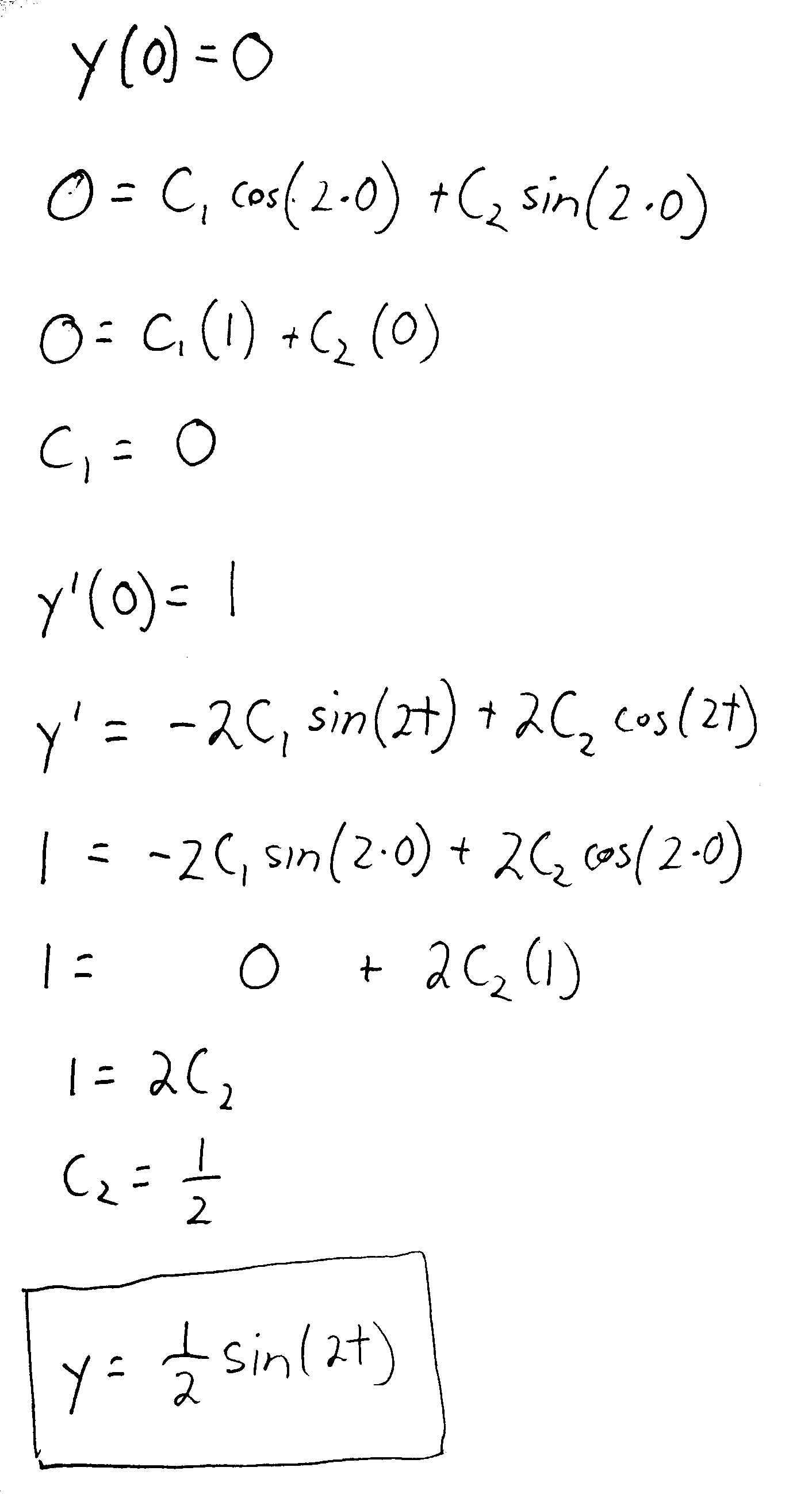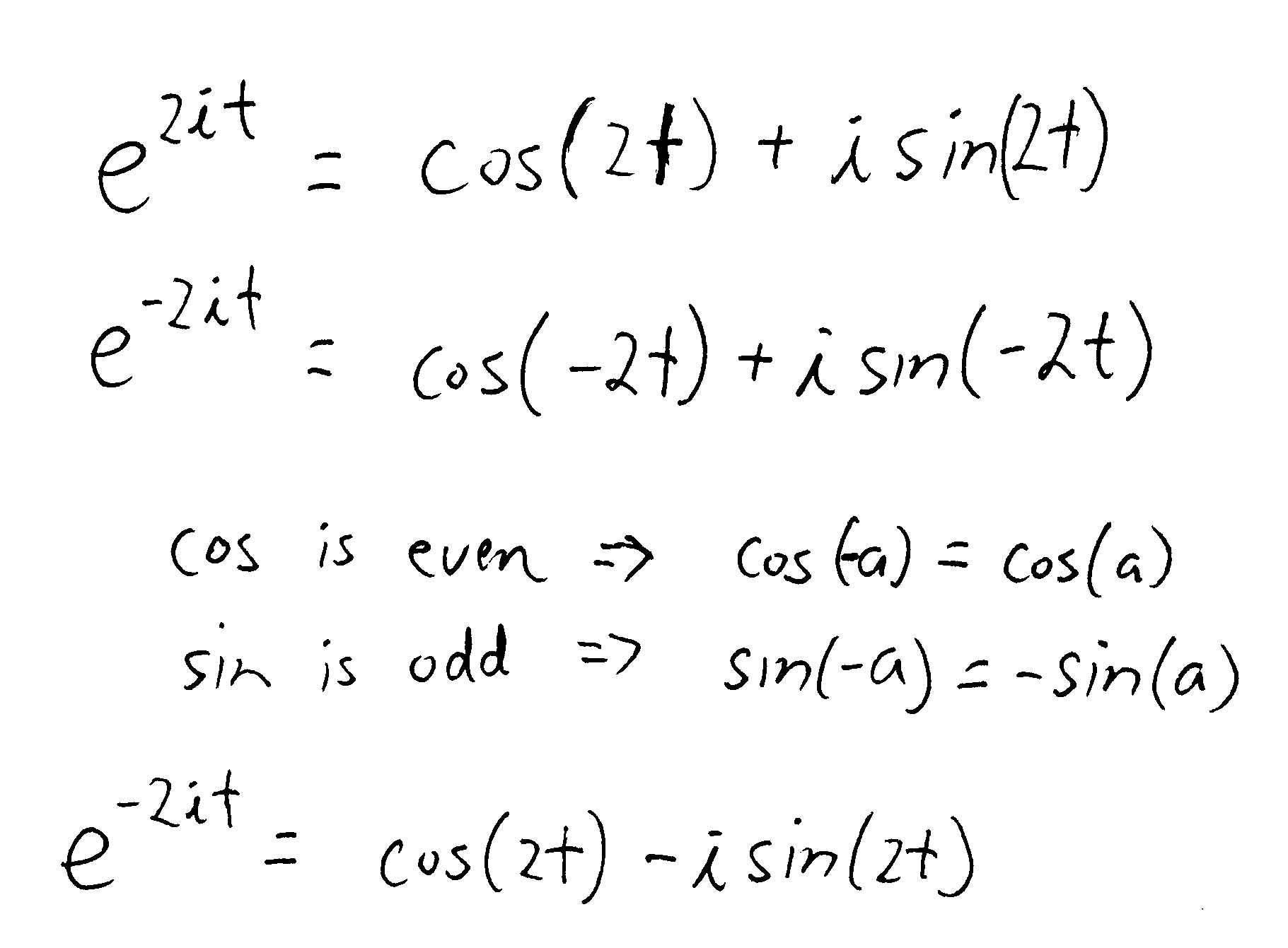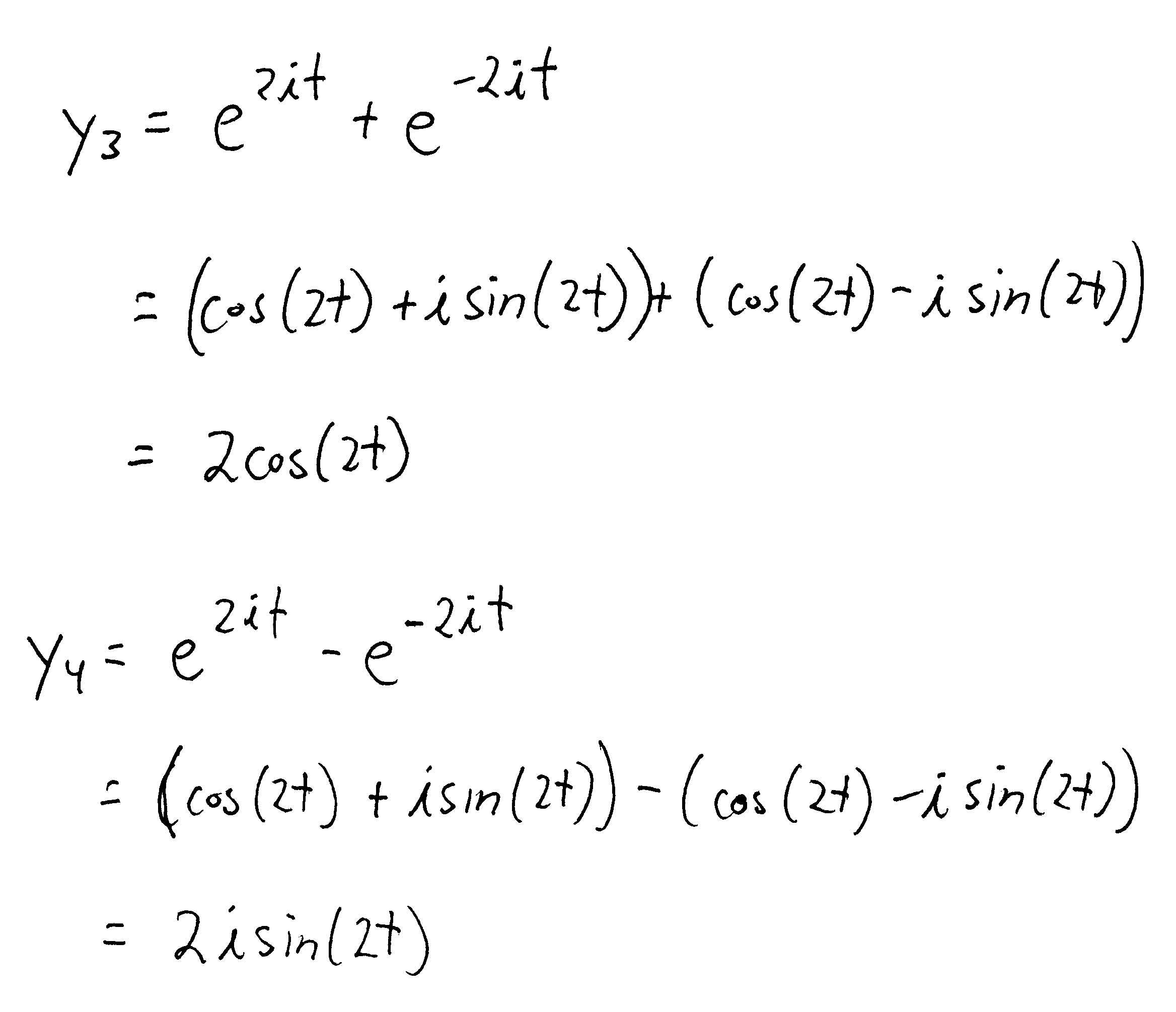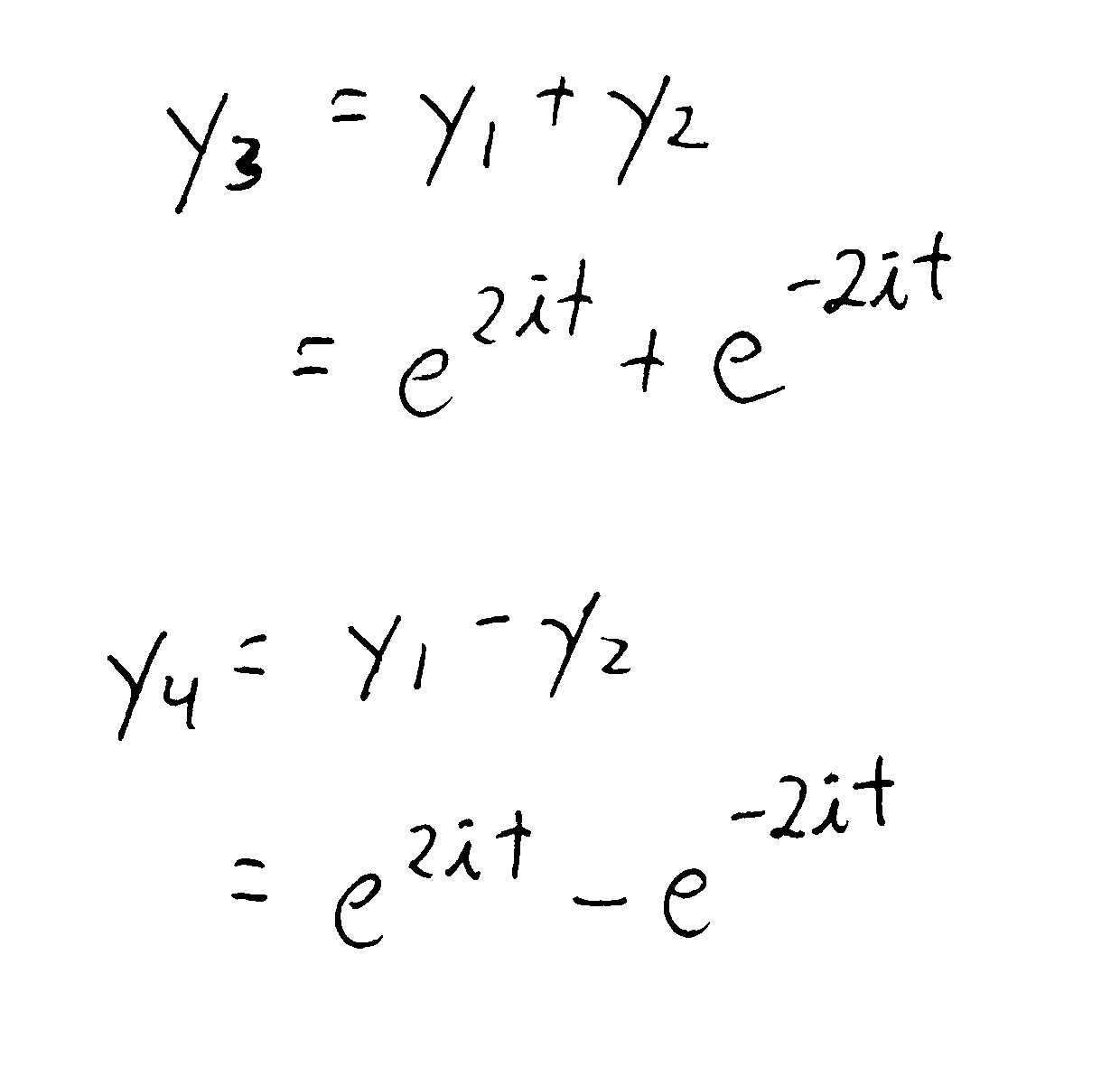Second Order Homogeneous Differential Equation - Constant coefficient second order linear odes we now proceed to study those second order linear equations which have constant. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. Second order (the highest derivative is of. A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form:
We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form: A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: Constant coefficient second order linear odes we now proceed to study those second order linear equations which have constant. Second order (the highest derivative is of.
A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form: A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: Second order (the highest derivative is of. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. Constant coefficient second order linear odes we now proceed to study those second order linear equations which have constant.
Solved For a homogeneous second order differential equation
Constant coefficient second order linear odes we now proceed to study those second order linear equations which have constant. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. Second order (the highest derivative is of. In this tutorial,.
SOLUTION Second order homogeneous linear differential equation Studypool
A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form: Constant coefficient second order linear odes we now proceed to study those second order linear equations which have constant. Second order (the highest derivative is of. A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation.
College Park Tutors Blog Differential Equations Solving a second
A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form: Constant coefficient second order linear odes we now proceed to study those second order linear equations which have constant. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous.
College Park Tutors Blog Differential Equations Solving a second
A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: Constant coefficient second order linear odes we now proceed to study those second order linear equations which have constant. Second order (the highest derivative is of. In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form: We define fundamental sets of solutions.
Can the solutions to a homogeneous second order differential equation
In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form: A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. Second order (the highest derivative is of. Constant coefficient second order linear odes we now proceed to study those second order linear equations which have constant. A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation.
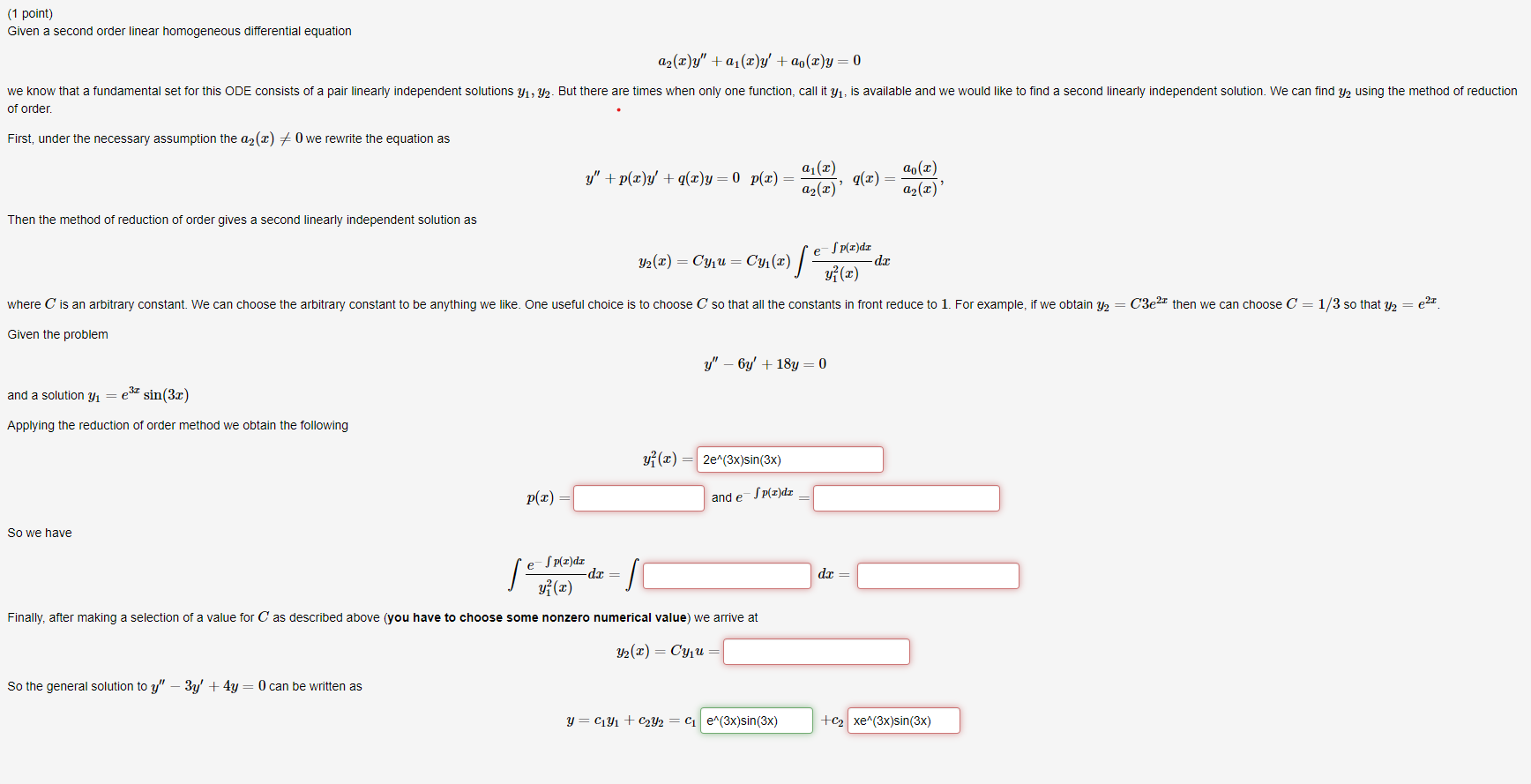
Solved Given a second order linear homogeneous differential
A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form: Constant coefficient second order linear odes we now proceed to study those second order linear equations which have constant. Second order (the highest derivative is of. We define fundamental sets of solutions.
College Park Tutors Blog Differential Equations Solving a second
Second order (the highest derivative is of. In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form: We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an.
Solved (1 point) Given a second order linear homogeneous
Second order (the highest derivative is of. Constant coefficient second order linear odes we now proceed to study those second order linear equations which have constant. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary.
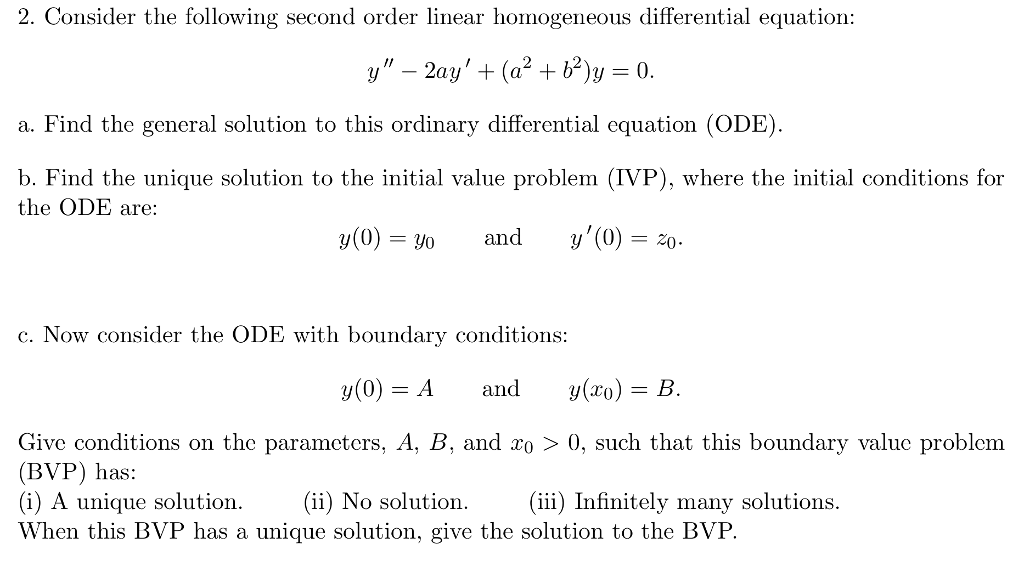
Solved 2. Consider the following second order linear
Second order (the highest derivative is of. A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. In this tutorial, we will.
College Park Tutors Blog Differential Equations Solving a second
In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form: Second order (the highest derivative is of. A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: Constant coefficient second order linear odes we now proceed to study those second order linear equations.
Second Order (The Highest Derivative Is Of.
A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form: A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: