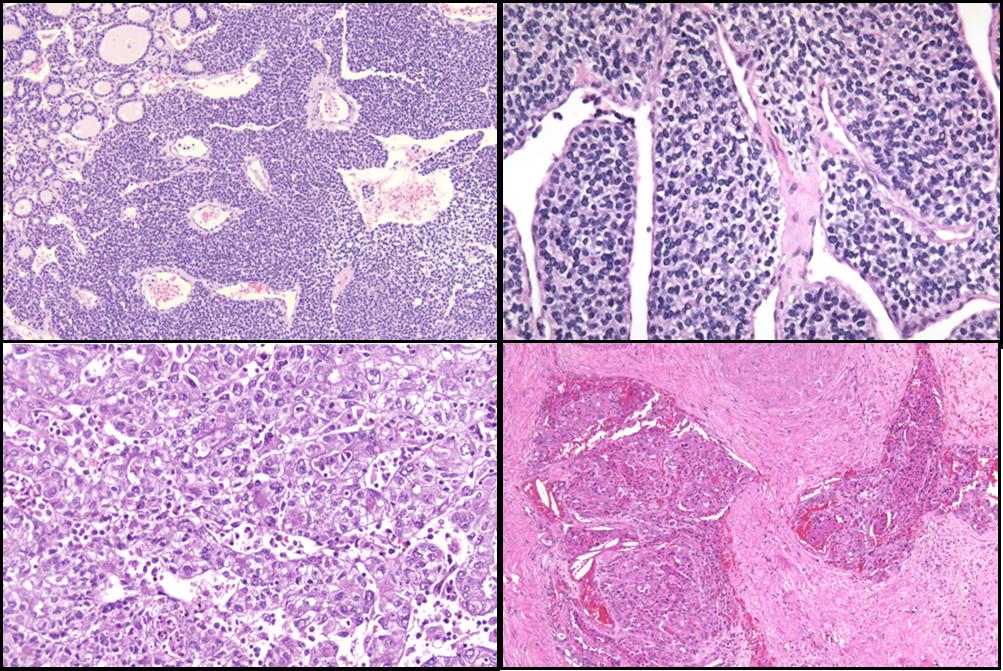
Poorly Differentiated Metastatic Carcinoma - Approximately 80 percent of these poorly differentiated tumors have features of carcinoma and are termed poorly differentiated. One third of patients with cancer of unknown primary origin have poorly or undifferentiated carcinoma. The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and. When cancer is found in one or more metastatic sites but the primary site cannot be determined, it is called a cancer of unknown primary (cup) or. Poorly differentiated carcinoma is a diagnosis, not a stage. Treatment of poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary, including tumors in the neuroendocrine system (the part of the.
One third of patients with cancer of unknown primary origin have poorly or undifferentiated carcinoma. Approximately 80 percent of these poorly differentiated tumors have features of carcinoma and are termed poorly differentiated. When cancer is found in one or more metastatic sites but the primary site cannot be determined, it is called a cancer of unknown primary (cup) or. Treatment of poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary, including tumors in the neuroendocrine system (the part of the. The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and. Poorly differentiated carcinoma is a diagnosis, not a stage.
Approximately 80 percent of these poorly differentiated tumors have features of carcinoma and are termed poorly differentiated. Poorly differentiated carcinoma is a diagnosis, not a stage. When cancer is found in one or more metastatic sites but the primary site cannot be determined, it is called a cancer of unknown primary (cup) or. Treatment of poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary, including tumors in the neuroendocrine system (the part of the. The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and. One third of patients with cancer of unknown primary origin have poorly or undifferentiated carcinoma.
Poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma with ulceration
The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and. One third of patients with cancer of unknown primary origin have poorly or undifferentiated carcinoma. Treatment of poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary, including tumors in the neuroendocrine system (the part of the. Approximately 80 percent of these poorly differentiated tumors have features of carcinoma and are termed.
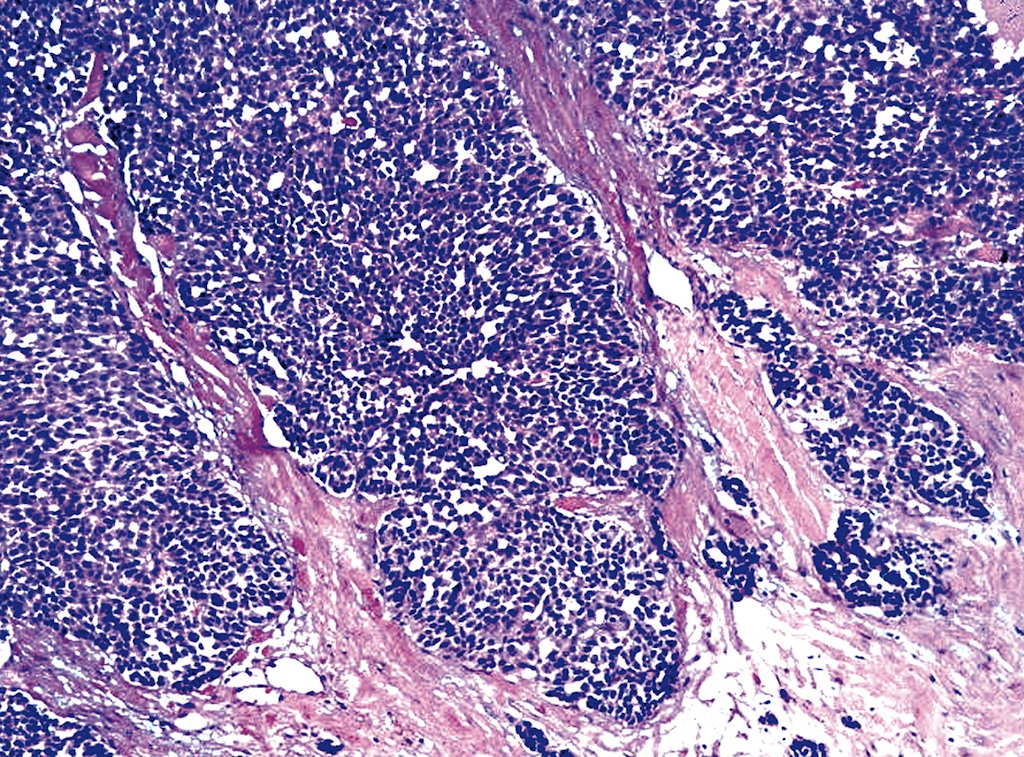
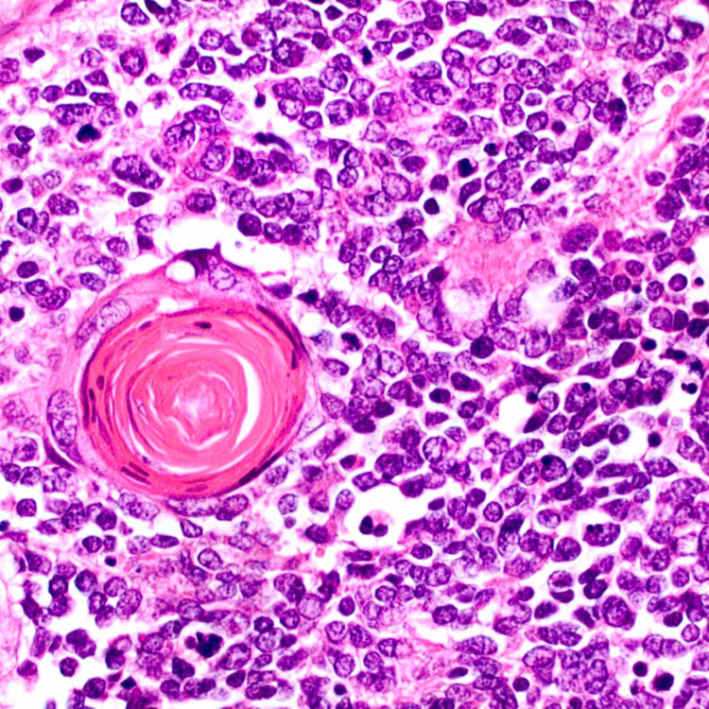
Metastatic poorly differentiated carcinoma to lymph node. The
When cancer is found in one or more metastatic sites but the primary site cannot be determined, it is called a cancer of unknown primary (cup) or. Approximately 80 percent of these poorly differentiated tumors have features of carcinoma and are termed poorly differentiated. One third of patients with cancer of unknown primary origin have poorly or undifferentiated carcinoma. Poorly.
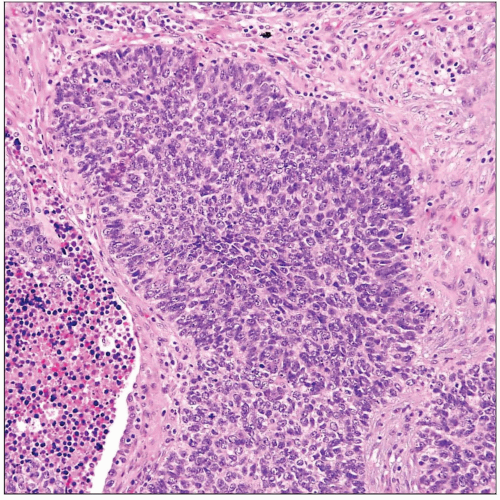
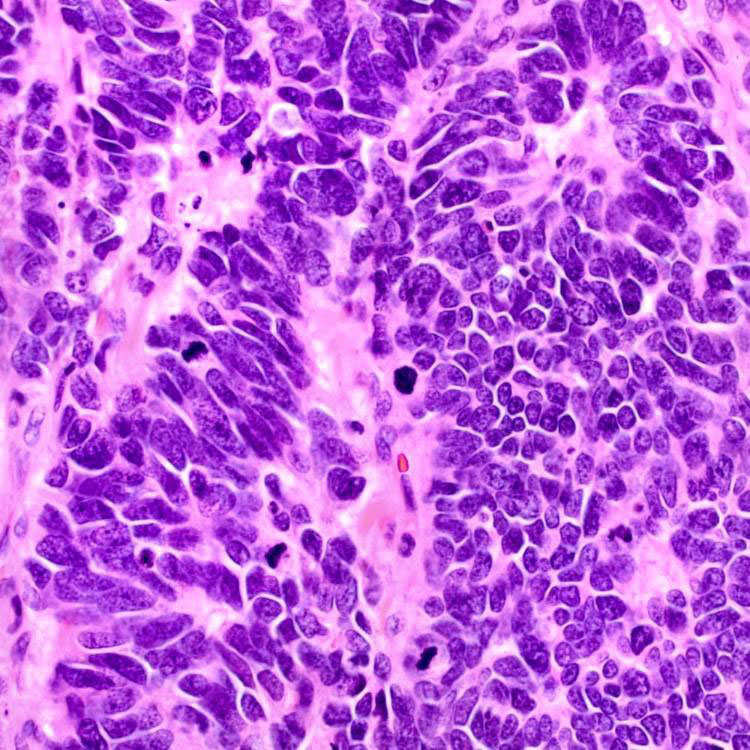
poorly differentiated carcinoma pathology
The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and. Poorly differentiated carcinoma is a diagnosis, not a stage. Approximately 80 percent of these poorly differentiated tumors have features of carcinoma and are termed poorly differentiated. When cancer is found in one or more metastatic sites but the primary site cannot be determined, it is called a cancer.
Poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma. Smear shows cohesive
The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and. Treatment of poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary, including tumors in the neuroendocrine system (the part of the. Approximately 80 percent of these poorly differentiated tumors have features of carcinoma and are termed poorly differentiated. When cancer is found in one or more metastatic sites but the primary.
Poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma MyPathologyReport.ca
One third of patients with cancer of unknown primary origin have poorly or undifferentiated carcinoma. Poorly differentiated carcinoma is a diagnosis, not a stage. Approximately 80 percent of these poorly differentiated tumors have features of carcinoma and are termed poorly differentiated. The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and. Treatment of poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown.
Poorly Differentiated Squamous Carcinoma, Small Cell Variant
Poorly differentiated carcinoma is a diagnosis, not a stage. Approximately 80 percent of these poorly differentiated tumors have features of carcinoma and are termed poorly differentiated. When cancer is found in one or more metastatic sites but the primary site cannot be determined, it is called a cancer of unknown primary (cup) or. The cancer’s stage is determined by additional.
GO BIG or GO HOME Poorly Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma (2)
When cancer is found in one or more metastatic sites but the primary site cannot be determined, it is called a cancer of unknown primary (cup) or. The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and. Poorly differentiated carcinoma is a diagnosis, not a stage. Treatment of poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary, including tumors in the.
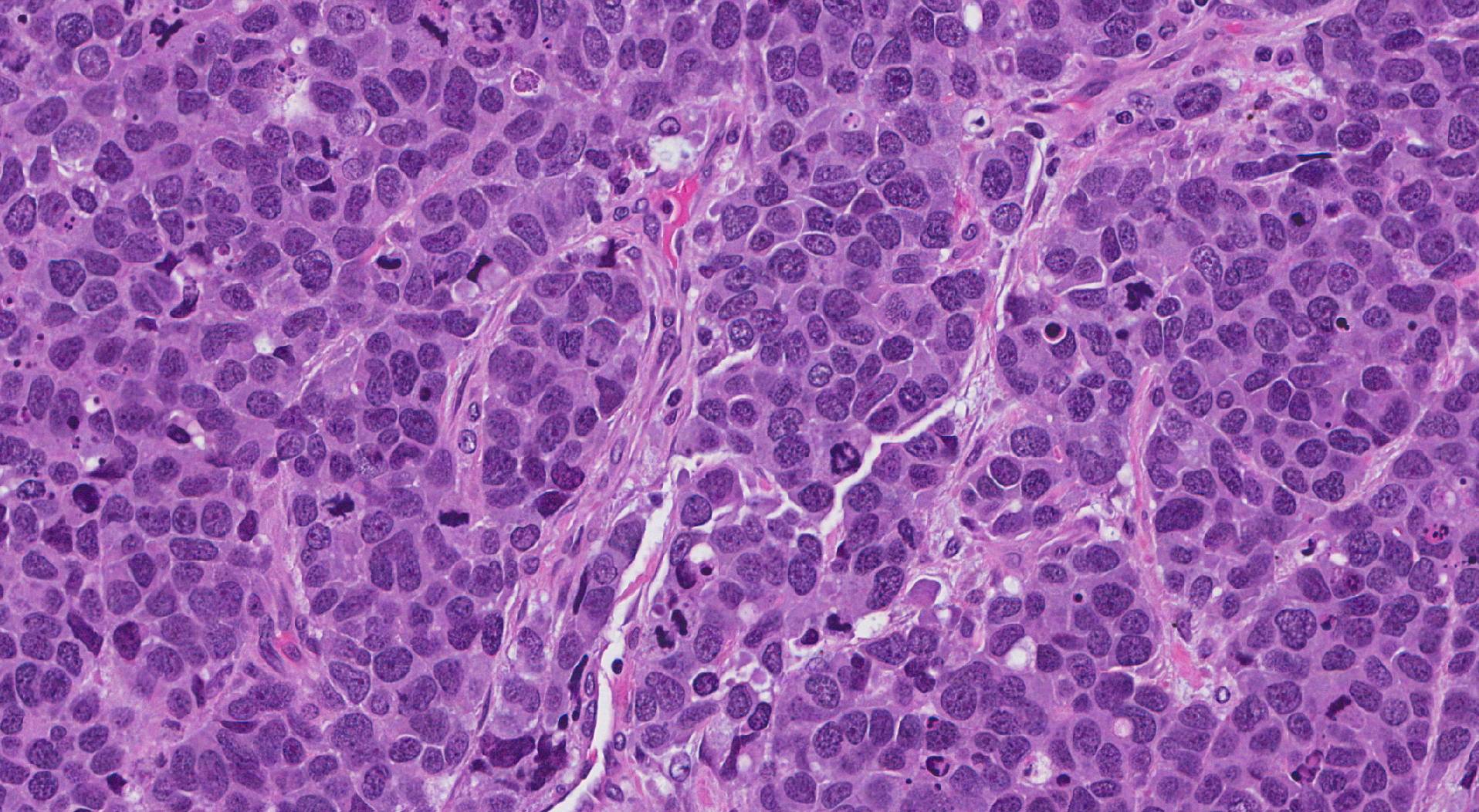
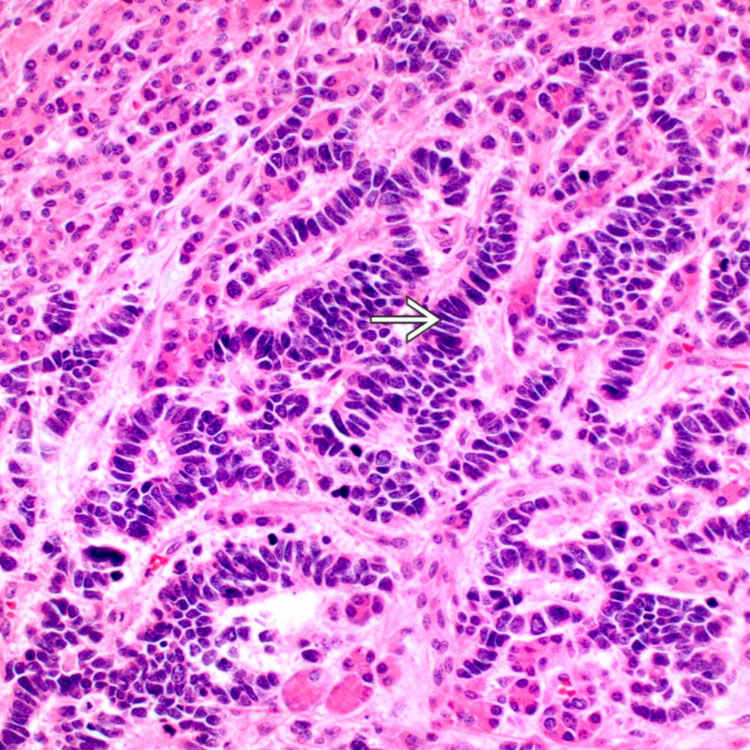
Poorly Differentiated Neuroendocrine Carcinoma, Pancreas Basicmedical Key
Poorly differentiated carcinoma is a diagnosis, not a stage. Approximately 80 percent of these poorly differentiated tumors have features of carcinoma and are termed poorly differentiated. Treatment of poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary, including tumors in the neuroendocrine system (the part of the. One third of patients with cancer of unknown primary origin have poorly or undifferentiated carcinoma. When.
Poorly Differentiated Neuroendocrine Carcinoma, Pancreas Basicmedical Key
One third of patients with cancer of unknown primary origin have poorly or undifferentiated carcinoma. The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and. Treatment of poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary, including tumors in the neuroendocrine system (the part of the. Poorly differentiated carcinoma is a diagnosis, not a stage. When cancer is found in one.
Poorly Differentiated Neuroendocrine Carcinoma, Pancreas Basicmedical Key
Treatment of poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary, including tumors in the neuroendocrine system (the part of the. When cancer is found in one or more metastatic sites but the primary site cannot be determined, it is called a cancer of unknown primary (cup) or. One third of patients with cancer of unknown primary origin have poorly or undifferentiated carcinoma..
Approximately 80 Percent Of These Poorly Differentiated Tumors Have Features Of Carcinoma And Are Termed Poorly Differentiated.
Treatment of poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary, including tumors in the neuroendocrine system (the part of the. One third of patients with cancer of unknown primary origin have poorly or undifferentiated carcinoma. When cancer is found in one or more metastatic sites but the primary site cannot be determined, it is called a cancer of unknown primary (cup) or. The cancer’s stage is determined by additional information, including the size and.