Find A Particular Solution To The Nonhomogeneous Differential Equation - In this section we will discuss the basics of solving nonhomogeneous differential equations. In this section we introduce the method of variation of parameters to find particular solutions to nonhomogeneous. Y p(x)y' q(x)y 0 2. The two most common methods when finding the particular. It works by dividing the forcing function into simpler components, finding a particular solution for each component, and then adding those. We define the complimentary and. How to find the particular solution of a non homogeneous differential equation. B)find the most general solution to the associated homogeneous differential equation. Determine the general solution y h c 1 y(x) c 2 y(x) to a homogeneous second order differential equation: Use c1 and c2 in your answer to denote arbitrary constants.
In this section we will discuss the basics of solving nonhomogeneous differential equations. We define the complimentary and. In this section we introduce the method of variation of parameters to find particular solutions to nonhomogeneous. Use c1 and c2 in your answer to denote arbitrary constants. In this section we introduce the method of undetermined coefficients to find particular solutions to nonhomogeneous. The two most common methods when finding the particular. B)find the most general solution to the associated homogeneous differential equation. How to find the particular solution of a non homogeneous differential equation. Determine the general solution y h c 1 y(x) c 2 y(x) to a homogeneous second order differential equation: It works by dividing the forcing function into simpler components, finding a particular solution for each component, and then adding those.
Y p(x)y' q(x)y 0 2. Use c1 and c2 in your answer to denote arbitrary constants. It works by dividing the forcing function into simpler components, finding a particular solution for each component, and then adding those. The two most common methods when finding the particular. B)find the most general solution to the associated homogeneous differential equation. We define the complimentary and. In this section we will discuss the basics of solving nonhomogeneous differential equations. In this section we introduce the method of variation of parameters to find particular solutions to nonhomogeneous. In this section we introduce the method of undetermined coefficients to find particular solutions to nonhomogeneous. How to find the particular solution of a non homogeneous differential equation.
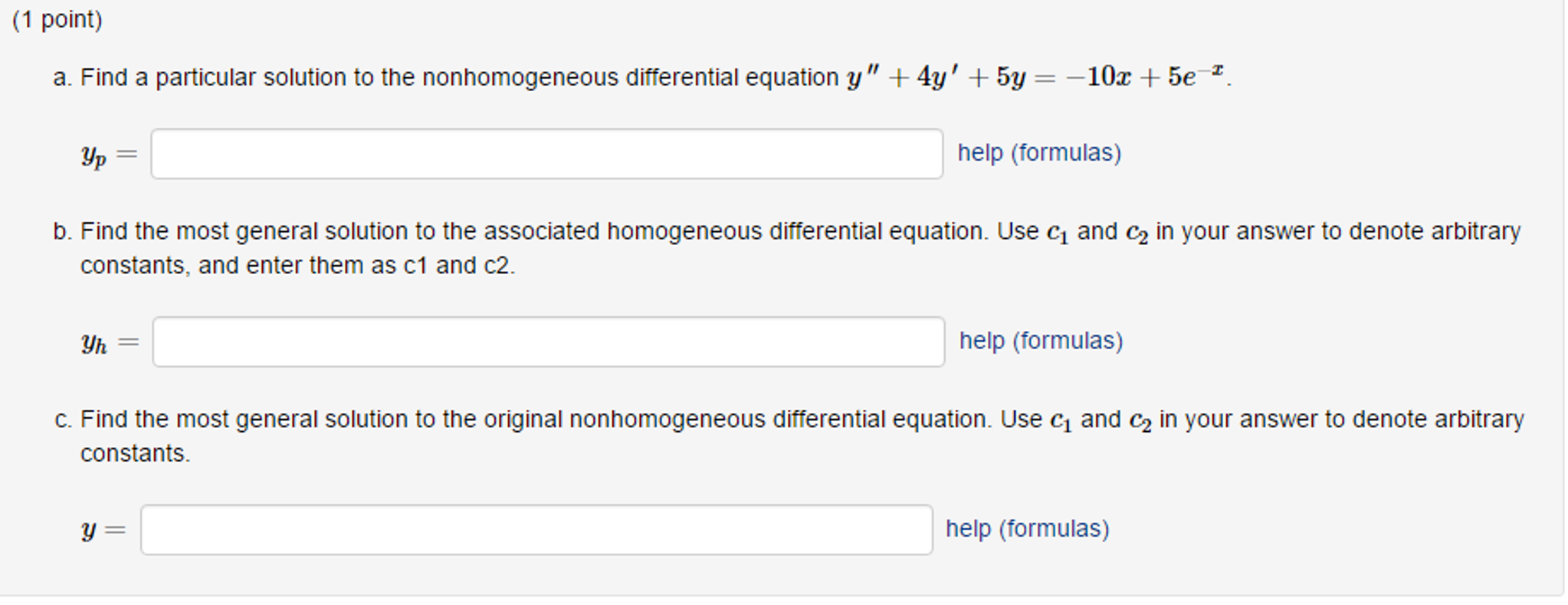
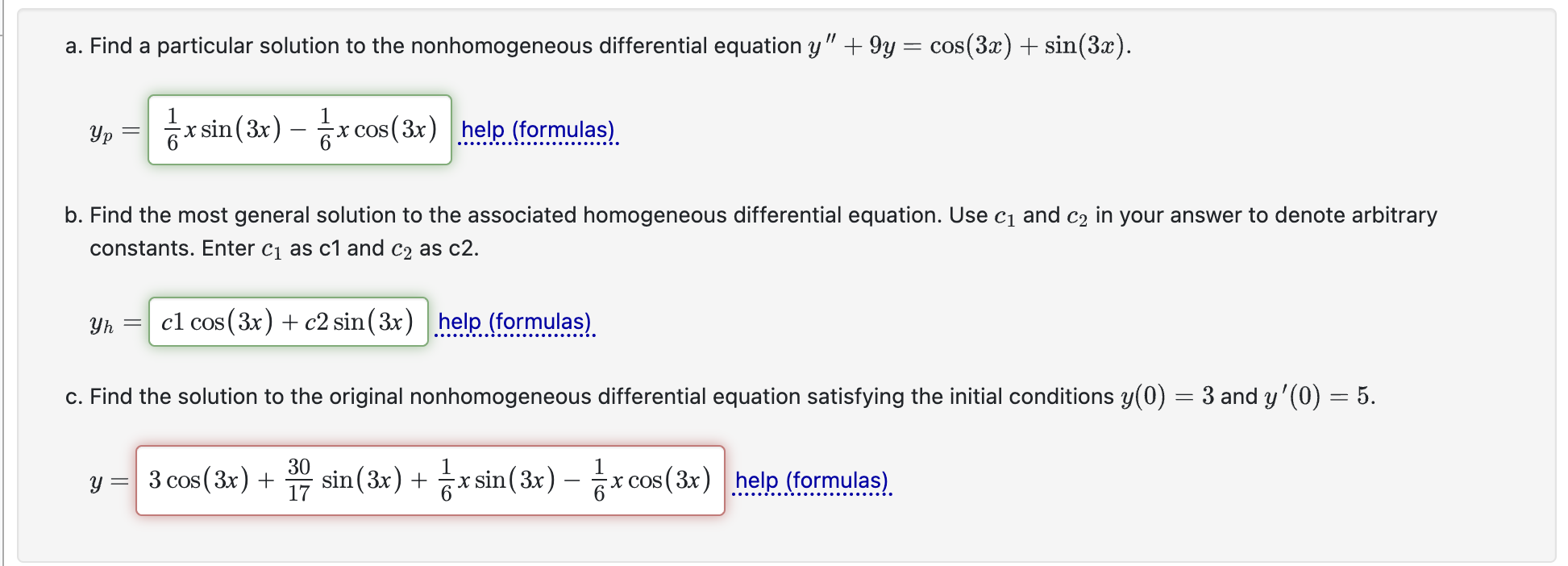
a. Find a particular solution to the nonhomogeneous
We define the complimentary and. B)find the most general solution to the associated homogeneous differential equation. Determine the general solution y h c 1 y(x) c 2 y(x) to a homogeneous second order differential equation: How to find the particular solution of a non homogeneous differential equation. Use c1 and c2 in your answer to denote arbitrary constants.
Solved a. Find a particular solution to the nonhomogeneous
In this section we will discuss the basics of solving nonhomogeneous differential equations. Determine the general solution y h c 1 y(x) c 2 y(x) to a homogeneous second order differential equation: The two most common methods when finding the particular. We define the complimentary and. In this section we introduce the method of undetermined coefficients to find particular solutions.
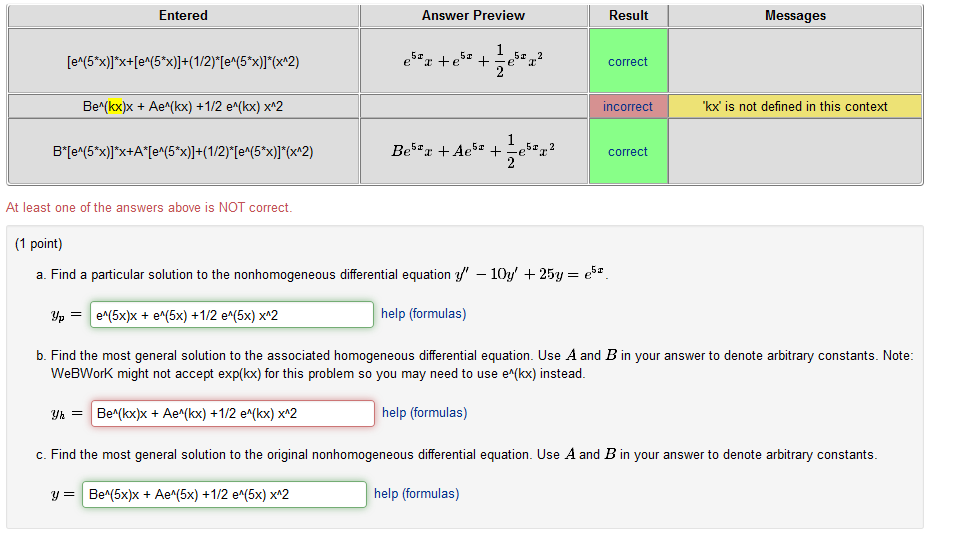
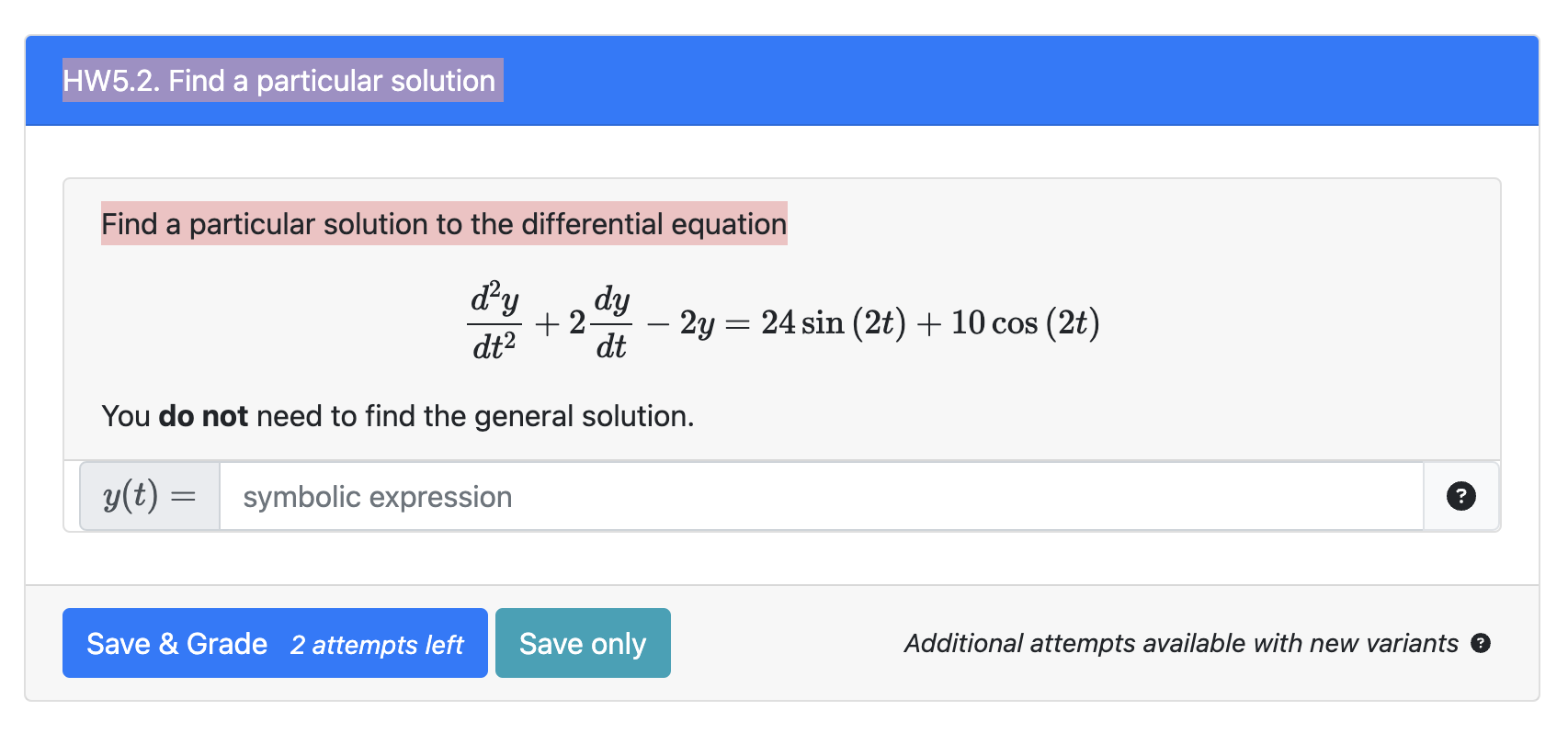
Solved Find a particular solution to the differential
Y p(x)y' q(x)y 0 2. In this section we introduce the method of variation of parameters to find particular solutions to nonhomogeneous. How to find the particular solution of a non homogeneous differential equation. The two most common methods when finding the particular. It works by dividing the forcing function into simpler components, finding a particular solution for each component,.
Solved Find a particular solution to the nonhomogeneous
We define the complimentary and. The two most common methods when finding the particular. It works by dividing the forcing function into simpler components, finding a particular solution for each component, and then adding those. Use c1 and c2 in your answer to denote arbitrary constants. Y p(x)y' q(x)y 0 2.
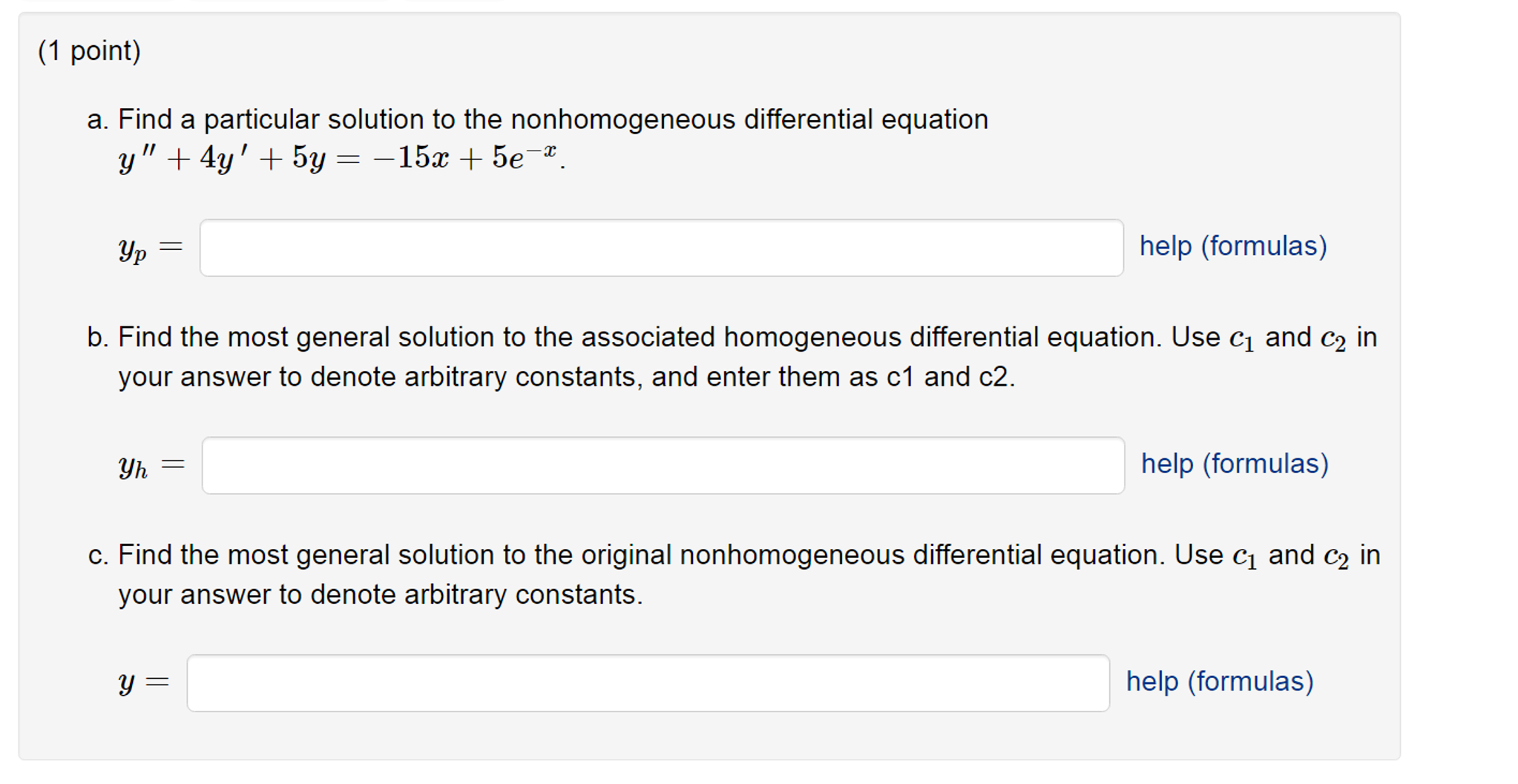
Solved Find the particular solution of the nonhomogeneous differential
We define the complimentary and. Determine the general solution y h c 1 y(x) c 2 y(x) to a homogeneous second order differential equation: In this section we introduce the method of undetermined coefficients to find particular solutions to nonhomogeneous. Use c1 and c2 in your answer to denote arbitrary constants. How to find the particular solution of a non.
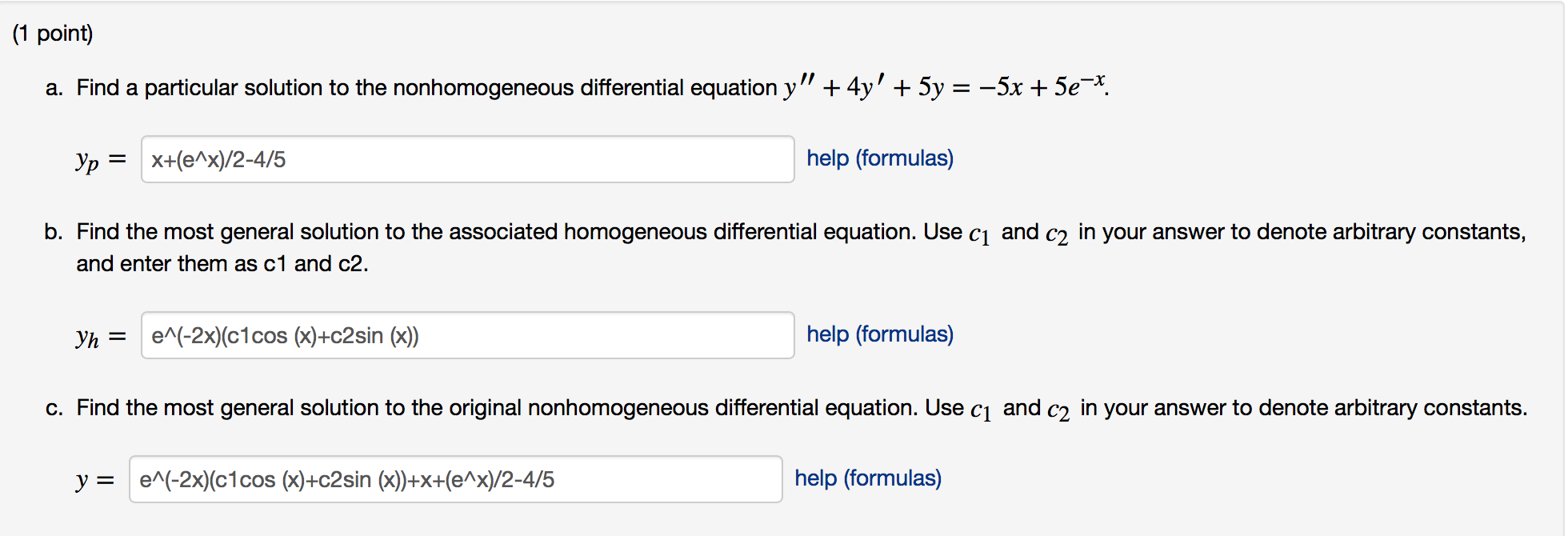
[Solved] a. Find a particular solution to the nonhomogene
We define the complimentary and. In this section we introduce the method of variation of parameters to find particular solutions to nonhomogeneous. B)find the most general solution to the associated homogeneous differential equation. In this section we will discuss the basics of solving nonhomogeneous differential equations. It works by dividing the forcing function into simpler components, finding a particular solution.
Solved Find a particular solution to the nonhomogeneous
Determine the general solution y h c 1 y(x) c 2 y(x) to a homogeneous second order differential equation: In this section we introduce the method of variation of parameters to find particular solutions to nonhomogeneous. B)find the most general solution to the associated homogeneous differential equation. We define the complimentary and. It works by dividing the forcing function into.
Solved Find a particular solution to the nonhomogeneous
B)find the most general solution to the associated homogeneous differential equation. It works by dividing the forcing function into simpler components, finding a particular solution for each component, and then adding those. Y p(x)y' q(x)y 0 2. We define the complimentary and. How to find the particular solution of a non homogeneous differential equation.
Solved a. Find a particular solution to the nonhomogeneous
How to find the particular solution of a non homogeneous differential equation. We define the complimentary and. In this section we introduce the method of undetermined coefficients to find particular solutions to nonhomogeneous. Determine the general solution y h c 1 y(x) c 2 y(x) to a homogeneous second order differential equation: The two most common methods when finding the.
Solved Find a particular solution to the nonhomogeneous
We define the complimentary and. Y p(x)y' q(x)y 0 2. How to find the particular solution of a non homogeneous differential equation. In this section we introduce the method of variation of parameters to find particular solutions to nonhomogeneous. It works by dividing the forcing function into simpler components, finding a particular solution for each component, and then adding those.
Use C1 And C2 In Your Answer To Denote Arbitrary Constants.
In this section we will discuss the basics of solving nonhomogeneous differential equations. We define the complimentary and. In this section we introduce the method of undetermined coefficients to find particular solutions to nonhomogeneous. Determine the general solution y h c 1 y(x) c 2 y(x) to a homogeneous second order differential equation:
In This Section We Introduce The Method Of Variation Of Parameters To Find Particular Solutions To Nonhomogeneous.
It works by dividing the forcing function into simpler components, finding a particular solution for each component, and then adding those. The two most common methods when finding the particular. B)find the most general solution to the associated homogeneous differential equation. How to find the particular solution of a non homogeneous differential equation.
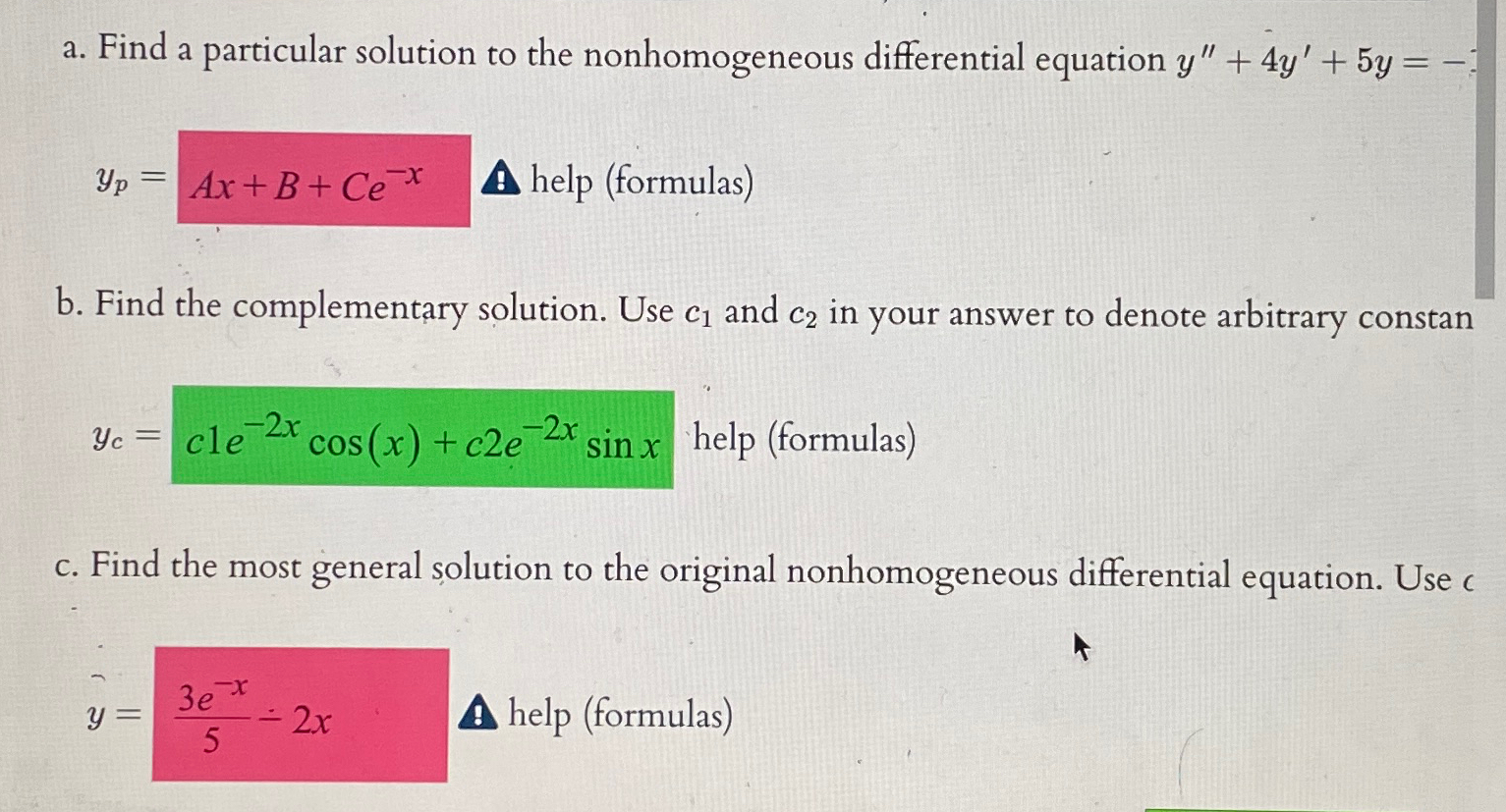
![[Solved] a. Find a particular solution to the nonhomogene](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/d9e/d9ebc5d5-b71a-4b4d-b4bb-2ba9ae9e8af9/phpEEbOI7)