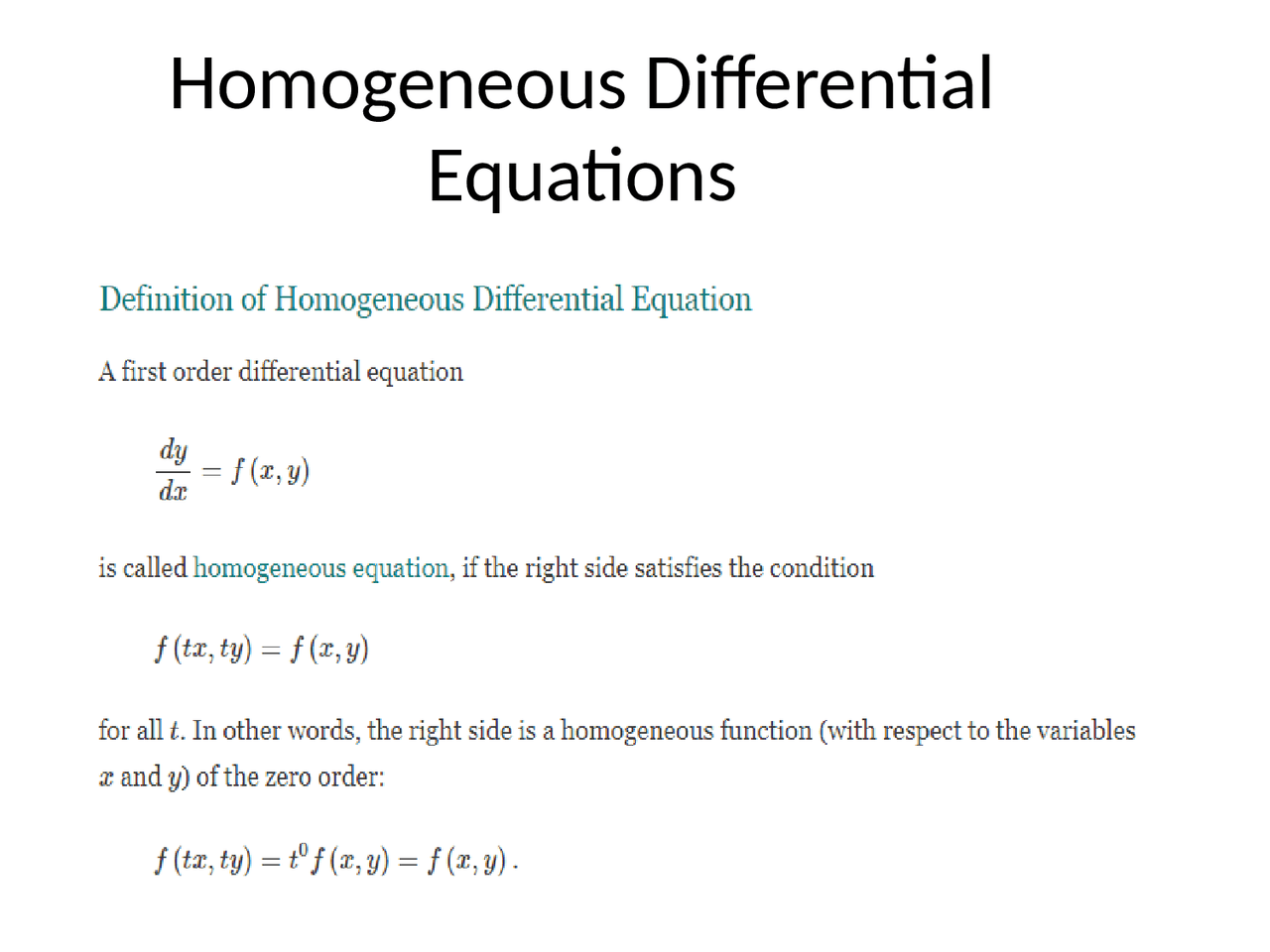
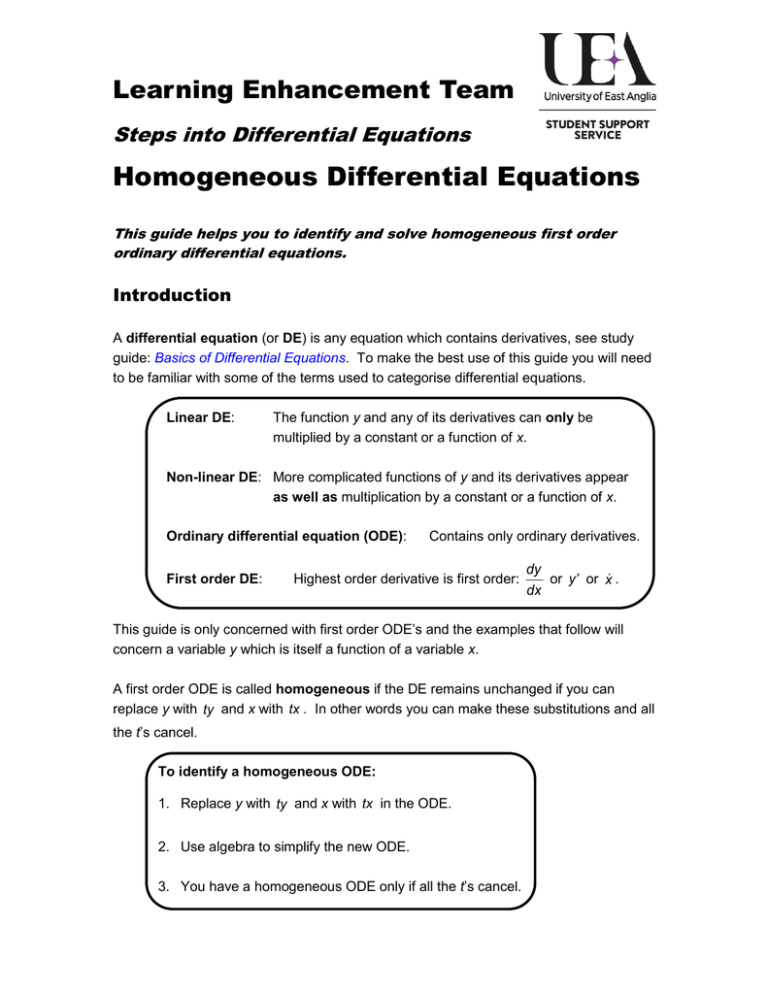
Homogeneous Equations Differential Equations - In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by making the substitution $v(x)=\dfrac{y}{x}$, where $v=v(x)$ is a. What is a homogeneous differential equation? Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the function f(x, y) is a homogeneous function of. An example will show how it is all done:
What is a homogeneous differential equation? A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by making the substitution $v(x)=\dfrac{y}{x}$, where $v=v(x)$ is a. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. An example will show how it is all done: Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the function f(x, y) is a homogeneous function of.
In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the function f(x, y) is a homogeneous function of. A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by making the substitution $v(x)=\dfrac{y}{x}$, where $v=v(x)$ is a. What is a homogeneous differential equation? Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. An example will show how it is all done:
Non homogeneous Linear differential equations HandwrittenNotes.in
In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the function f(x, y) is a homogeneous function of. An example will show how it is all done: Using y = vx and dy dx =.
[Solved] solve using homogenous equations (differential equations) show
A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by making the substitution $v(x)=\dfrac{y}{x}$, where $v=v(x)$ is a. Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential.
Homogeneous Differential Equations Docsity
What is a homogeneous differential equation? Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. An example will show how it is all done: Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the function f(x, y) is a homogeneous function of. A.
[Solved] solve using homogenous equations (differential equations) show
Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. An example will show how it is all done: Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the function f(x, y) is a homogeneous function of. In this section we will extend the.
Particular Solution of NonHomogeneous Differential Equations Mr
Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the function f(x, y) is a homogeneous function of. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. What is a homogeneous differential equation? An example will show how it is all done: A homogeneous.
[Solved] Determine whether the given differential equations are
In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by making the substitution $v(x)=\dfrac{y}{x}$, where $v=v(x)$ is a. What is a homogeneous differential equation? Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation..
Homogeneous differential equations
A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by making the substitution $v(x)=\dfrac{y}{x}$, where $v=v(x)$ is a. What is a homogeneous differential equation? In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. An example will show how it is all done: Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form.
Homogeneous Differential Equations
In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the function f(x, y) is a homogeneous function of. Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the.
2nd Order Homogeneous Equations
What is a homogeneous differential equation? In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the function f(x, y) is a homogeneous function of. A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by making the.
Homogeneous Differential Equations
Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the function f(x, y) is a homogeneous function of. What is a homogeneous differential equation? A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by making.
A Homogeneous Differential Equation Can Often Be Solved By Making The Substitution $V(X)=\Dfrac{Y}{X}$, Where $V=V(X)$ Is A.
In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. An example will show how it is all done: Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the function f(x, y) is a homogeneous function of. What is a homogeneous differential equation?