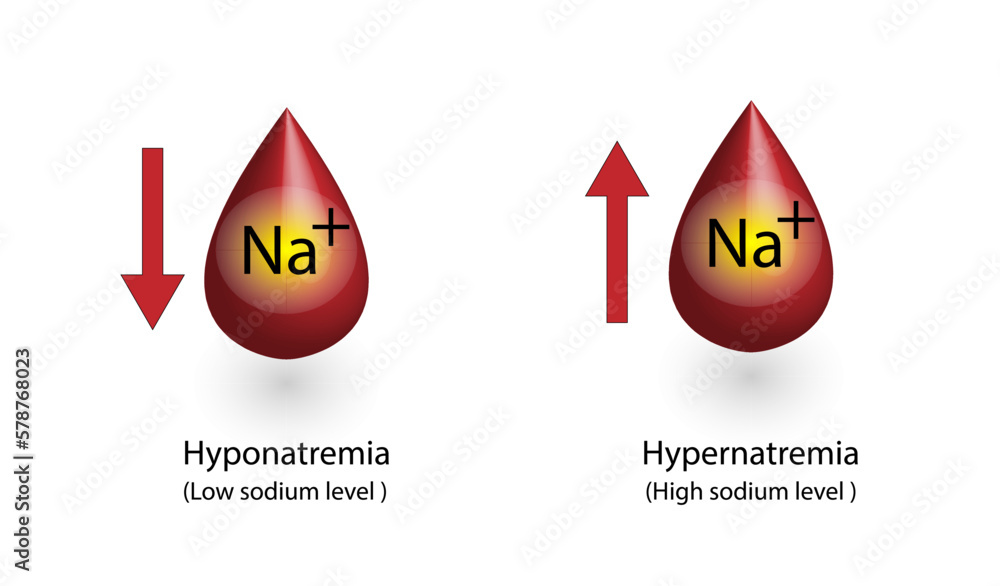
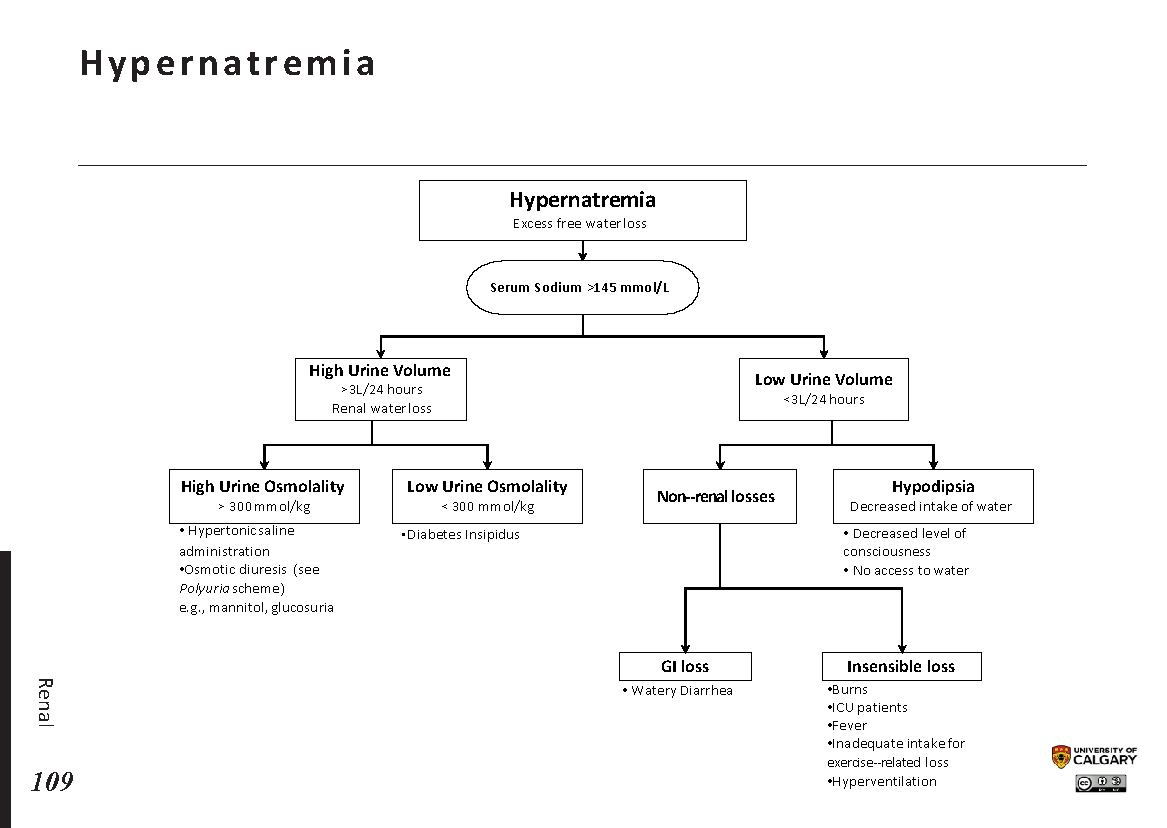
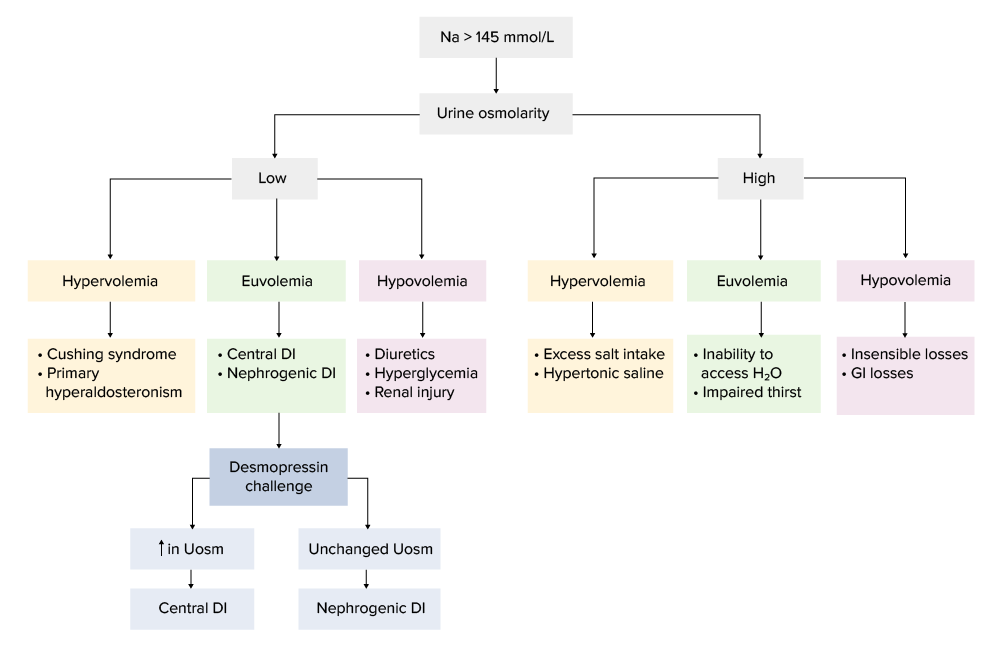
Hypernatremia Differential - Hypernatremia is a common electrolyte problem and is defined as a rise in. Hypernatremia is a plasma sodium concentration of >145 meq/l, usually due to. Hypernatremia is defined as serum sodium (sna) concentration exceeding 145 mmol/l and. Hypernatremia is usually caused by limited access to water or an impaired thirst. Because sodium and its anions make up most of the effective osmoles in the extracellular fluid,.
Hypernatremia is defined as serum sodium (sna) concentration exceeding 145 mmol/l and. Hypernatremia is a common electrolyte problem and is defined as a rise in. Hypernatremia is a plasma sodium concentration of >145 meq/l, usually due to. Hypernatremia is usually caused by limited access to water or an impaired thirst. Because sodium and its anions make up most of the effective osmoles in the extracellular fluid,.
Hypernatremia is a plasma sodium concentration of >145 meq/l, usually due to. Because sodium and its anions make up most of the effective osmoles in the extracellular fluid,. Hypernatremia is a common electrolyte problem and is defined as a rise in. Hypernatremia is usually caused by limited access to water or an impaired thirst. Hypernatremia is defined as serum sodium (sna) concentration exceeding 145 mmol/l and.
Hypernatremia The Clinical Problem Solvers
Hypernatremia is a plasma sodium concentration of >145 meq/l, usually due to. Hypernatremia is a common electrolyte problem and is defined as a rise in. Hypernatremia is usually caused by limited access to water or an impaired thirst. Hypernatremia is defined as serum sodium (sna) concentration exceeding 145 mmol/l and. Because sodium and its anions make up most of the.
Hypernatremia Video, Anatomy, Definition & Function Osmosis
Because sodium and its anions make up most of the effective osmoles in the extracellular fluid,. Hypernatremia is a plasma sodium concentration of >145 meq/l, usually due to. Hypernatremia is defined as serum sodium (sna) concentration exceeding 145 mmol/l and. Hypernatremia is usually caused by limited access to water or an impaired thirst. Hypernatremia is a common electrolyte problem and.
Hypernatremia High Plasma Sodium Level And Hyponatremia Low Plasma
Hypernatremia is defined as serum sodium (sna) concentration exceeding 145 mmol/l and. Because sodium and its anions make up most of the effective osmoles in the extracellular fluid,. Hypernatremia is usually caused by limited access to water or an impaired thirst. Hypernatremia is a plasma sodium concentration of >145 meq/l, usually due to. Hypernatremia is a common electrolyte problem and.
Causes Of Hypernatremia Differential Diagnosis Algorithm The Best
Because sodium and its anions make up most of the effective osmoles in the extracellular fluid,. Hypernatremia is a plasma sodium concentration of >145 meq/l, usually due to. Hypernatremia is defined as serum sodium (sna) concentration exceeding 145 mmol/l and. Hypernatremia is a common electrolyte problem and is defined as a rise in. Hypernatremia is usually caused by limited access.
Hypernatremia Physiology Calgary Guide
Because sodium and its anions make up most of the effective osmoles in the extracellular fluid,. Hypernatremia is a common electrolyte problem and is defined as a rise in. Hypernatremia is usually caused by limited access to water or an impaired thirst. Hypernatremia is a plasma sodium concentration of >145 meq/l, usually due to. Hypernatremia is defined as serum sodium.
Hypernatremia (Clinical) Concise Medical Knowledge
Hypernatremia is defined as serum sodium (sna) concentration exceeding 145 mmol/l and. Hypernatremia is a plasma sodium concentration of >145 meq/l, usually due to. Because sodium and its anions make up most of the effective osmoles in the extracellular fluid,. Hypernatremia is usually caused by limited access to water or an impaired thirst. Hypernatremia is a common electrolyte problem and.
[PDF] Hypernatremia in dogs. Semantic Scholar
Hypernatremia is defined as serum sodium (sna) concentration exceeding 145 mmol/l and. Hypernatremia is usually caused by limited access to water or an impaired thirst. Because sodium and its anions make up most of the effective osmoles in the extracellular fluid,. Hypernatremia is a common electrolyte problem and is defined as a rise in. Hypernatremia is a plasma sodium concentration.
nephrologyhypernatremiadifferentialalgorithmcausesoriginal PDF
Hypernatremia is a plasma sodium concentration of >145 meq/l, usually due to. Hypernatremia is a common electrolyte problem and is defined as a rise in. Because sodium and its anions make up most of the effective osmoles in the extracellular fluid,. Hypernatremia is defined as serum sodium (sna) concentration exceeding 145 mmol/l and. Hypernatremia is usually caused by limited access.
Hypernatremia Notability Gallery
Hypernatremia is usually caused by limited access to water or an impaired thirst. Hypernatremia is a common electrolyte problem and is defined as a rise in. Because sodium and its anions make up most of the effective osmoles in the extracellular fluid,. Hypernatremia is a plasma sodium concentration of >145 meq/l, usually due to. Hypernatremia is defined as serum sodium.
[DIAGRAM] Diagram Of Hypernatremia
Hypernatremia is a common electrolyte problem and is defined as a rise in. Hypernatremia is usually caused by limited access to water or an impaired thirst. Hypernatremia is a plasma sodium concentration of >145 meq/l, usually due to. Hypernatremia is defined as serum sodium (sna) concentration exceeding 145 mmol/l and. Because sodium and its anions make up most of the.
Hypernatremia Is A Plasma Sodium Concentration Of >145 Meq/L, Usually Due To.
Hypernatremia is defined as serum sodium (sna) concentration exceeding 145 mmol/l and. Because sodium and its anions make up most of the effective osmoles in the extracellular fluid,. Hypernatremia is usually caused by limited access to water or an impaired thirst. Hypernatremia is a common electrolyte problem and is defined as a rise in.



![[PDF] Hypernatremia in dogs. Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/be2ba66edf0c1fd3d5def7ad52e47a3adb82b388/7-Figure1-1.png)


![[DIAGRAM] Diagram Of Hypernatremia](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Joseph_Noto/publication/329833408/figure/tbl1/AS:709769652355072@1546233680771/Differential-diagnosis-of-hypernatremia.png)