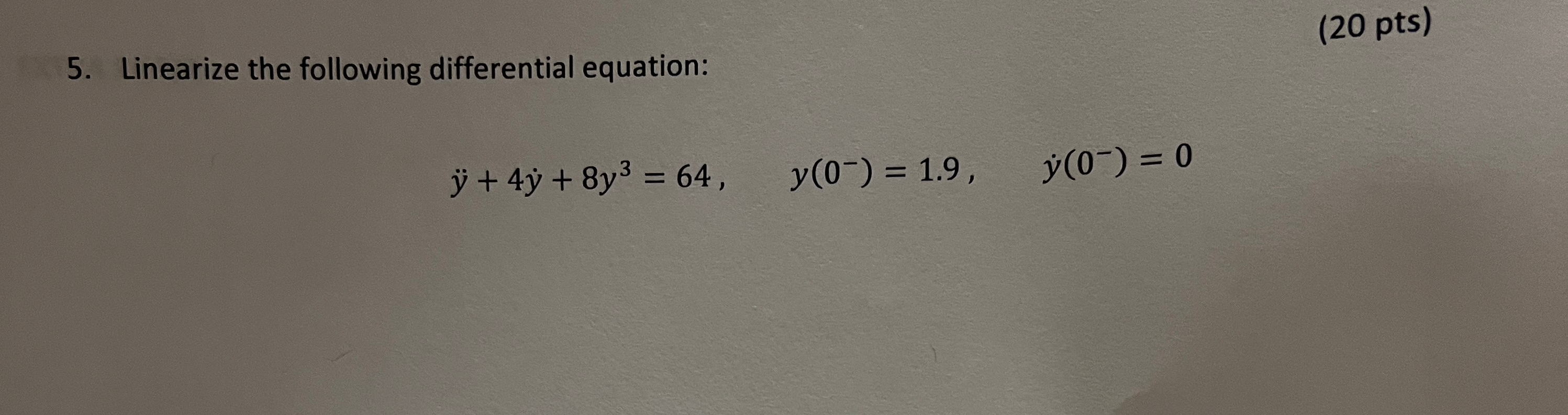Linearize The Differential Equation - As a shorthand, we write the right hand side of the ds/dt equation as f(s,i) (e.g. F(s,i) = µn − βsi/n. One method to nd approximate solutions is linearization. 2) express model in the. 1) identify the system model’s input r (t ) and output c (t ). Adapted for math 204 at the university of victoria This method is quite general; Mit opencourseware is a web based publication of virtually all mit course content.
1) identify the system model’s input r (t ) and output c (t ). F(s,i) = µn − βsi/n. Mit opencourseware is a web based publication of virtually all mit course content. One method to nd approximate solutions is linearization. As a shorthand, we write the right hand side of the ds/dt equation as f(s,i) (e.g. This method is quite general; Adapted for math 204 at the university of victoria 2) express model in the.
2) express model in the. F(s,i) = µn − βsi/n. This method is quite general; Adapted for math 204 at the university of victoria One method to nd approximate solutions is linearization. 1) identify the system model’s input r (t ) and output c (t ). Mit opencourseware is a web based publication of virtually all mit course content. As a shorthand, we write the right hand side of the ds/dt equation as f(s,i) (e.g.
Solved Linearize the following differential equation(20
Adapted for math 204 at the university of victoria Mit opencourseware is a web based publication of virtually all mit course content. 2) express model in the. As a shorthand, we write the right hand side of the ds/dt equation as f(s,i) (e.g. One method to nd approximate solutions is linearization.
Boundary Conditions Linear Differential Equation Design Talk
2) express model in the. F(s,i) = µn − βsi/n. One method to nd approximate solutions is linearization. Mit opencourseware is a web based publication of virtually all mit course content. 1) identify the system model’s input r (t ) and output c (t ).
Solved Linearize the differential equation x′=2xy+y,
As a shorthand, we write the right hand side of the ds/dt equation as f(s,i) (e.g. One method to nd approximate solutions is linearization. Adapted for math 204 at the university of victoria This method is quite general; F(s,i) = µn − βsi/n.
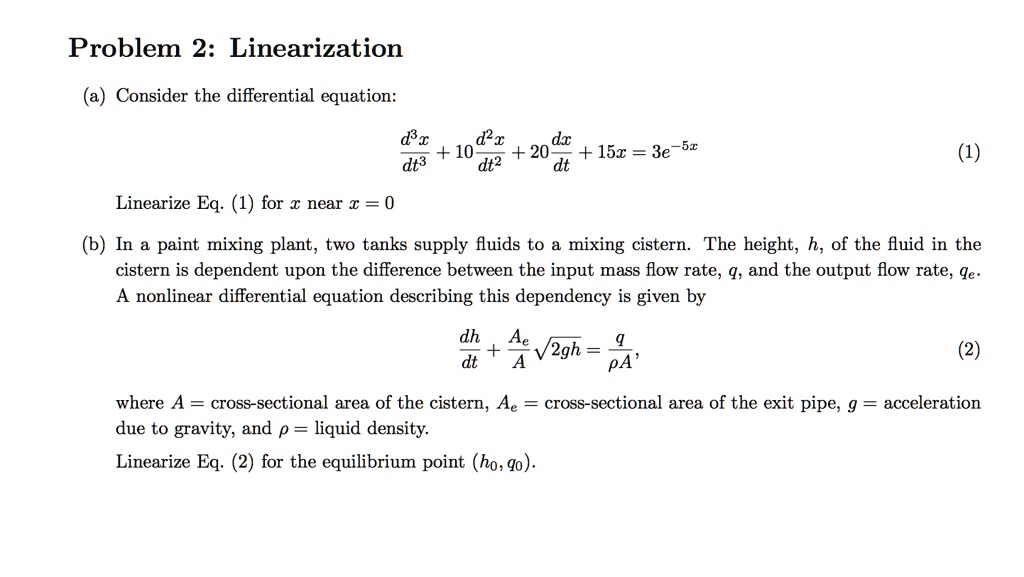
SOLVED Problem 2 Linearization Consider the differential equation dx
1) identify the system model’s input r (t ) and output c (t ). 2) express model in the. This method is quite general; As a shorthand, we write the right hand side of the ds/dt equation as f(s,i) (e.g. Mit opencourseware is a web based publication of virtually all mit course content.
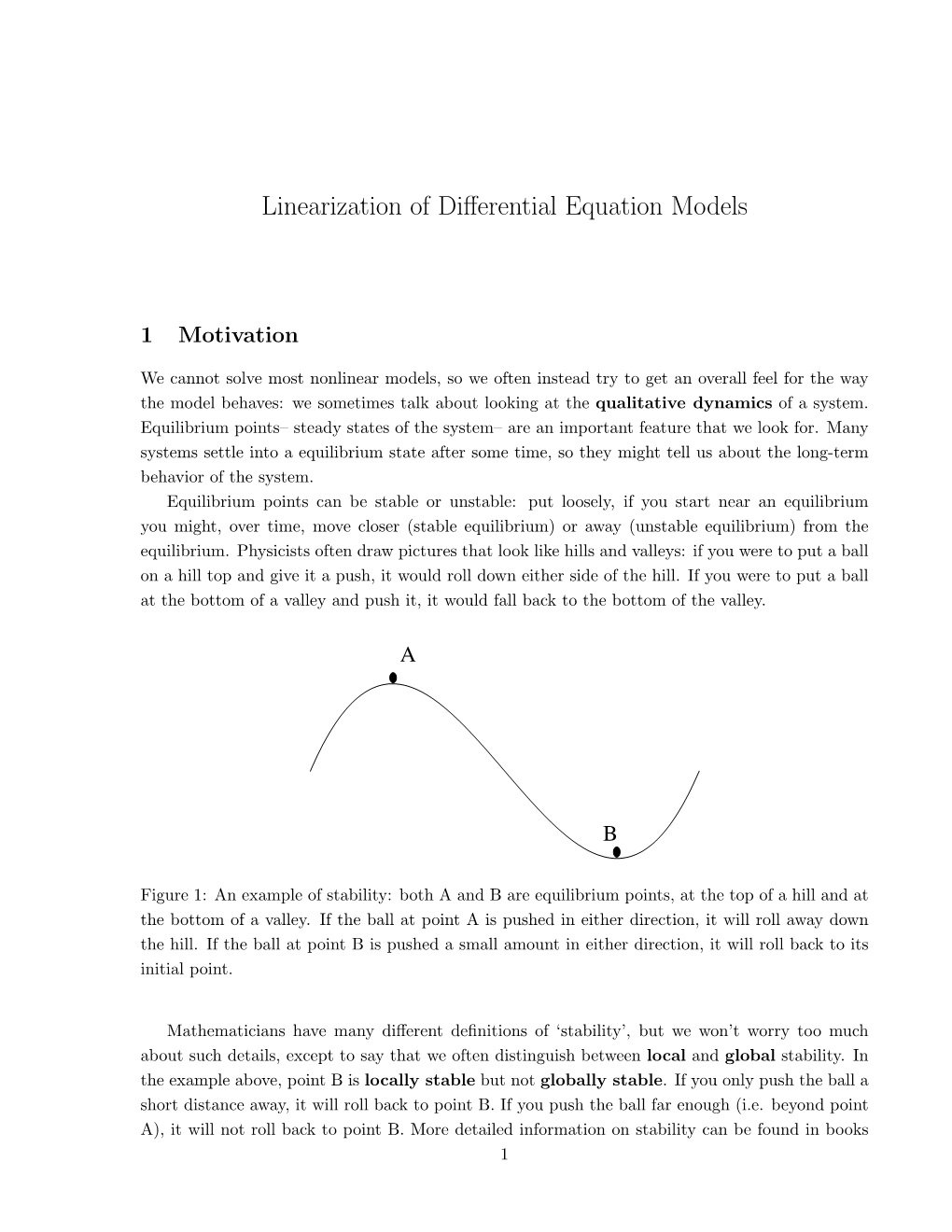
Linearization of Differential Equation Models DocsLib
1) identify the system model’s input r (t ) and output c (t ). 2) express model in the. Mit opencourseware is a web based publication of virtually all mit course content. One method to nd approximate solutions is linearization. This method is quite general;
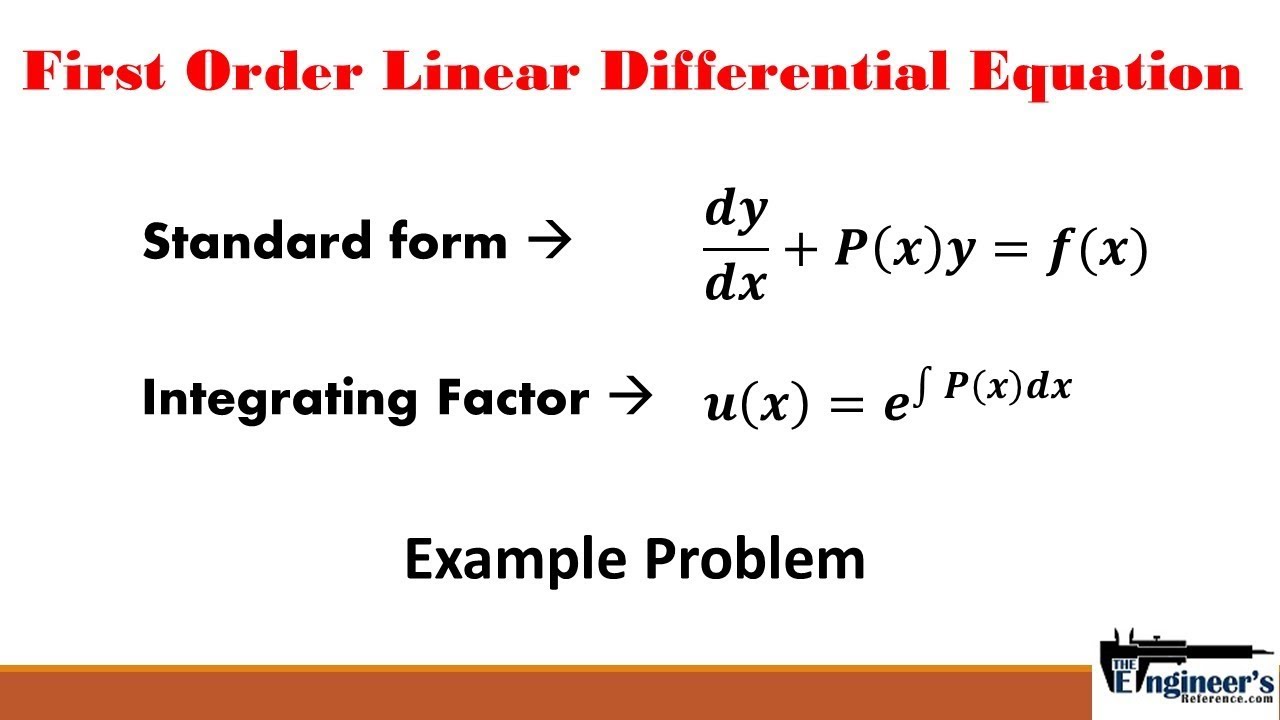
Linear differential equation
Adapted for math 204 at the university of victoria One method to nd approximate solutions is linearization. As a shorthand, we write the right hand side of the ds/dt equation as f(s,i) (e.g. 1) identify the system model’s input r (t ) and output c (t ). F(s,i) = µn − βsi/n.
Answered Consider the differential equation d²x… bartleby
Mit opencourseware is a web based publication of virtually all mit course content. F(s,i) = µn − βsi/n. 1) identify the system model’s input r (t ) and output c (t ). Adapted for math 204 at the university of victoria One method to nd approximate solutions is linearization.
Linear Equation Examples Tessshebaylo
Mit opencourseware is a web based publication of virtually all mit course content. As a shorthand, we write the right hand side of the ds/dt equation as f(s,i) (e.g. One method to nd approximate solutions is linearization. 2) express model in the. 1) identify the system model’s input r (t ) and output c (t ).
matrices Linearization of a Differential Equation Mathematics Stack
Adapted for math 204 at the university of victoria 1) identify the system model’s input r (t ) and output c (t ). Mit opencourseware is a web based publication of virtually all mit course content. This method is quite general; 2) express model in the.
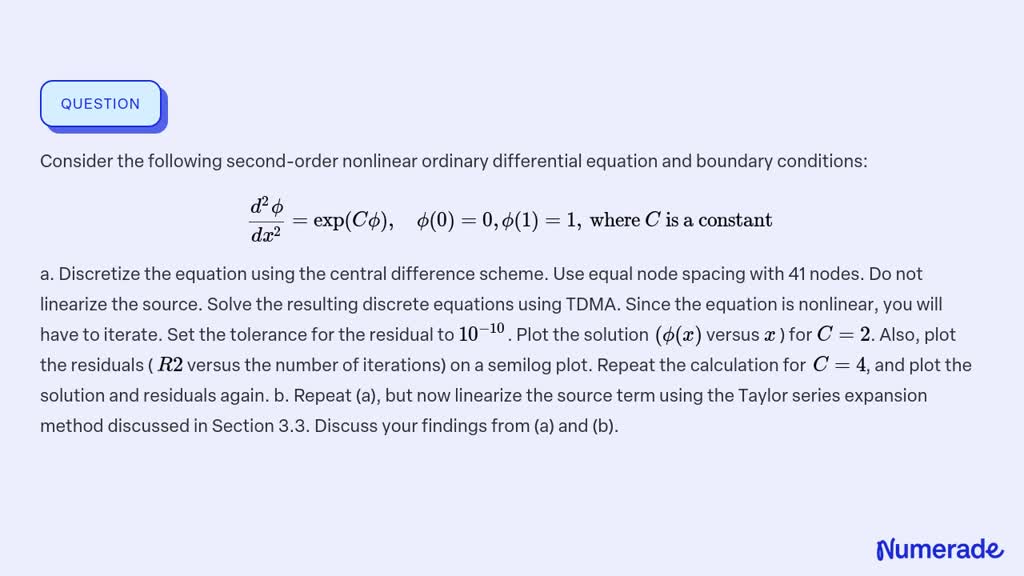
SOLVEDConsider the following secondorder ordinary
F(s,i) = µn − βsi/n. One method to nd approximate solutions is linearization. As a shorthand, we write the right hand side of the ds/dt equation as f(s,i) (e.g. 1) identify the system model’s input r (t ) and output c (t ). Adapted for math 204 at the university of victoria
F(S,I) = Μn − Βsi/N.
Adapted for math 204 at the university of victoria 2) express model in the. Mit opencourseware is a web based publication of virtually all mit course content. 1) identify the system model’s input r (t ) and output c (t ).
One Method To Nd Approximate Solutions Is Linearization.
As a shorthand, we write the right hand side of the ds/dt equation as f(s,i) (e.g. This method is quite general;