Differentiate The Function Y Tan Ln Ax B - Not the question you’re looking for? This can also be written as. The chain rule states that if you. The outer function is \( \tan(u) \). There are 3 steps to solve this one. The derivative of a function describes the instantaneous rate of. Use the derivative of the tangent. To differentiate the function y = tan (ln (a x + b)), we will use the chain rule of differentiation. The chain rule formula is \( \frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{dy}{du} \cdot. The inner function is \( u = \ln(ax + b) \).
The chain rule states that if you. To differentiate the function y = tan (ln (a x + b)), we will use the chain rule of differentiation. Use the derivative of the tangent. Not the question you’re looking for? There are 3 steps to solve this one. The derivative of a function describes the instantaneous rate of. Post any question and get expert help quickly. Y' = asec2(ln(ax +b)) ax + b. This can also be written as. Not the question you’re looking for?
Y' = asec2(ln(ax +b)) ax + b. The inner function is \( u = \ln(ax + b) \). Use the derivative of the tangent. There are 3 steps to solve this one. The chain rule states that if you. The chain rule formula is \( \frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{dy}{du} \cdot. The derivative of a function describes the instantaneous rate of. There are 2 steps to solve this one. Ax +b derived gives you: This can also be written as.
Solved Differentiate and simplify y = ln(tan 3x) y =
Not the question you’re looking for? Identify the outermost function, which in this case is the tangent function, y = tan (u), where u = ln (a x + b). The chain rule states that if you. Y' = asec2(ln(ax +b)) ax + b. The inner function is \( u = \ln(ax + b) \).
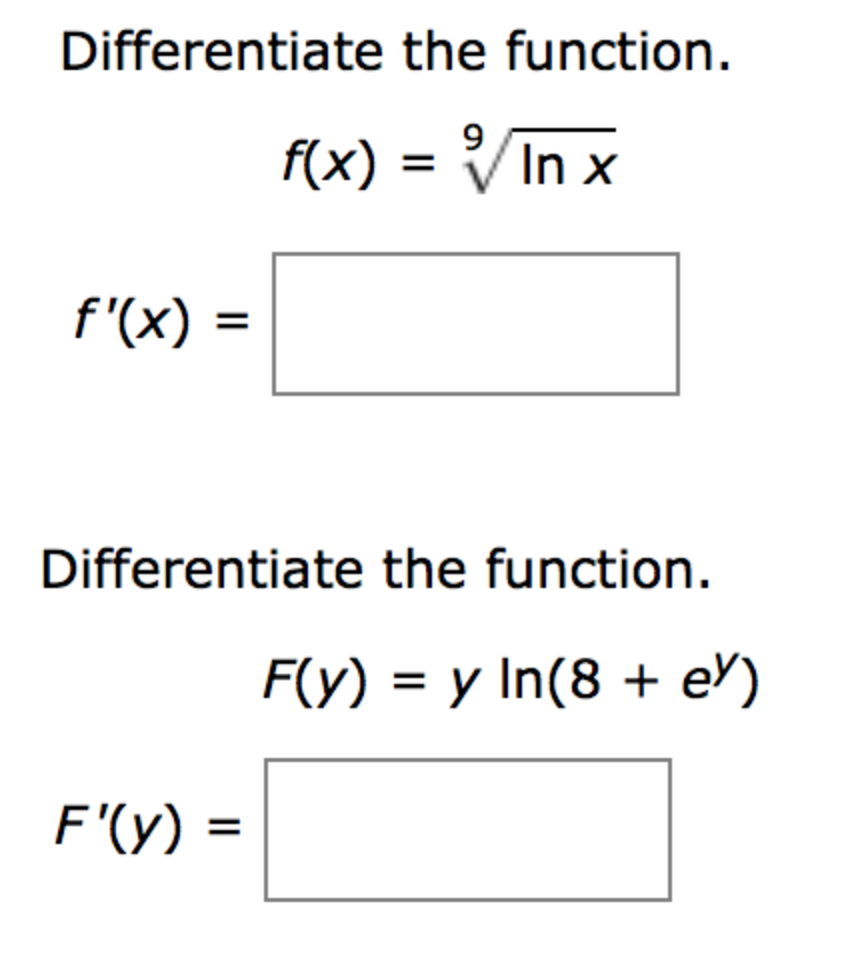
Solved Differentiate the function. f (x) = 9 Squareroot ln x
The outer function is \( \tan(u) \). Y' = asec2(ln(ax +b)) ax + b. This can also be written as. There are 3 steps to solve this one. To differentiate the function y = tan (ln (a x + b)), we will use the chain rule of differentiation.
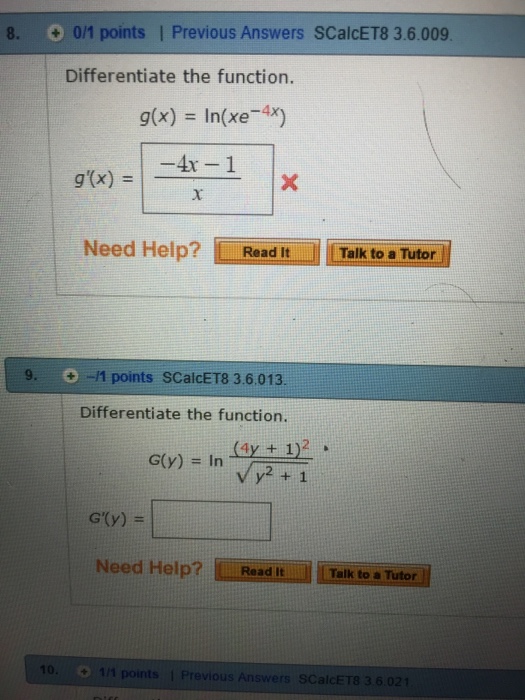
Solved Differentiate the function.g(x) =ln(xe^4x)g'(x) =
The chain rule formula is \( \frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{dy}{du} \cdot. This can also be written as. There are 3 steps to solve this one. Derivatives and tangents what is the derivative of a function? Ax +b derived gives you:
Solved Differentiate the function y = ln (cos^2(ln x)) y' =
Not the question you’re looking for? Identify the outermost function, which in this case is the tangent function, y = tan (u), where u = ln (a x + b). There are 3 steps to solve this one. Not the question you’re looking for? Ax +b derived gives you:
(a) Differentiate The Following Function With Resp...
Not the question you’re looking for? The chain rule formula is \( \frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{dy}{du} \cdot. Y' = asec2(ln(ax +b)) ax + b. Not the question you’re looking for? Identify the outermost function, which in this case is the tangent function, y = tan (u), where u = ln (a x + b).
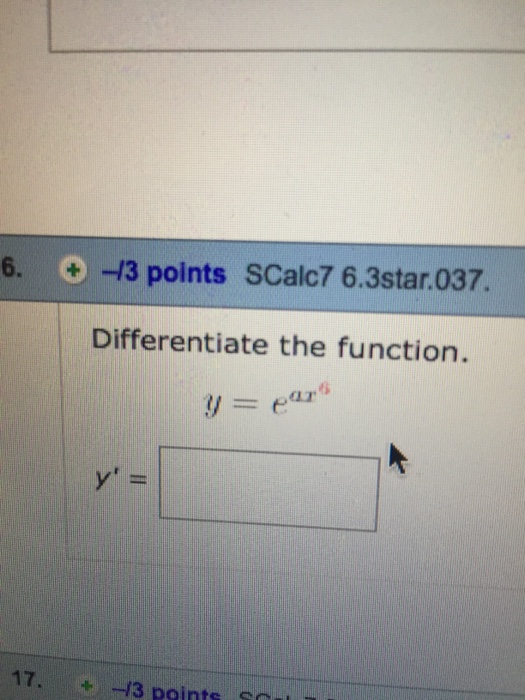
Solved Differentiate the function. y = e^ax^6 y' =
To differentiate the function y = tan (ln (a x + b)), we will use the chain rule of differentiation. The chain rule formula is \( \frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{dy}{du} \cdot. Not the question you’re looking for? The derivative of a function describes the instantaneous rate of. Y' = asec2(ln(ax +b)) ax + b.
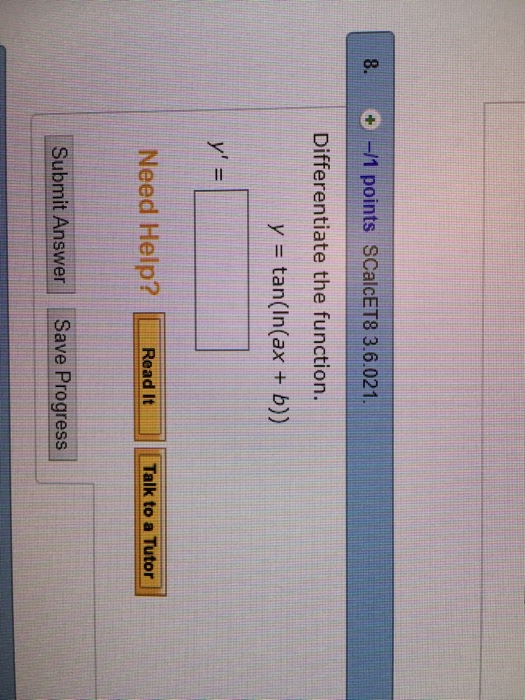
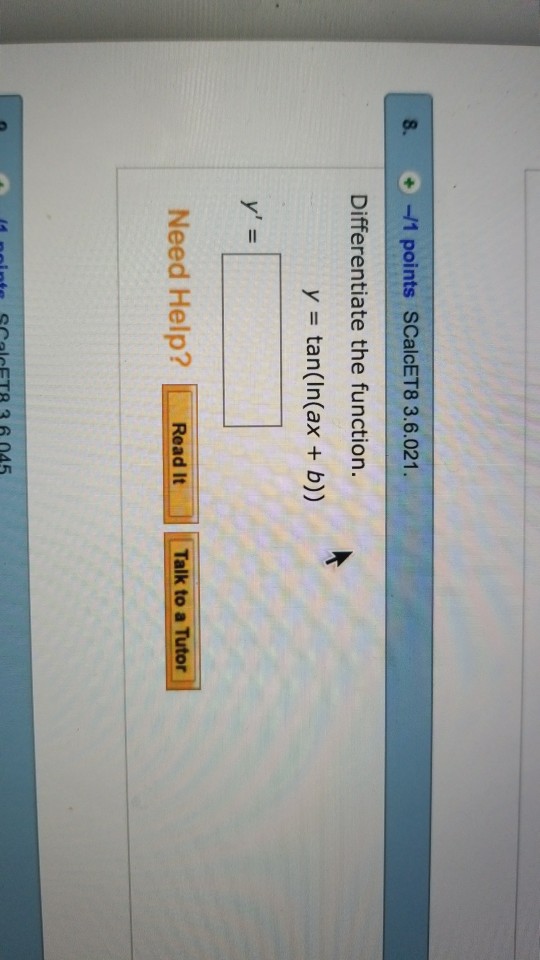
Solved Differentiate the function. y = tan(ln(ax + b)) y'
Not the question you’re looking for? To differentiate the function y = tan (ln (a x + b)), we will use the chain rule of differentiation. Y' = asec2(ln(ax +b)) ax + b. This can also be written as. The derivative of a function describes the instantaneous rate of.
Solved points SCalcET8 3.6.021. + Differentiate the
Ax +b derived gives you: There are 2 steps to solve this one. The chain rule formula is \( \frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{dy}{du} \cdot. There are 3 steps to solve this one. Here you have a function (tan) of a function (ln).
Differentiate the function. y=tan[ln(a x+b)] Numerade
The derivative of a function describes the instantaneous rate of. The chain rule formula is \( \frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{dy}{du} \cdot. The chain rule states that if you. There are 2 steps to solve this one. This can also be written as.
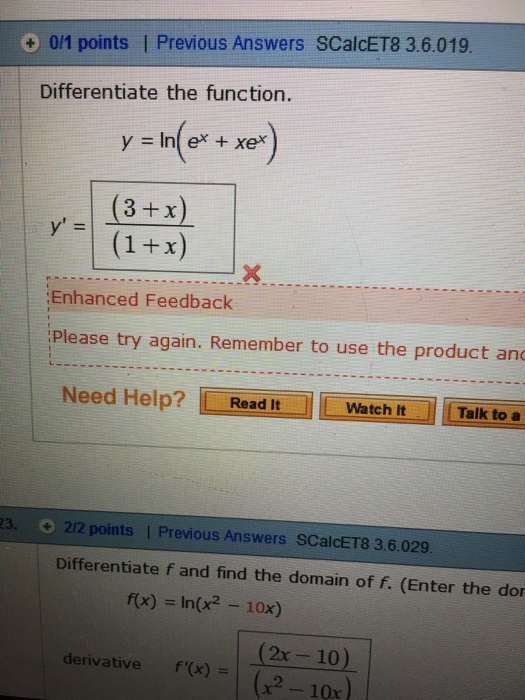
Solved Differentiate the function. y = ln(e^x + xe^x) y' =
This can also be written as. Here you have a function (tan) of a function (ln). To differentiate the function y = tan (ln (a x + b)), we will use the chain rule of differentiation. The derivative of a function describes the instantaneous rate of. There are 3 steps to solve this one.
The Outer Function Is \( \Tan(U) \).
The chain rule states that if you. Not the question you’re looking for? Here you have a function (tan) of a function (ln). Not the question you’re looking for?
Ax +B Derived Gives You:
Post any question and get expert help quickly. To differentiate the function y = tan (ln (a x + b)), we will use the chain rule of differentiation. Use the derivative of the tangent. The inner function is \( u = \ln(ax + b) \).
Derivatives And Tangents What Is The Derivative Of A Function?
Y' = asec2(ln(ax +b)) ax + b. The chain rule formula is \( \frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{dy}{du} \cdot. There are 2 steps to solve this one. Identify the outermost function, which in this case is the tangent function, y = tan (u), where u = ln (a x + b).
There Are 3 Steps To Solve This One.
This can also be written as. The derivative of a function describes the instantaneous rate of.
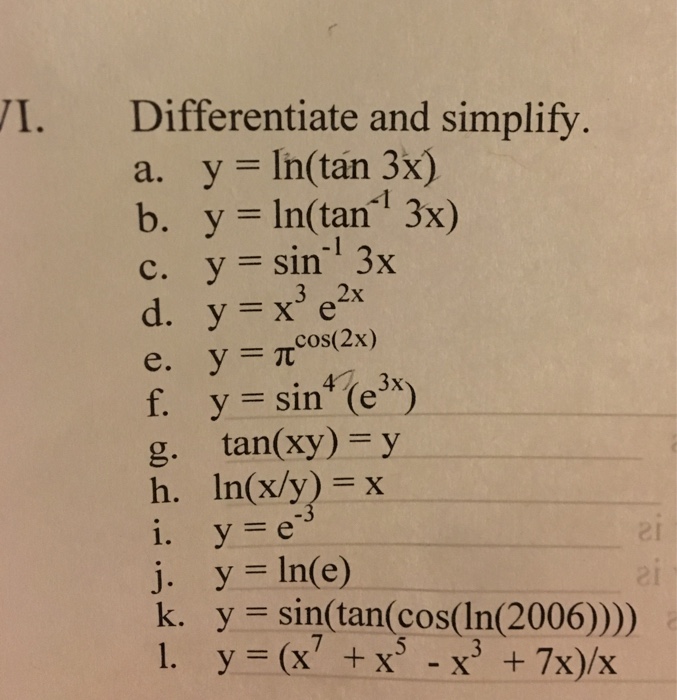


![Differentiate the function. y=tan[ln(a x+b)] Numerade](https://cdn.numerade.com/previews/2a69205e-6520-4a3c-9d45-25b1a38687f5_large.jpg)