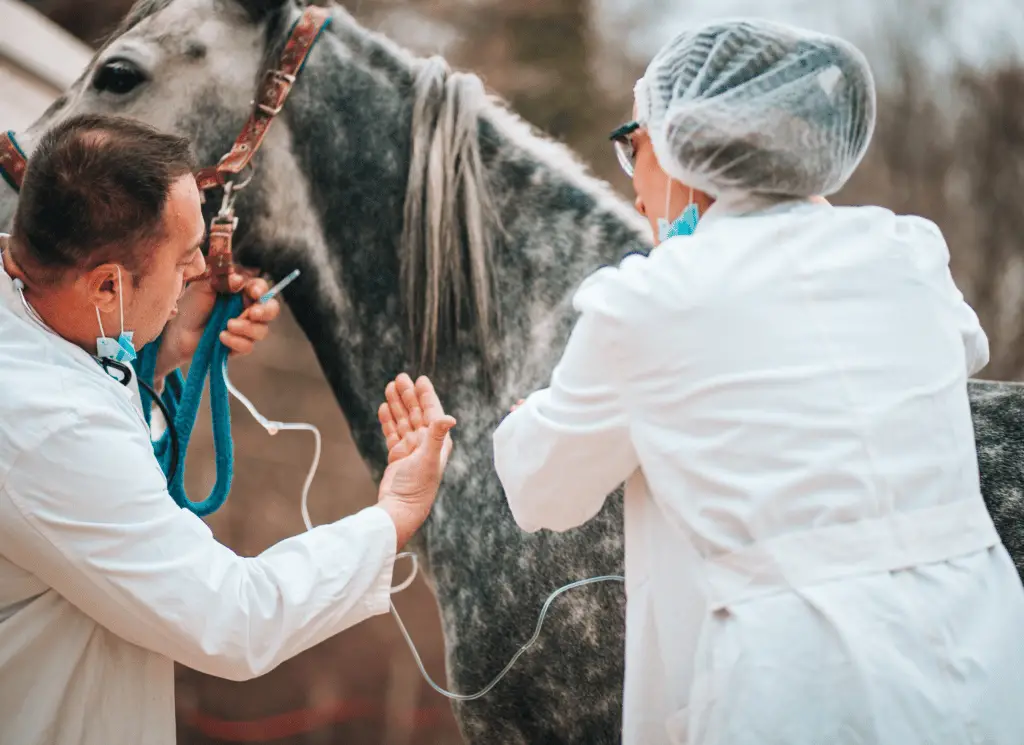
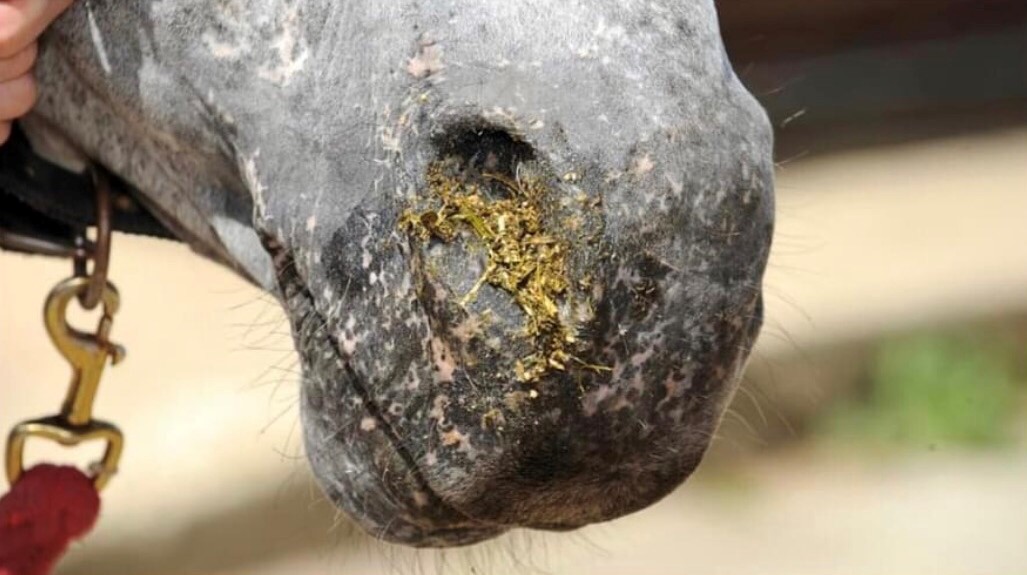
How To Prevent Choke In Horses - Feeding horses off the ground to keep the head and neck in a more natural feeding position is the first step in avoiding choke. Some chokes resolve without treatment, but in many cases a veterinarian must administer sedatives or muscle relaxants to loosen. Certain management strategies and nutritional interventions can reduce the risk. Oesophageal obstruction, commonly referred to as 'choke', is an emergency condition in horses caused by the acute obstruction of the.
Some chokes resolve without treatment, but in many cases a veterinarian must administer sedatives or muscle relaxants to loosen. Oesophageal obstruction, commonly referred to as 'choke', is an emergency condition in horses caused by the acute obstruction of the. Feeding horses off the ground to keep the head and neck in a more natural feeding position is the first step in avoiding choke. Certain management strategies and nutritional interventions can reduce the risk.
Oesophageal obstruction, commonly referred to as 'choke', is an emergency condition in horses caused by the acute obstruction of the. Certain management strategies and nutritional interventions can reduce the risk. Feeding horses off the ground to keep the head and neck in a more natural feeding position is the first step in avoiding choke. Some chokes resolve without treatment, but in many cases a veterinarian must administer sedatives or muscle relaxants to loosen.
How to Prevent Choke
Oesophageal obstruction, commonly referred to as 'choke', is an emergency condition in horses caused by the acute obstruction of the. Some chokes resolve without treatment, but in many cases a veterinarian must administer sedatives or muscle relaxants to loosen. Feeding horses off the ground to keep the head and neck in a more natural feeding position is the first step.
When horses 'choke' Manitoba Cooperator
Oesophageal obstruction, commonly referred to as 'choke', is an emergency condition in horses caused by the acute obstruction of the. Feeding horses off the ground to keep the head and neck in a more natural feeding position is the first step in avoiding choke. Some chokes resolve without treatment, but in many cases a veterinarian must administer sedatives or muscle.
Choke in Horses Symptoms, Treatment, Prevention, & More Equestrian
Feeding horses off the ground to keep the head and neck in a more natural feeding position is the first step in avoiding choke. Certain management strategies and nutritional interventions can reduce the risk. Some chokes resolve without treatment, but in many cases a veterinarian must administer sedatives or muscle relaxants to loosen. Oesophageal obstruction, commonly referred to as 'choke',.
Choke In Horses Points To Consider Star Milling Co.
Some chokes resolve without treatment, but in many cases a veterinarian must administer sedatives or muscle relaxants to loosen. Oesophageal obstruction, commonly referred to as 'choke', is an emergency condition in horses caused by the acute obstruction of the. Certain management strategies and nutritional interventions can reduce the risk. Feeding horses off the ground to keep the head and neck.
choke Prana Horse
Feeding horses off the ground to keep the head and neck in a more natural feeding position is the first step in avoiding choke. Certain management strategies and nutritional interventions can reduce the risk. Oesophageal obstruction, commonly referred to as 'choke', is an emergency condition in horses caused by the acute obstruction of the. Some chokes resolve without treatment, but.
Avoiding Choke in Horses KPP
Some chokes resolve without treatment, but in many cases a veterinarian must administer sedatives or muscle relaxants to loosen. Certain management strategies and nutritional interventions can reduce the risk. Feeding horses off the ground to keep the head and neck in a more natural feeding position is the first step in avoiding choke. Oesophageal obstruction, commonly referred to as 'choke',.
Choke in Horses Symptoms, Treatment, Prevention, & More Equestrian
Oesophageal obstruction, commonly referred to as 'choke', is an emergency condition in horses caused by the acute obstruction of the. Certain management strategies and nutritional interventions can reduce the risk. Some chokes resolve without treatment, but in many cases a veterinarian must administer sedatives or muscle relaxants to loosen. Feeding horses off the ground to keep the head and neck.
Choke in Horses Symptoms, Treatment, Prevention, & More Equestrian
Some chokes resolve without treatment, but in many cases a veterinarian must administer sedatives or muscle relaxants to loosen. Certain management strategies and nutritional interventions can reduce the risk. Feeding horses off the ground to keep the head and neck in a more natural feeding position is the first step in avoiding choke. Oesophageal obstruction, commonly referred to as 'choke',.
Understanding Choke In Horses
Some chokes resolve without treatment, but in many cases a veterinarian must administer sedatives or muscle relaxants to loosen. Feeding horses off the ground to keep the head and neck in a more natural feeding position is the first step in avoiding choke. Oesophageal obstruction, commonly referred to as 'choke', is an emergency condition in horses caused by the acute.
Choke in Horses Symptoms, Treatment, Prevention, & More Equestrian
Oesophageal obstruction, commonly referred to as 'choke', is an emergency condition in horses caused by the acute obstruction of the. Feeding horses off the ground to keep the head and neck in a more natural feeding position is the first step in avoiding choke. Certain management strategies and nutritional interventions can reduce the risk. Some chokes resolve without treatment, but.
Oesophageal Obstruction, Commonly Referred To As 'Choke', Is An Emergency Condition In Horses Caused By The Acute Obstruction Of The.
Feeding horses off the ground to keep the head and neck in a more natural feeding position is the first step in avoiding choke. Some chokes resolve without treatment, but in many cases a veterinarian must administer sedatives or muscle relaxants to loosen. Certain management strategies and nutritional interventions can reduce the risk.