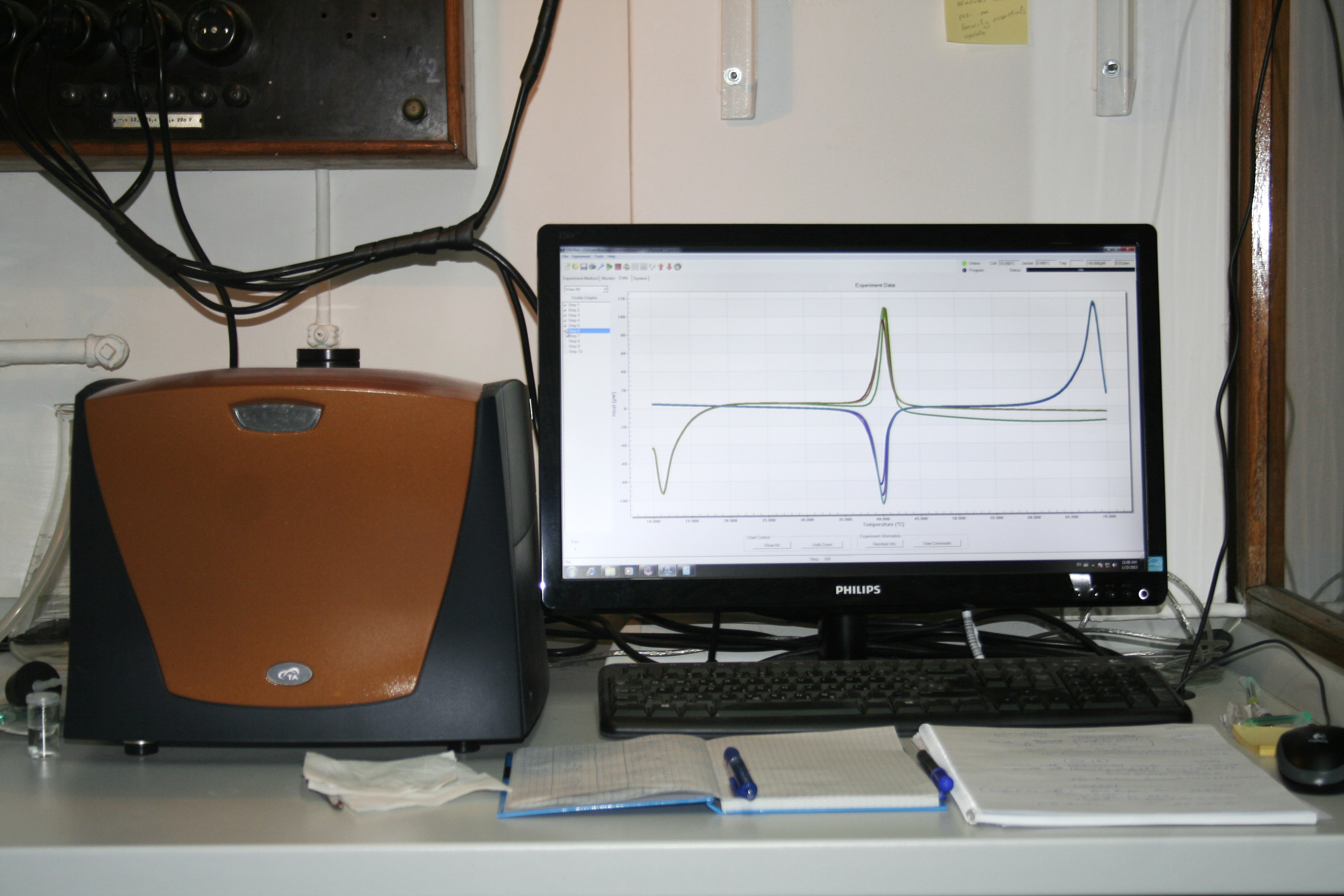
Dsc Differential Scanning Calorimeter - Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample.
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by.
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample. Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization.
Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC)
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by.
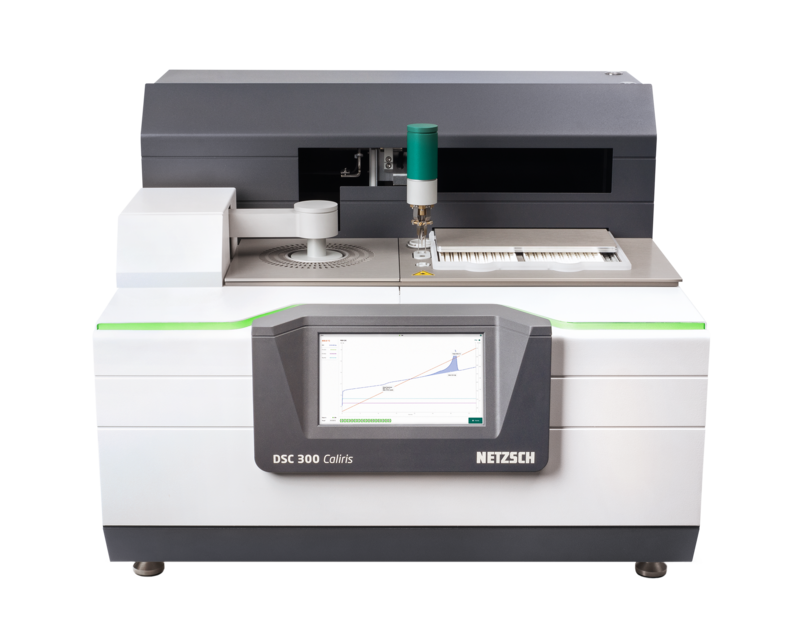
DSC600 Differential Scanning Calorimeter Manufacturers&Suppliers China
Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample.
Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC) Differential, 51 OFF
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by.
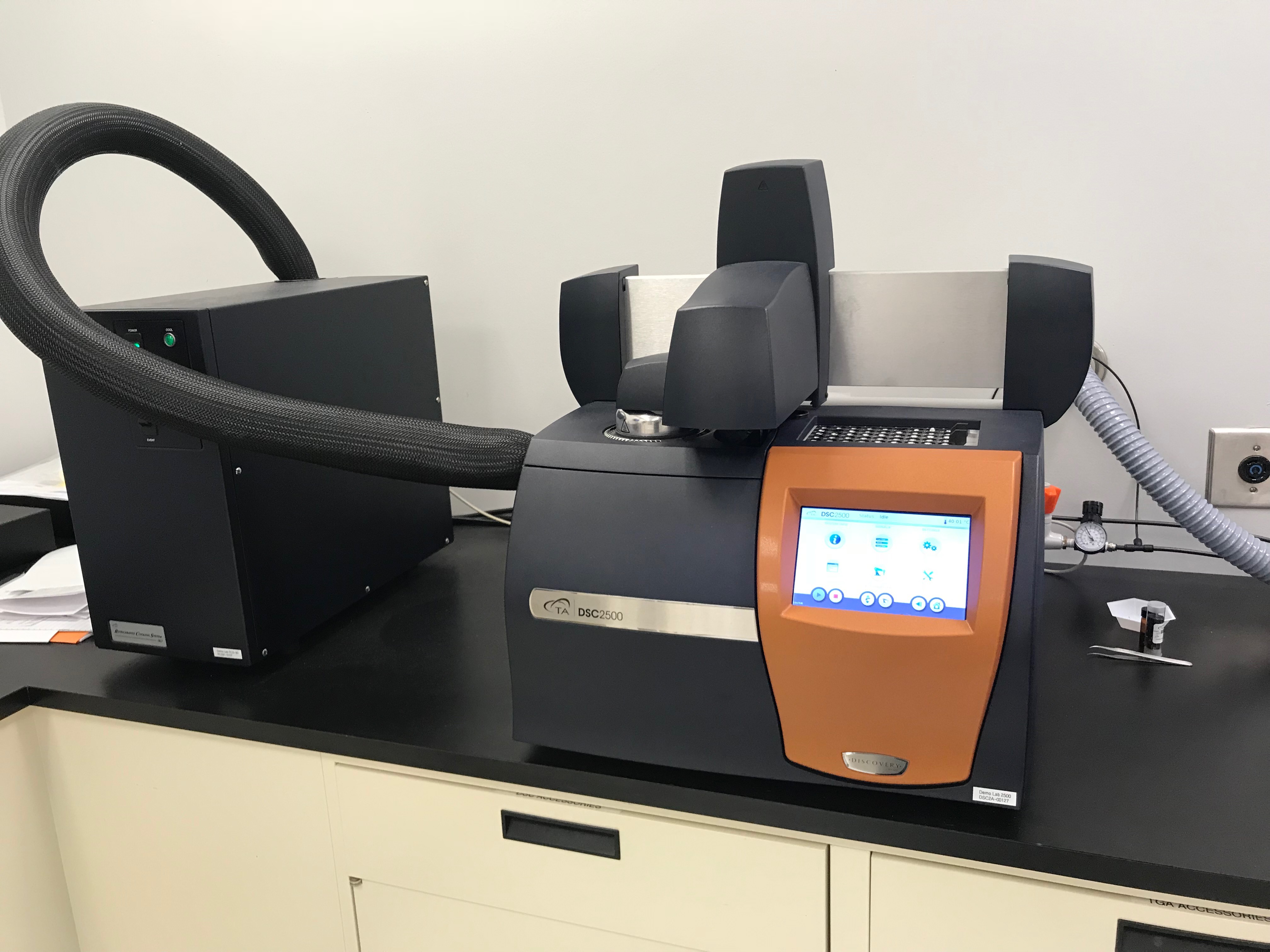
Differential Scanning Calorimeter DSC2500 (includes auto sampler and
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample. Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization.
Differential Scanning Calorimeter DSC 2500 (includes auto sampler, MDSC
Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization.
DSC 1 Differential Scanning Calorimeter CSI Malaysia
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by.
Differential Scanning Calorimeter DSC2500 (includes auto sampler, MDSC
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample. Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization.
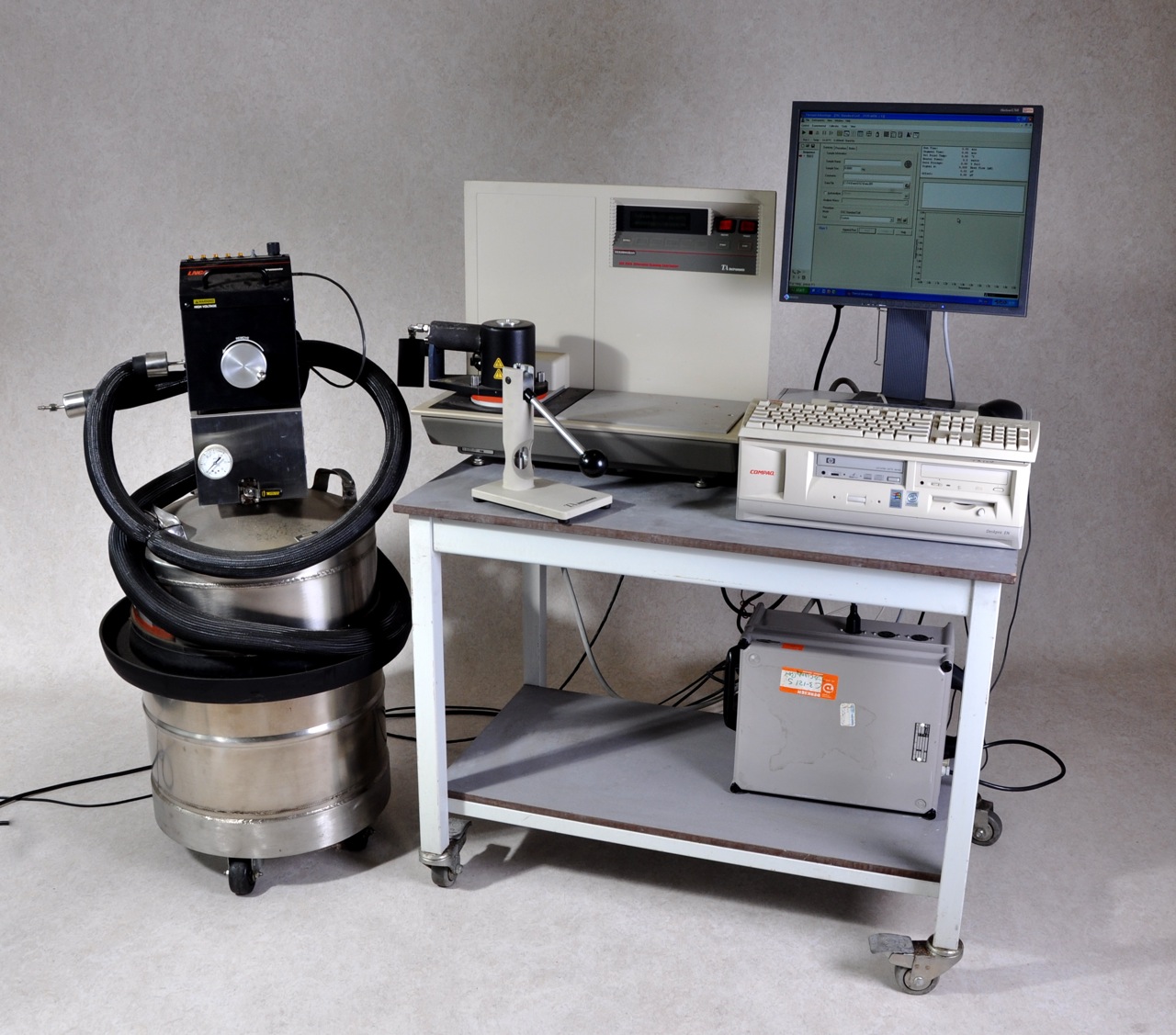
Differential Scanning Calorimeter DSC 2920 CE Gemini BV
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by.
Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC) / Differential Thermal Analyzer
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by.
Differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) InnoMol
Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry, Or Dsc, Is A Thermal Analysis Technique That Looks At How A Material’s Heat Capacity (Cp) Is Changed By.
Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample.