =tanht, ⇒.
Solving Second Order Differential Equation Images and Photos finder
Corresponding second order ode’s are obtained by taking another derivative, as x =tant, ⇒ x˙ =1+x2, ⇒ x¨ =2xx˙ =2x(1+x2), (1.3.17) and x =tanht, ⇒. The solution of these equations is achieved in stages.
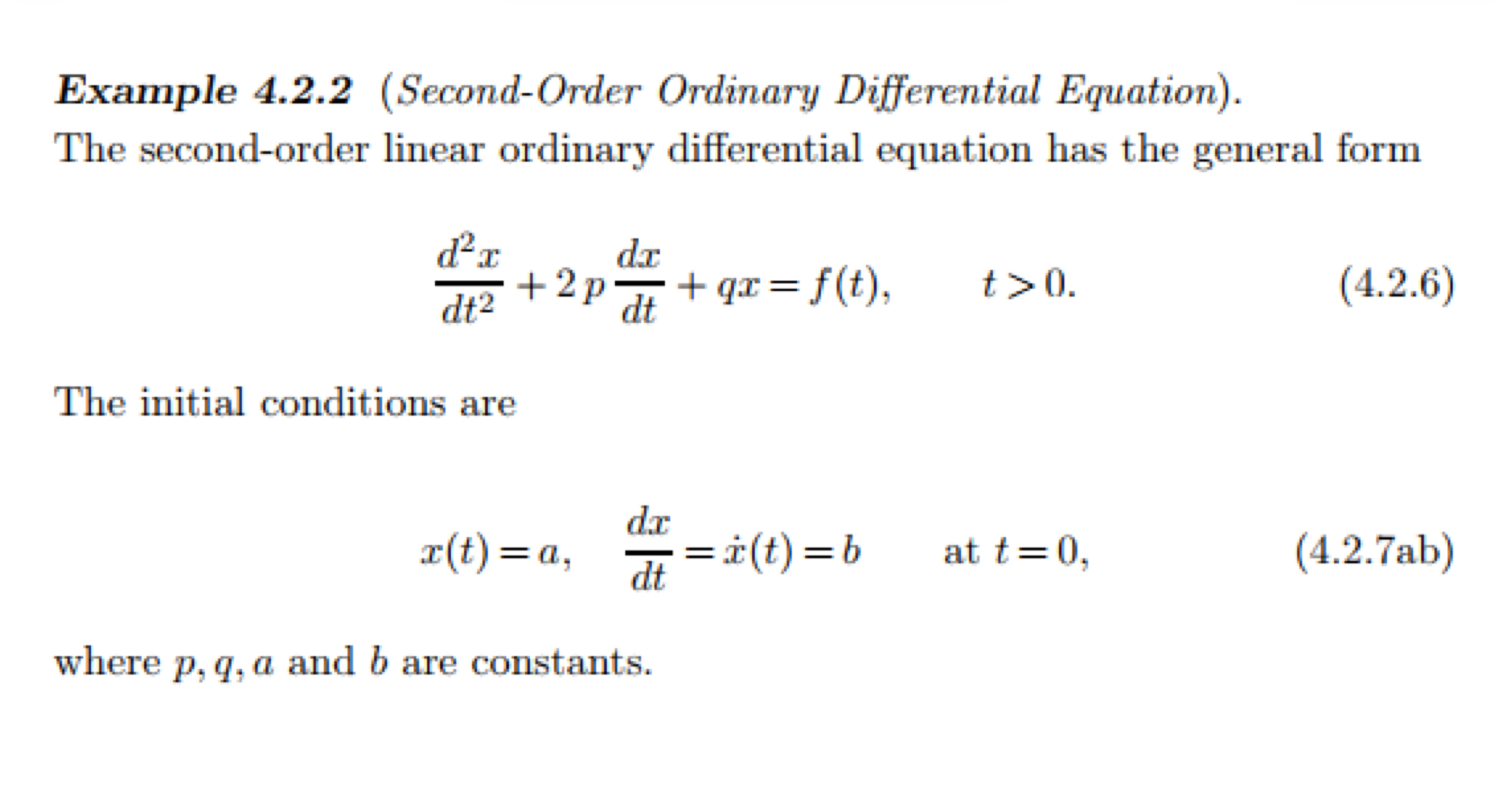
Example 4.2.2 (SecondOrder Ordinary Differential
Corresponding second order ode’s are obtained by taking another derivative, as x =tant, ⇒ x˙ =1+x2, ⇒ x¨ =2xx˙ =2x(1+x2), (1.3.17) and x =tanht, ⇒. The solution of these equations is achieved in stages.
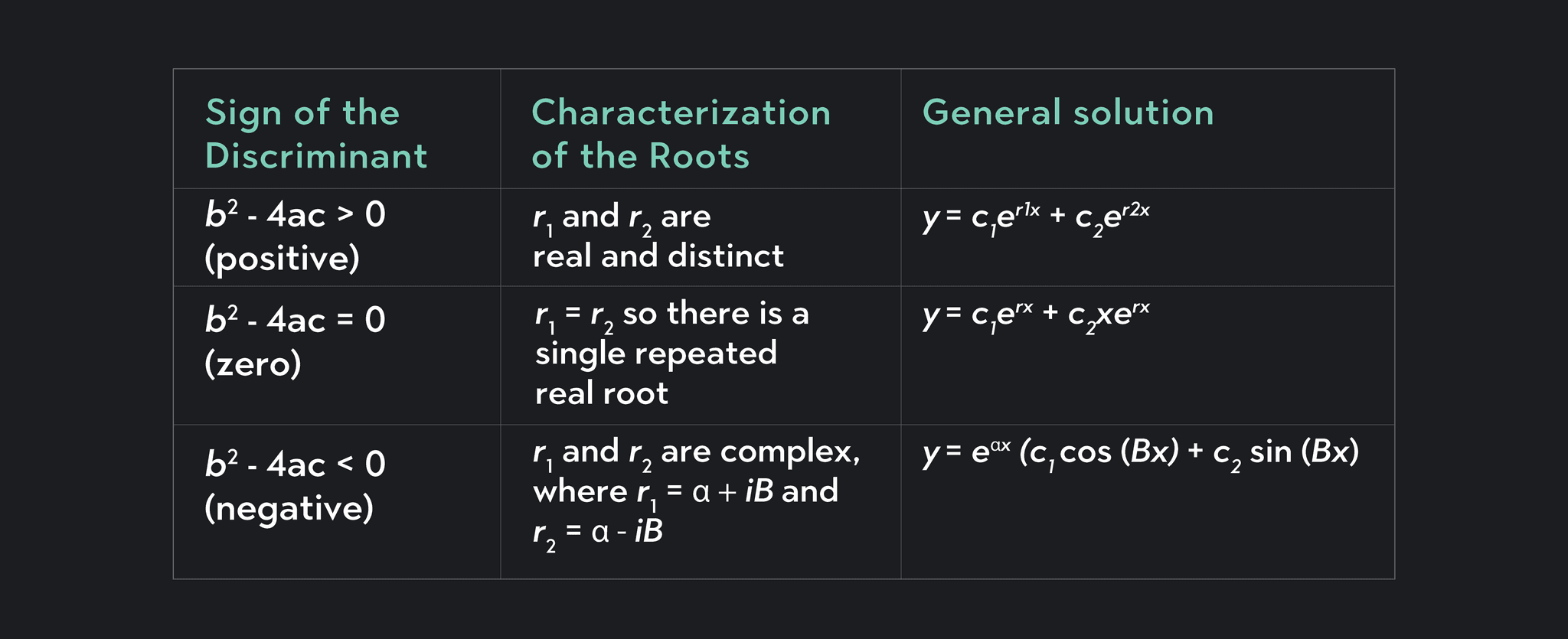
Finding a second solution to a 2nd order differential equation
Corresponding second order ode’s are obtained by taking another derivative, as x =tant, ⇒ x˙ =1+x2, ⇒ x¨ =2xx˙ =2x(1+x2), (1.3.17) and x =tanht, ⇒. The solution of these equations is achieved in stages.
Solved Problem 10.1 FirstOrder Ordinary Differential
The solution of these equations is achieved in stages. Corresponding second order ode’s are obtained by taking another derivative, as x =tant, ⇒ x˙ =1+x2, ⇒ x¨ =2xx˙ =2x(1+x2), (1.3.17) and x =tanht, ⇒.
The Solution Of These Equations Is Achieved In Stages.
Corresponding second order ode’s are obtained by taking another derivative, as x =tant, ⇒ x˙ =1+x2, ⇒ x¨ =2xx˙ =2x(1+x2), (1.3.17) and x =tanht, ⇒.