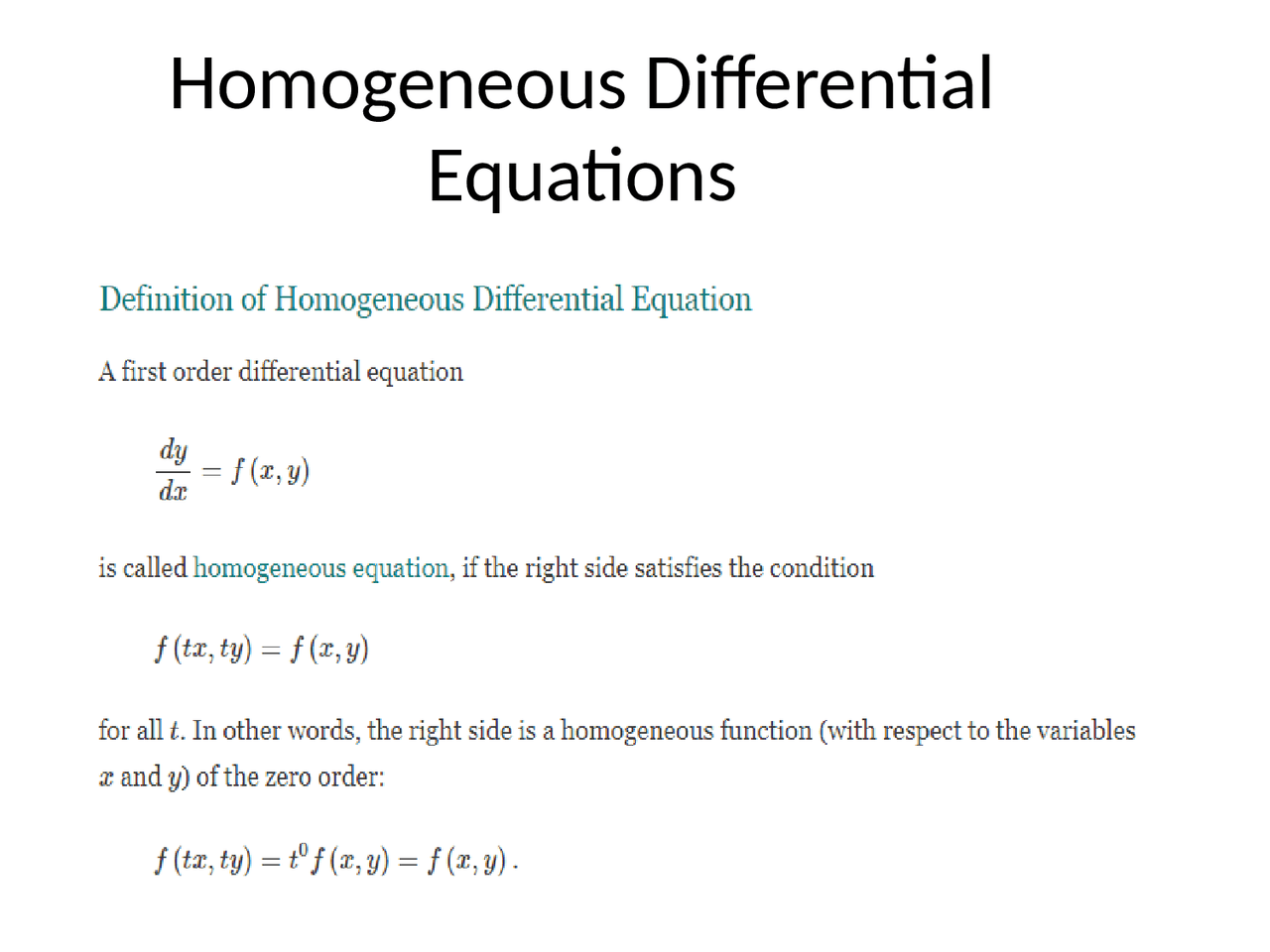
Homogeneous Vs Inhomogeneous Differential Equation - The simplest way to test whether an equation (here the equation for the boundary conditions) is homogeneous is to substitute the. (1) and (2) are of the form $$ \mathcal{d} u = 0 $$ where $\mathcal d$ is a differential operator. Where f i(x) f i (x) and g(x) g (x) are functions of x, x, the differential equation is said to be homogeneous if g(x)= 0 g. If all the terms of the equation contain the unknown function or its derivative then the equation is homogeneous;. Thus, these differential equations are. Homogeneity of a linear de.
Where f i(x) f i (x) and g(x) g (x) are functions of x, x, the differential equation is said to be homogeneous if g(x)= 0 g. The simplest way to test whether an equation (here the equation for the boundary conditions) is homogeneous is to substitute the. Homogeneity of a linear de. Thus, these differential equations are. (1) and (2) are of the form $$ \mathcal{d} u = 0 $$ where $\mathcal d$ is a differential operator. If all the terms of the equation contain the unknown function or its derivative then the equation is homogeneous;.
(1) and (2) are of the form $$ \mathcal{d} u = 0 $$ where $\mathcal d$ is a differential operator. Thus, these differential equations are. Where f i(x) f i (x) and g(x) g (x) are functions of x, x, the differential equation is said to be homogeneous if g(x)= 0 g. Homogeneity of a linear de. If all the terms of the equation contain the unknown function or its derivative then the equation is homogeneous;. The simplest way to test whether an equation (here the equation for the boundary conditions) is homogeneous is to substitute the.
Ex 9.5, 17 Which is a homogeneous differential equation
Thus, these differential equations are. If all the terms of the equation contain the unknown function or its derivative then the equation is homogeneous;. The simplest way to test whether an equation (here the equation for the boundary conditions) is homogeneous is to substitute the. Homogeneity of a linear de. Where f i(x) f i (x) and g(x) g (x).
Homogeneous Differential Equation Know types, Steps to solve
If all the terms of the equation contain the unknown function or its derivative then the equation is homogeneous;. Thus, these differential equations are. Where f i(x) f i (x) and g(x) g (x) are functions of x, x, the differential equation is said to be homogeneous if g(x)= 0 g. The simplest way to test whether an equation (here.
SOLVED Question 1 Consider the inhomogeneous differential equation 5
(1) and (2) are of the form $$ \mathcal{d} u = 0 $$ where $\mathcal d$ is a differential operator. If all the terms of the equation contain the unknown function or its derivative then the equation is homogeneous;. Homogeneity of a linear de. Thus, these differential equations are. Where f i(x) f i (x) and g(x) g (x) are.
SOLUTION Chapter 4 homogeneous differential equation Studypool
Where f i(x) f i (x) and g(x) g (x) are functions of x, x, the differential equation is said to be homogeneous if g(x)= 0 g. The simplest way to test whether an equation (here the equation for the boundary conditions) is homogeneous is to substitute the. Thus, these differential equations are. If all the terms of the equation.
02 Tugas Kelompok Homogeneous Vs Inhomogeneous PDF
The simplest way to test whether an equation (here the equation for the boundary conditions) is homogeneous is to substitute the. (1) and (2) are of the form $$ \mathcal{d} u = 0 $$ where $\mathcal d$ is a differential operator. Homogeneity of a linear de. Where f i(x) f i (x) and g(x) g (x) are functions of x,.
Solved 4. (5 pts) Classify these equations as being
Where f i(x) f i (x) and g(x) g (x) are functions of x, x, the differential equation is said to be homogeneous if g(x)= 0 g. (1) and (2) are of the form $$ \mathcal{d} u = 0 $$ where $\mathcal d$ is a differential operator. Homogeneity of a linear de. The simplest way to test whether an equation.
Homogeneous Differential Equations Docsity
Homogeneity of a linear de. The simplest way to test whether an equation (here the equation for the boundary conditions) is homogeneous is to substitute the. Thus, these differential equations are. (1) and (2) are of the form $$ \mathcal{d} u = 0 $$ where $\mathcal d$ is a differential operator. Where f i(x) f i (x) and g(x) g.
Must Do Problems Of Homogeneous Differential Equation Livedu
If all the terms of the equation contain the unknown function or its derivative then the equation is homogeneous;. Homogeneity of a linear de. Where f i(x) f i (x) and g(x) g (x) are functions of x, x, the differential equation is said to be homogeneous if g(x)= 0 g. (1) and (2) are of the form $$ \mathcal{d}.
Solved Consider the homogeneous differential equation Show
Homogeneity of a linear de. (1) and (2) are of the form $$ \mathcal{d} u = 0 $$ where $\mathcal d$ is a differential operator. Thus, these differential equations are. If all the terms of the equation contain the unknown function or its derivative then the equation is homogeneous;. Where f i(x) f i (x) and g(x) g (x) are.
Inhomogeneous Linear Differential Equations KZHU.ai 🚀
The simplest way to test whether an equation (here the equation for the boundary conditions) is homogeneous is to substitute the. Where f i(x) f i (x) and g(x) g (x) are functions of x, x, the differential equation is said to be homogeneous if g(x)= 0 g. If all the terms of the equation contain the unknown function or.
The Simplest Way To Test Whether An Equation (Here The Equation For The Boundary Conditions) Is Homogeneous Is To Substitute The.
If all the terms of the equation contain the unknown function or its derivative then the equation is homogeneous;. (1) and (2) are of the form $$ \mathcal{d} u = 0 $$ where $\mathcal d$ is a differential operator. Where f i(x) f i (x) and g(x) g (x) are functions of x, x, the differential equation is said to be homogeneous if g(x)= 0 g. Homogeneity of a linear de.