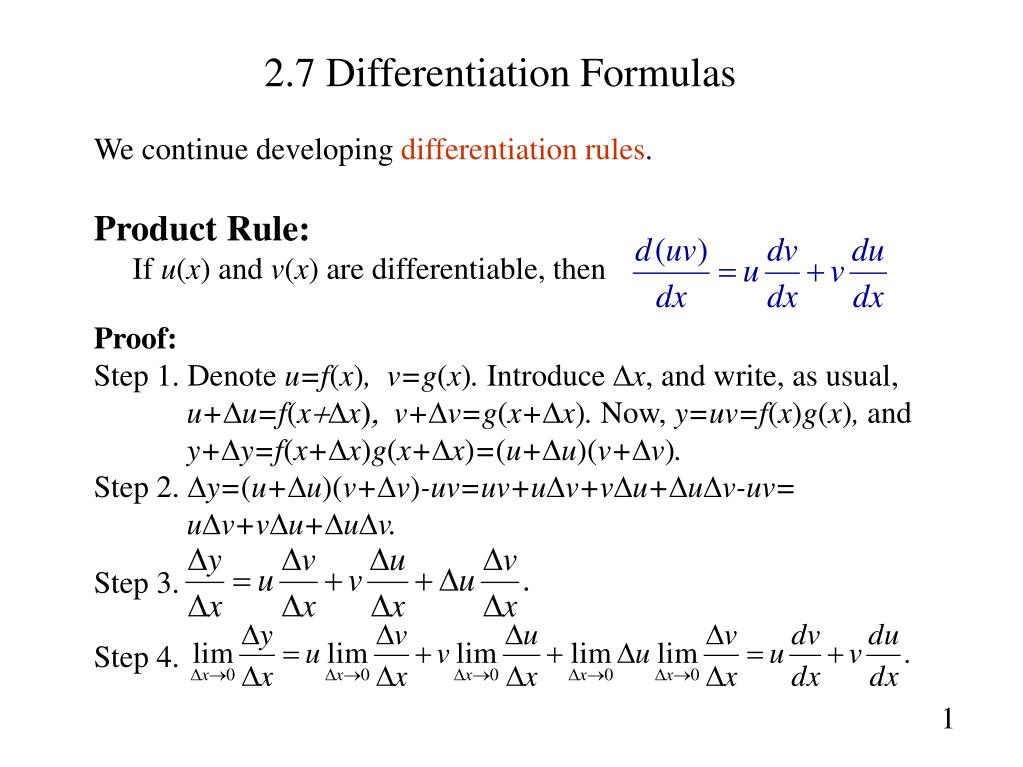
Differentiation Uv Rule - Learn how to differentiate a function that is the product of two or more functions using the product rule. The product and quotient rules are covered in this section. X and v = cos 3x. Leibnitz's theorem, also known as the leibniz rule for differentiation under the integral sign, is a powerful tool in calculus that. Find the formula, proof and examples for. Uv differentiation formula (also known as the product rule) is a fundamental concept in calculus used to differentiate the. This is another very useful formula: Notice that we can write this as y = uv where u = 2. D (uv) = vdu + udv dx dx dx.
This is another very useful formula: Uv differentiation formula (also known as the product rule) is a fundamental concept in calculus used to differentiate the. Learn how to differentiate a function that is the product of two or more functions using the product rule. X and v = cos 3x. The product and quotient rules are covered in this section. Find the formula, proof and examples for. D (uv) = vdu + udv dx dx dx. Leibnitz's theorem, also known as the leibniz rule for differentiation under the integral sign, is a powerful tool in calculus that. Notice that we can write this as y = uv where u = 2.
This is another very useful formula: Leibnitz's theorem, also known as the leibniz rule for differentiation under the integral sign, is a powerful tool in calculus that. Uv differentiation formula (also known as the product rule) is a fundamental concept in calculus used to differentiate the. Notice that we can write this as y = uv where u = 2. D (uv) = vdu + udv dx dx dx. Learn how to differentiate a function that is the product of two or more functions using the product rule. Find the formula, proof and examples for. The product and quotient rules are covered in this section. X and v = cos 3x.
優雅 Uv Differentiation カサノバトーム
Leibnitz's theorem, also known as the leibniz rule for differentiation under the integral sign, is a powerful tool in calculus that. Learn how to differentiate a function that is the product of two or more functions using the product rule. Uv differentiation formula (also known as the product rule) is a fundamental concept in calculus used to differentiate the. Notice.
SOLUTION Differentiation by uv rule explained in simple language, also
Uv differentiation formula (also known as the product rule) is a fundamental concept in calculus used to differentiate the. D (uv) = vdu + udv dx dx dx. Notice that we can write this as y = uv where u = 2. Learn how to differentiate a function that is the product of two or more functions using the product.
Solved Judv=uvfvdu the product rule for differentiation d
Leibnitz's theorem, also known as the leibniz rule for differentiation under the integral sign, is a powerful tool in calculus that. Notice that we can write this as y = uv where u = 2. This is another very useful formula: Find the formula, proof and examples for. D (uv) = vdu + udv dx dx dx.
Uv Formula In Differentiation With Example Big Sales www
The product and quotient rules are covered in this section. D (uv) = vdu + udv dx dx dx. Learn how to differentiate a function that is the product of two or more functions using the product rule. Notice that we can write this as y = uv where u = 2. This is another very useful formula:
SOLUTION Differentiation by uv rule explained in simple language, also
Find the formula, proof and examples for. Leibnitz's theorem, also known as the leibniz rule for differentiation under the integral sign, is a powerful tool in calculus that. The product and quotient rules are covered in this section. Learn how to differentiate a function that is the product of two or more functions using the product rule. This is another.
SOLUTION Differentiation by uv rule explained in simple language, also
Find the formula, proof and examples for. Notice that we can write this as y = uv where u = 2. X and v = cos 3x. Uv differentiation formula (also known as the product rule) is a fundamental concept in calculus used to differentiate the. Leibnitz's theorem, also known as the leibniz rule for differentiation under the integral sign,.
SOLUTION Differentiation by uv rule explained in simple language, also
X and v = cos 3x. This is another very useful formula: Uv differentiation formula (also known as the product rule) is a fundamental concept in calculus used to differentiate the. D (uv) = vdu + udv dx dx dx. Find the formula, proof and examples for.
Uv Formula In Differentiation With Example Big Sales www
Find the formula, proof and examples for. X and v = cos 3x. The product and quotient rules are covered in this section. D (uv) = vdu + udv dx dx dx. This is another very useful formula:
Uv Formula In Differentiation With Example Big Sales www
Uv differentiation formula (also known as the product rule) is a fundamental concept in calculus used to differentiate the. Leibnitz's theorem, also known as the leibniz rule for differentiation under the integral sign, is a powerful tool in calculus that. Find the formula, proof and examples for. Learn how to differentiate a function that is the product of two or.
Uv Formula In Differentiation With Example Big Sales www
The product and quotient rules are covered in this section. Leibnitz's theorem, also known as the leibniz rule for differentiation under the integral sign, is a powerful tool in calculus that. Learn how to differentiate a function that is the product of two or more functions using the product rule. Uv differentiation formula (also known as the product rule) is.
Find The Formula, Proof And Examples For.
Learn how to differentiate a function that is the product of two or more functions using the product rule. This is another very useful formula: Uv differentiation formula (also known as the product rule) is a fundamental concept in calculus used to differentiate the. X and v = cos 3x.
D (Uv) = Vdu + Udv Dx Dx Dx.
Leibnitz's theorem, also known as the leibniz rule for differentiation under the integral sign, is a powerful tool in calculus that. The product and quotient rules are covered in this section. Notice that we can write this as y = uv where u = 2.