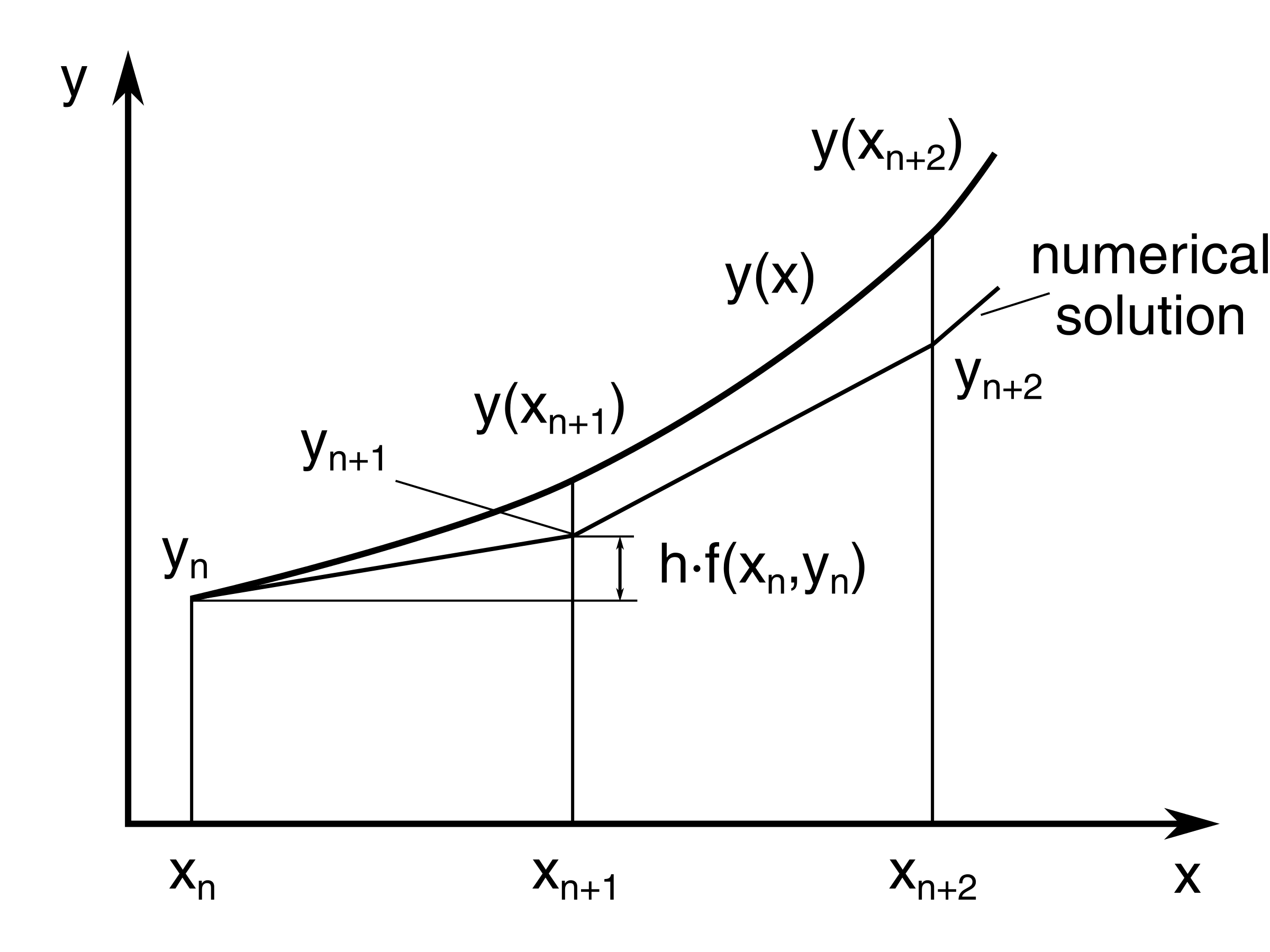
Euler Equation Differential Equation - In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. An euler equation is a second order differential equation of the form x2y′′ + αxy′ + βy = 0. To solve the differential equation we assume that a solution is of the form. Now we proceed in a similar way to how we tackled. Note that while this does not involve a. Recall that l is a linear function and if f is a solution to. Y = xr y = x r.
An euler equation is a second order differential equation of the form x2y′′ + αxy′ + βy = 0. In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. Now we proceed in a similar way to how we tackled. Note that while this does not involve a. Recall that l is a linear function and if f is a solution to. Y = xr y = x r. To solve the differential equation we assume that a solution is of the form.
Recall that l is a linear function and if f is a solution to. An euler equation is a second order differential equation of the form x2y′′ + αxy′ + βy = 0. In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. To solve the differential equation we assume that a solution is of the form. Now we proceed in a similar way to how we tackled. Note that while this does not involve a. Y = xr y = x r.
Euler's Method on differential equation Mathematics Stack Exchange
An euler equation is a second order differential equation of the form x2y′′ + αxy′ + βy = 0. Note that while this does not involve a. In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. Y = xr y = x r. Recall that l is a linear function and.
fluid dynamics Deriving an Euler Equation Physics Stack Exchange
Recall that l is a linear function and if f is a solution to. An euler equation is a second order differential equation of the form x2y′′ + αxy′ + βy = 0. To solve the differential equation we assume that a solution is of the form. Now we proceed in a similar way to how we tackled. Note that.
Solved 8. Solve the CauchyEuler differential equations 9.
To solve the differential equation we assume that a solution is of the form. Now we proceed in a similar way to how we tackled. Note that while this does not involve a. Y = xr y = x r. Recall that l is a linear function and if f is a solution to.
[Solved] Differential EquationsUse the substitutionx = etto
In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. To solve the differential equation we assume that a solution is of the form. Y = xr y = x r. Note that while this does not involve a. An euler equation is a second order differential equation of the form x2y′′.
Linear Differential Equation denis
Recall that l is a linear function and if f is a solution to. To solve the differential equation we assume that a solution is of the form. Now we proceed in a similar way to how we tackled. Y = xr y = x r. An euler equation is a second order differential equation of the form x2y′′ +.
[Solved] Transform the following Euler differential equation into a
Y = xr y = x r. Note that while this does not involve a. To solve the differential equation we assume that a solution is of the form. In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. Recall that l is a linear function and if f is a solution.
Solved 1. Given the EulerCauchy differential equation
Recall that l is a linear function and if f is a solution to. In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. Now we proceed in a similar way to how we tackled. Y = xr y = x r. Note that while this does not involve a.
Euler's Method Explained with Examples
In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. Recall that l is a linear function and if f is a solution to. An euler equation is a second order differential equation of the form x2y′′ + αxy′ + βy = 0. To solve the differential equation we assume that a.
SOLUTION Exercise 12 cauchy eulers differential equation Studypool
Now we proceed in a similar way to how we tackled. An euler equation is a second order differential equation of the form x2y′′ + αxy′ + βy = 0. Note that while this does not involve a. Y = xr y = x r. To solve the differential equation we assume that a solution is of the form.
[Solved] Transform the following Euler differential equation into a
In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. To solve the differential equation we assume that a solution is of the form. Now we proceed in a similar way to how we tackled. Note that while this does not involve a. Y = xr y = x r.
In This Section We Will Discuss How To Solve Euler’s Differential Equation, Ax^2Y'' + Bxy' +Cy = 0.
Y = xr y = x r. Now we proceed in a similar way to how we tackled. To solve the differential equation we assume that a solution is of the form. An euler equation is a second order differential equation of the form x2y′′ + αxy′ + βy = 0.
Note That While This Does Not Involve A.
Recall that l is a linear function and if f is a solution to.


![[Solved] Differential EquationsUse the substitutionx = etto](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/1ac/1acbfb5d-6d11-4c85-b497-04352a9fd5f2/phpWAtgmd)