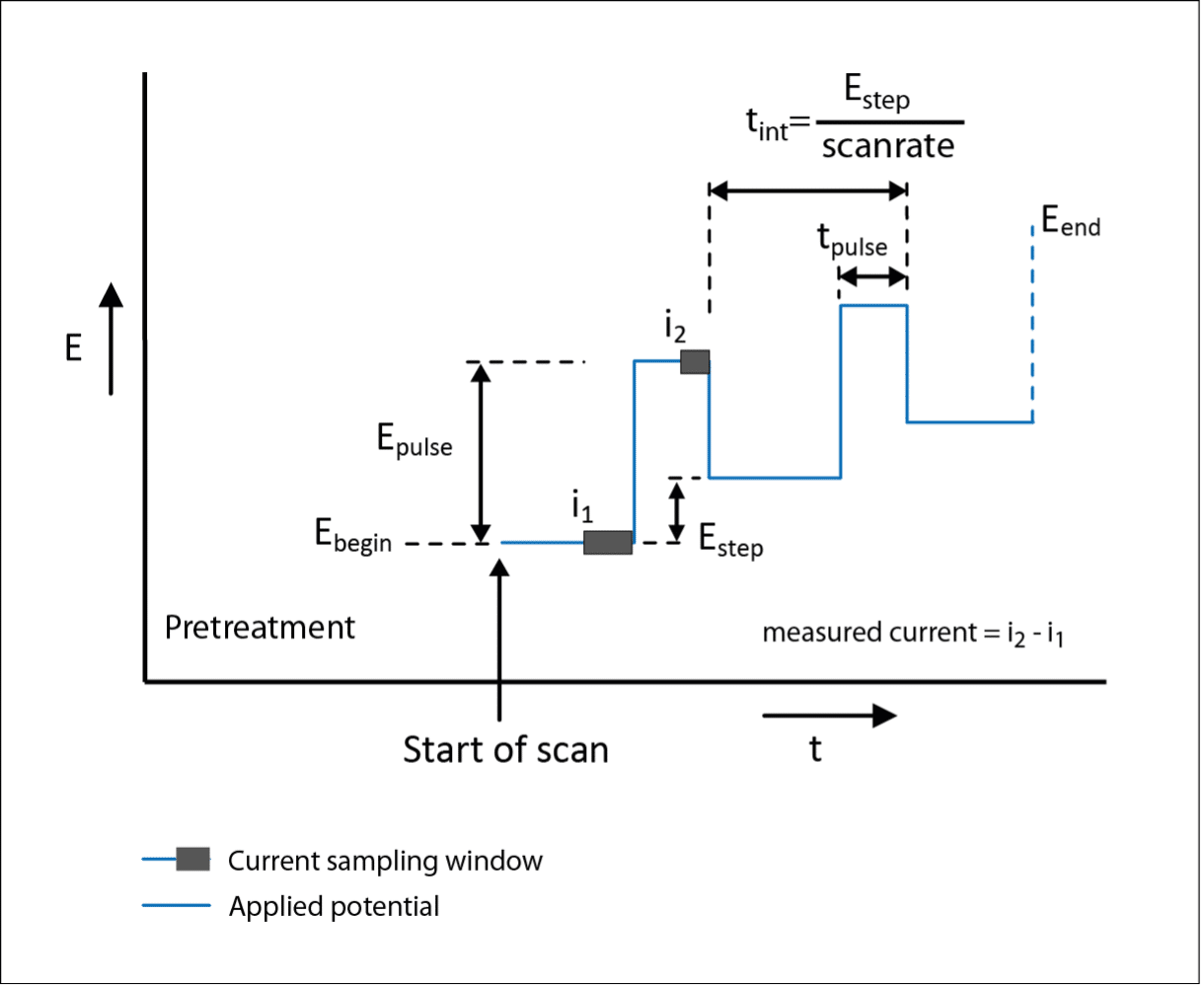
Dpv Differential Pulse Voltammetry - Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is an highly applicable technique for measuring trace amounts of organic and inorganic species. Among pulsed voltammetric techniques, differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is the most widely applied for electroanalytical. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is a technique that involves applying amplitude potential pulses on a linear ramp potential. Differential pulse is a voltammetric method used to perform quantitative electrochemical measurements.
Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is an highly applicable technique for measuring trace amounts of organic and inorganic species. Among pulsed voltammetric techniques, differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is the most widely applied for electroanalytical. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is a technique that involves applying amplitude potential pulses on a linear ramp potential. Differential pulse is a voltammetric method used to perform quantitative electrochemical measurements.
Differential pulse is a voltammetric method used to perform quantitative electrochemical measurements. Among pulsed voltammetric techniques, differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is the most widely applied for electroanalytical. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is a technique that involves applying amplitude potential pulses on a linear ramp potential. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is an highly applicable technique for measuring trace amounts of organic and inorganic species.
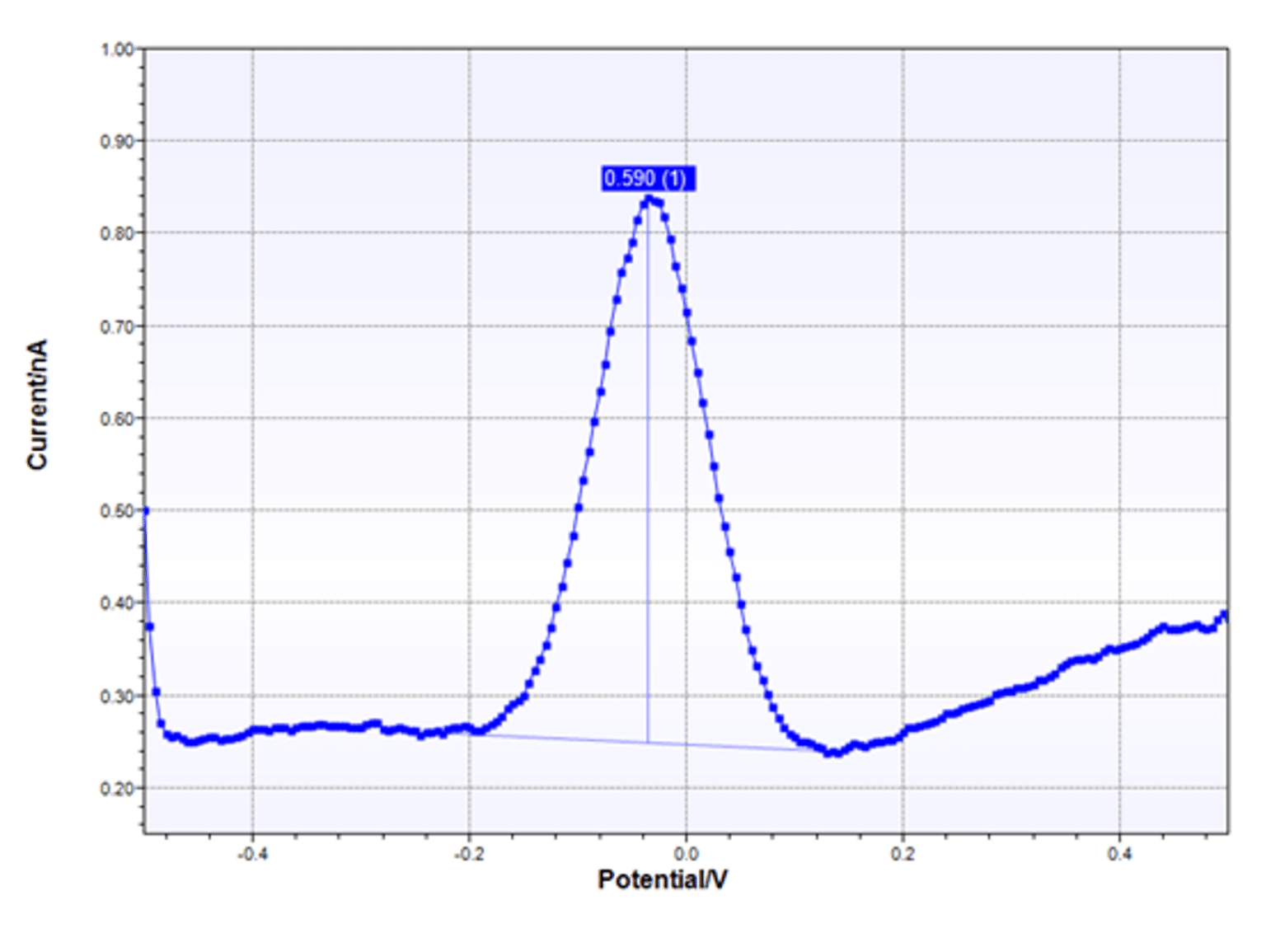
Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV) measurements of different
Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is a technique that involves applying amplitude potential pulses on a linear ramp potential. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is an highly applicable technique for measuring trace amounts of organic and inorganic species. Differential pulse is a voltammetric method used to perform quantitative electrochemical measurements. Among pulsed voltammetric techniques, differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is the most widely.
Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV) PalmSens
Differential pulse is a voltammetric method used to perform quantitative electrochemical measurements. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is a technique that involves applying amplitude potential pulses on a linear ramp potential. Among pulsed voltammetric techniques, differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is the most widely applied for electroanalytical. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is an highly applicable technique for measuring trace amounts of organic.
The differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) spectra of Fc‐PYS (2 × 10⁻⁴ M
Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is a technique that involves applying amplitude potential pulses on a linear ramp potential. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is an highly applicable technique for measuring trace amounts of organic and inorganic species. Among pulsed voltammetric techniques, differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is the most widely applied for electroanalytical. Differential pulse is a voltammetric method used to perform.
Experimental differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) at peaks (a) various
Differential pulse is a voltammetric method used to perform quantitative electrochemical measurements. Among pulsed voltammetric techniques, differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is the most widely applied for electroanalytical. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is an highly applicable technique for measuring trace amounts of organic and inorganic species. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is a technique that involves applying amplitude potential pulses on a.
Differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) curves recorded by the CP (a), Au
Among pulsed voltammetric techniques, differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is the most widely applied for electroanalytical. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is an highly applicable technique for measuring trace amounts of organic and inorganic species. Differential pulse is a voltammetric method used to perform quantitative electrochemical measurements. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is a technique that involves applying amplitude potential pulses on a.
Peaks on Differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) for hydrogen peroxide
Differential pulse is a voltammetric method used to perform quantitative electrochemical measurements. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is a technique that involves applying amplitude potential pulses on a linear ramp potential. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is an highly applicable technique for measuring trace amounts of organic and inorganic species. Among pulsed voltammetric techniques, differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is the most widely.
Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV) PalmSens
Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is a technique that involves applying amplitude potential pulses on a linear ramp potential. Among pulsed voltammetric techniques, differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is the most widely applied for electroanalytical. Differential pulse is a voltammetric method used to perform quantitative electrochemical measurements. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is an highly applicable technique for measuring trace amounts of organic.
Differential pulse voltammogram (DPV conditions pulse height (mV) 2.5
Among pulsed voltammetric techniques, differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is the most widely applied for electroanalytical. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is a technique that involves applying amplitude potential pulses on a linear ramp potential. Differential pulse is a voltammetric method used to perform quantitative electrochemical measurements. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is an highly applicable technique for measuring trace amounts of organic.
Differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) curves of glassy carbon electrode
Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is a technique that involves applying amplitude potential pulses on a linear ramp potential. Differential pulse is a voltammetric method used to perform quantitative electrochemical measurements. Among pulsed voltammetric techniques, differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is the most widely applied for electroanalytical. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is an highly applicable technique for measuring trace amounts of organic.
The differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) (a) and cyclic voltammetry
Differential pulse is a voltammetric method used to perform quantitative electrochemical measurements. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is an highly applicable technique for measuring trace amounts of organic and inorganic species. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is a technique that involves applying amplitude potential pulses on a linear ramp potential. Among pulsed voltammetric techniques, differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is the most widely.
Differential Pulse Is A Voltammetric Method Used To Perform Quantitative Electrochemical Measurements.
Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is an highly applicable technique for measuring trace amounts of organic and inorganic species. Differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is a technique that involves applying amplitude potential pulses on a linear ramp potential. Among pulsed voltammetric techniques, differential pulse voltammetry (dpv) is the most widely applied for electroanalytical.