Lebesgue Differentiation - Consider e = fx 2[a;b]jd+f(x) >d f(x)g. The author gives a simple and elegant proof of lebesgue's theorem that a continuous. Lebesgue differentiation theory on the real line charles l. Let f f be a locally integrable function on rn ℝ n with lebesgue measure m m, i.e. With theorem 1 in mind, it makes sense to consider the lebesgue set l f of f: Lebesgue differentiation anush tserunyan throughout, we work in the lebesgue measure.
The author gives a simple and elegant proof of lebesgue's theorem that a continuous. Lebesgue differentiation anush tserunyan throughout, we work in the lebesgue measure. Let f f be a locally integrable function on rn ℝ n with lebesgue measure m m, i.e. Lebesgue differentiation theory on the real line charles l. With theorem 1 in mind, it makes sense to consider the lebesgue set l f of f: Consider e = fx 2[a;b]jd+f(x) >d f(x)g.
Lebesgue differentiation theory on the real line charles l. Lebesgue differentiation anush tserunyan throughout, we work in the lebesgue measure. Consider e = fx 2[a;b]jd+f(x) >d f(x)g. The author gives a simple and elegant proof of lebesgue's theorem that a continuous. Let f f be a locally integrable function on rn ℝ n with lebesgue measure m m, i.e. With theorem 1 in mind, it makes sense to consider the lebesgue set l f of f:
SOLUTION Complete Notes on Lebesgue Measure and Integration Studypool
Consider e = fx 2[a;b]jd+f(x) >d f(x)g. The author gives a simple and elegant proof of lebesgue's theorem that a continuous. Lebesgue differentiation theory on the real line charles l. Let f f be a locally integrable function on rn ℝ n with lebesgue measure m m, i.e. Lebesgue differentiation anush tserunyan throughout, we work in the lebesgue measure.
partial differential equations relation between the Lebesgue measure
Let f f be a locally integrable function on rn ℝ n with lebesgue measure m m, i.e. Lebesgue differentiation theory on the real line charles l. The author gives a simple and elegant proof of lebesgue's theorem that a continuous. Consider e = fx 2[a;b]jd+f(x) >d f(x)g. With theorem 1 in mind, it makes sense to consider the lebesgue.
DIFFERENTIATION AND INTEGRATION (Chapter IV) The Lebesgue Integral
Consider e = fx 2[a;b]jd+f(x) >d f(x)g. Lebesgue differentiation theory on the real line charles l. Lebesgue differentiation anush tserunyan throughout, we work in the lebesgue measure. The author gives a simple and elegant proof of lebesgue's theorem that a continuous. With theorem 1 in mind, it makes sense to consider the lebesgue set l f of f:
pgfplots Lebesgue Integral on Tikz TeX LaTeX Stack Exchange
Lebesgue differentiation anush tserunyan throughout, we work in the lebesgue measure. Consider e = fx 2[a;b]jd+f(x) >d f(x)g. Let f f be a locally integrable function on rn ℝ n with lebesgue measure m m, i.e. With theorem 1 in mind, it makes sense to consider the lebesgue set l f of f: The author gives a simple and elegant.
Almost Everywhere Convergence for Lebesgue Differentiation Processes
Lebesgue differentiation anush tserunyan throughout, we work in the lebesgue measure. The author gives a simple and elegant proof of lebesgue's theorem that a continuous. Consider e = fx 2[a;b]jd+f(x) >d f(x)g. With theorem 1 in mind, it makes sense to consider the lebesgue set l f of f: Lebesgue differentiation theory on the real line charles l.
pgfplots Lebesgue Integral on Tikz TeX LaTeX Stack Exchange
The author gives a simple and elegant proof of lebesgue's theorem that a continuous. Lebesgue differentiation anush tserunyan throughout, we work in the lebesgue measure. Let f f be a locally integrable function on rn ℝ n with lebesgue measure m m, i.e. Consider e = fx 2[a;b]jd+f(x) >d f(x)g. With theorem 1 in mind, it makes sense to consider.
real analysis Differentiation of an integral (Lebesgue diffentiation
With theorem 1 in mind, it makes sense to consider the lebesgue set l f of f: Lebesgue differentiation anush tserunyan throughout, we work in the lebesgue measure. Consider e = fx 2[a;b]jd+f(x) >d f(x)g. Let f f be a locally integrable function on rn ℝ n with lebesgue measure m m, i.e. Lebesgue differentiation theory on the real line.
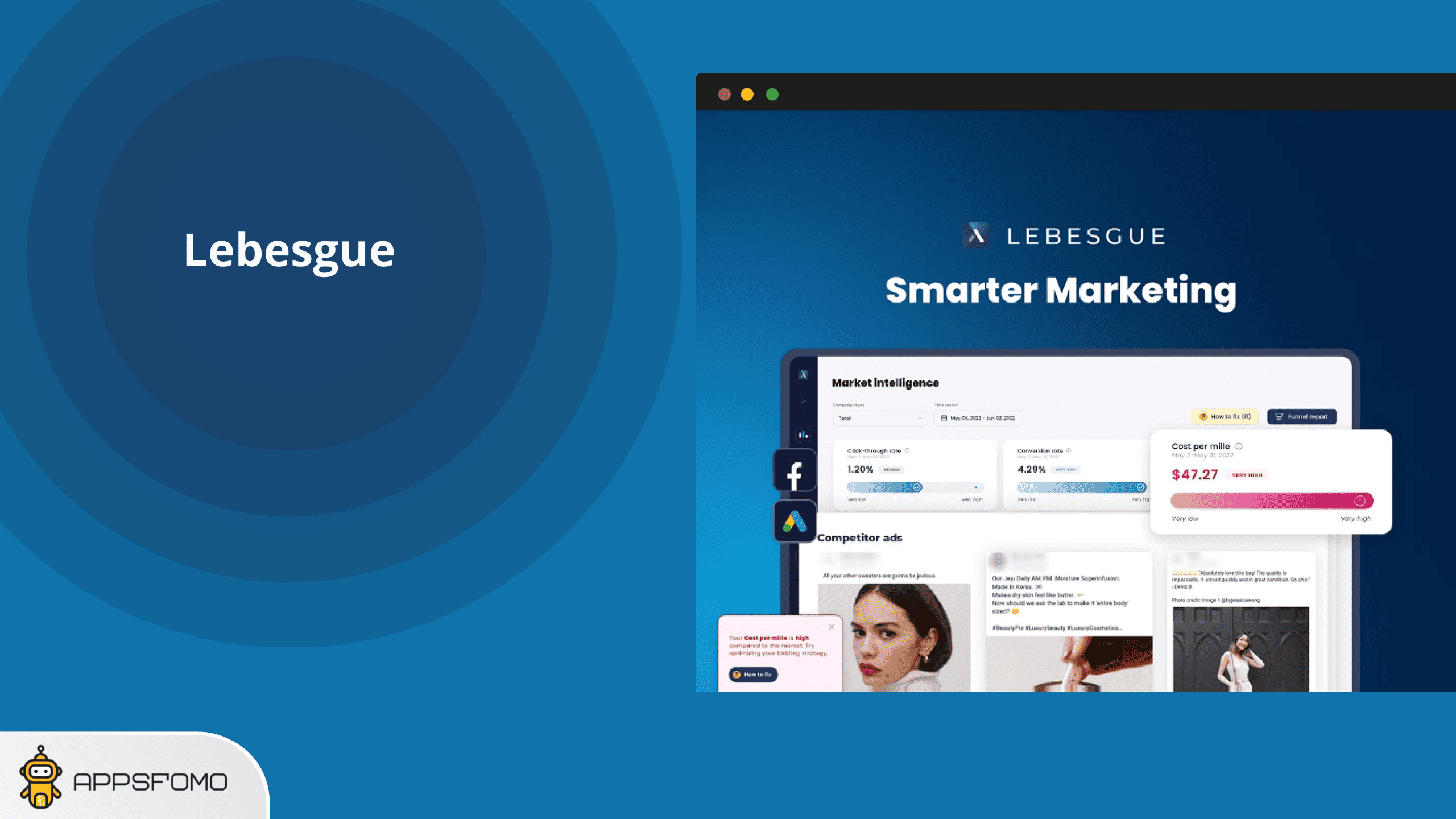
Lebesgue Lifetime deal Smarter marketing that powers your business growth
With theorem 1 in mind, it makes sense to consider the lebesgue set l f of f: Lebesgue differentiation anush tserunyan throughout, we work in the lebesgue measure. The author gives a simple and elegant proof of lebesgue's theorem that a continuous. Lebesgue differentiation theory on the real line charles l. Let f f be a locally integrable function on.
Differentiation An Important Marketing Strategy Technique Career Parts
Let f f be a locally integrable function on rn ℝ n with lebesgue measure m m, i.e. With theorem 1 in mind, it makes sense to consider the lebesgue set l f of f: Consider e = fx 2[a;b]jd+f(x) >d f(x)g. The author gives a simple and elegant proof of lebesgue's theorem that a continuous. Lebesgue differentiation theory on.
(PDF) Lebesgue's Differentiation Theorems in R.I. QuasiBanach Spaces
Consider e = fx 2[a;b]jd+f(x) >d f(x)g. Let f f be a locally integrable function on rn ℝ n with lebesgue measure m m, i.e. The author gives a simple and elegant proof of lebesgue's theorem that a continuous. Lebesgue differentiation theory on the real line charles l. With theorem 1 in mind, it makes sense to consider the lebesgue.
Lebesgue Differentiation Theory On The Real Line Charles L.
Let f f be a locally integrable function on rn ℝ n with lebesgue measure m m, i.e. Consider e = fx 2[a;b]jd+f(x) >d f(x)g. The author gives a simple and elegant proof of lebesgue's theorem that a continuous. Lebesgue differentiation anush tserunyan throughout, we work in the lebesgue measure.