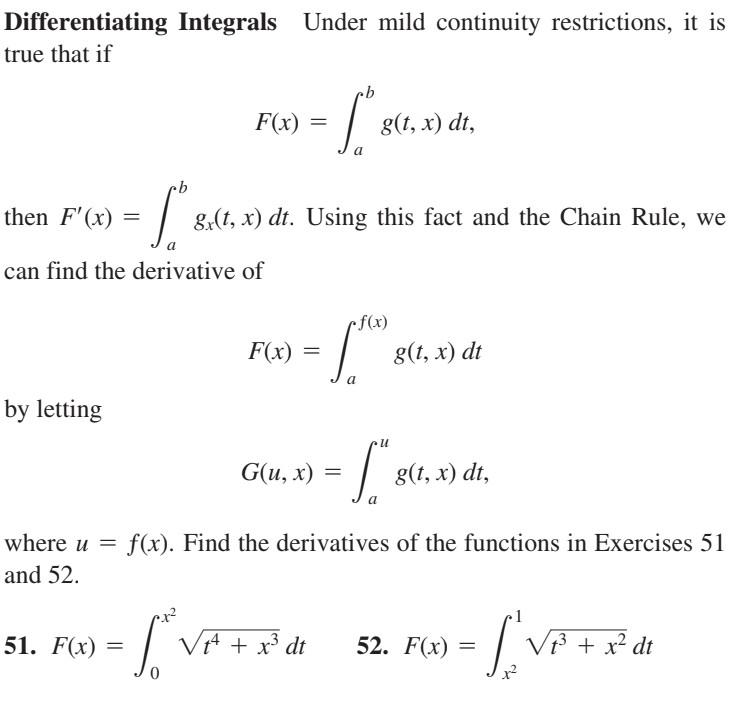
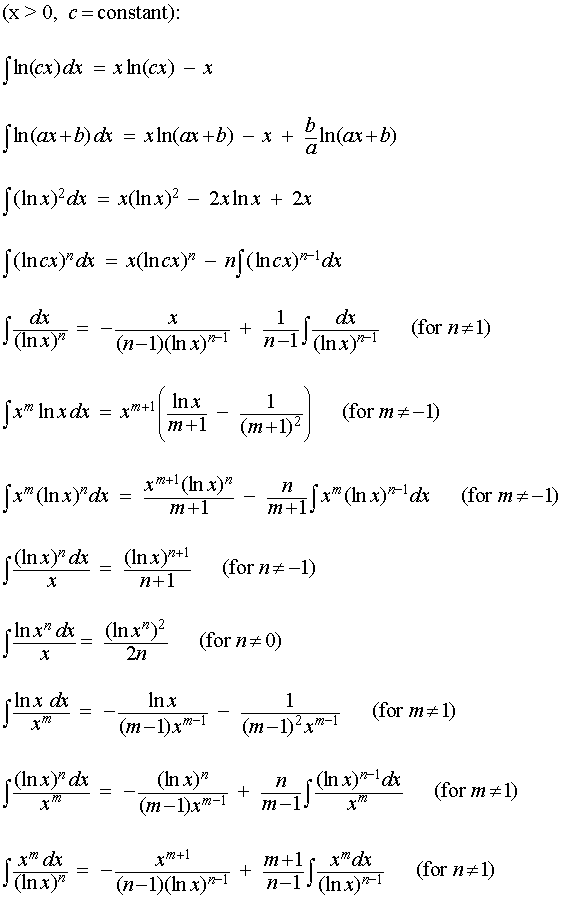Differentiating Integrals - We derive one of euler’s formulas by employing the trick of differentiating under the integral sign. Under fairly loose conditions on the. I learned about this method from the website of. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. We integrate over x and are left with something that depends only on t, not x. T) dx is a function of t, so we can ask about its t. Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits of integration, the result of the definite integral will not involve x, and so the derivative.
I learned about this method from the website of. Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits of integration, the result of the definite integral will not involve x, and so the derivative. T) dx is a function of t, so we can ask about its t. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. Under fairly loose conditions on the. We derive one of euler’s formulas by employing the trick of differentiating under the integral sign. We integrate over x and are left with something that depends only on t, not x.
We integrate over x and are left with something that depends only on t, not x. I learned about this method from the website of. We derive one of euler’s formulas by employing the trick of differentiating under the integral sign. Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits of integration, the result of the definite integral will not involve x, and so the derivative. Under fairly loose conditions on the. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. T) dx is a function of t, so we can ask about its t.
Indefinite Integrals 7 VividMath — US..
T) dx is a function of t, so we can ask about its t. Under fairly loose conditions on the. I learned about this method from the website of. We derive one of euler’s formulas by employing the trick of differentiating under the integral sign. Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits of integration, the.
DIFFERENTIATING INTEGRALS OR INTEGRATING DERIVATIVES Transport Phenomena
Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits of integration, the result of the definite integral will not involve x, and so the derivative. T) dx is a function of t, so we can ask about its t. Under fairly loose conditions on the. I learned about this method from the website of. We integrate over.
Solved Differentiating Integrals Under mild continuity
I learned about this method from the website of. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits of integration, the result of the definite integral will not involve x, and so the derivative. Under fairly loose conditions on the. We derive.
Calculus Integrals Reference Sheet (with Formulas) EEWeb
Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits of integration, the result of the definite integral will not involve x, and so the derivative. Under fairly loose conditions on the. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. We integrate over x and are left with something that depends.
Definite Integrals 3 VividMath — US..
We derive one of euler’s formulas by employing the trick of differentiating under the integral sign. We integrate over x and are left with something that depends only on t, not x. T) dx is a function of t, so we can ask about its t. Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits of integration,.
[1st year uni calculus] Differentiating integrals with chain rule r
Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. We derive one of euler’s formulas by employing the trick of differentiating under the integral sign. Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits of integration, the result of the definite integral will not involve x, and so the derivative. We.
List of Integrals Containing ln
We derive one of euler’s formulas by employing the trick of differentiating under the integral sign. Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits of integration, the result of the definite integral will not involve x, and so the derivative. We integrate over x and are left with something that depends only on t, not x..
Solved Exercise 2.11 Differentiating integrals Use the
Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits of integration, the result of the definite integral will not involve x, and so the derivative. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. We integrate over x and are left with something that depends only on t, not x. I.
Integrals ONE GREAT WORLD FOR ALL
We integrate over x and are left with something that depends only on t, not x. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. Under fairly loose conditions on the. Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits of integration, the result of the definite integral will not involve.
Definite Integrals 5 VividMath — US..
Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. Under fairly loose conditions on the. I learned about this method from the website of. T) dx is a function of t, so we can ask about its t. We integrate over x and are left with something that depends only on t, not x.
I Learned About This Method From The Website Of.
Unless the variable x appears in either (or both) of the limits of integration, the result of the definite integral will not involve x, and so the derivative. We derive one of euler’s formulas by employing the trick of differentiating under the integral sign. Under fairly loose conditions on the. We integrate over x and are left with something that depends only on t, not x.
Differentiation Under The Integral Sign Is An Operation In Calculus Used To Evaluate Certain Integrals.
T) dx is a function of t, so we can ask about its t.



![[1st year uni calculus] Differentiating integrals with chain rule r](https://i.imgur.com/P5cyd16.png)