Differentiate Sec 3X - Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = sec(x) f (x) = sec (x). What is the derivative of y = sec3(x)? Y' = 3 ⋅ sec2x ⋅ secx ⋅ tanx. The solution is, for problems like these, y = f. Differentiate both sides of the equation. The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′. Secx is equal to 1 cosx. What is the derivative of y = sec3(x)? Differentiate the right side of the equation. The differentiation formula for the secant trigonometry ratio is given by \[\dfrac{d}{{dx}}(\sec (x)) = \sec (x).\tan (x)\],.
Thus, sec3x is an equivalent statement to 1 (cosx)3. The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′. The solution is, for problems like these, y = f. Y' = 3 ⋅ sec2x ⋅ secx ⋅ tanx. Differentiate both sides of the equation. The differentiation formula for the secant trigonometry ratio is given by \[\dfrac{d}{{dx}}(\sec (x)) = \sec (x).\tan (x)\],. What is the derivative of y = sec3(x)? Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = sec(x) f (x) = sec (x). What is the derivative of y = sec3(x)? Secx is equal to 1 cosx.
Differentiate both sides of the equation. The solution is, for problems like these, y = f. The differentiation formula for the secant trigonometry ratio is given by \[\dfrac{d}{{dx}}(\sec (x)) = \sec (x).\tan (x)\],. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = sec(x) f (x) = sec (x). What is the derivative of y = sec3(x)? Differentiate the right side of the equation. The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′. Thus, sec3x is an equivalent statement to 1 (cosx)3. What is the derivative of y = sec3(x)? Y' = 3 ⋅ sec2x ⋅ secx ⋅ tanx.
Differentiate each of the following w.r.t. x sec^3 (x^2 + 1)
What is the derivative of y = sec3(x)? Differentiate both sides of the equation. Differentiate the right side of the equation. Y' = 3 ⋅ sec2x ⋅ secx ⋅ tanx. Secx is equal to 1 cosx.
Differentiate sin(2x3) from first principles Maths Limits and
What is the derivative of y = sec3(x)? Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = sec(x) f (x) = sec (x). The differentiation formula for the secant trigonometry ratio is given by \[\dfrac{d}{{dx}}(\sec (x)) =.
Derivative of Sec^2x Detailed Explanation and Examples The Story of
Thus, sec3x is an equivalent statement to 1 (cosx)3. Differentiate both sides of the equation. What is the derivative of y = sec3(x)? Secx is equal to 1 cosx. What is the derivative of y = sec3(x)?
Derivative of Sec^2x Detailed Explanation and Examples The Story of
The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′. Secx is equal to 1 cosx. What is the derivative of y = sec3(x)? The solution is, for problems like these, y = f. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f.
[Solved] . 1 Let f(x) = Find f'(x). (+3 sec(3x2 2)) 3
The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′. Y' = 3 ⋅ sec2x ⋅ secx ⋅ tanx. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = sec(x) f (x) = sec.
Solved 1. Differentiate sec x and csc x using quotient
Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = sec(x) f (x) = sec (x). Differentiate the right side of the equation. The solution is, for problems like these, y = f. Y' = 3 ⋅ sec2x.
65. Differentiate log sec x using first principle
What is the derivative of y = sec3(x)? Secx is equal to 1 cosx. The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) =.
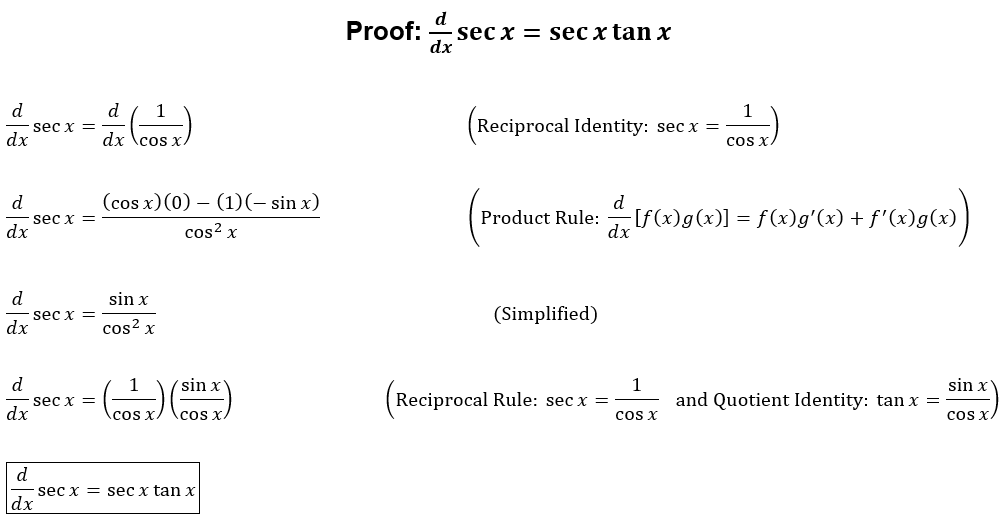
Brandi's Buzzar Blog Proof Derivative sec x = sec x tan x
Thus, sec3x is an equivalent statement to 1 (cosx)3. Secx is equal to 1 cosx. Differentiate the right side of the equation. What is the derivative of y = sec3(x)? The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′.
Differentiate sec5x w.r.t. x using first principle.
What is the derivative of y = sec3(x)? Secx is equal to 1 cosx. Y' = 3 ⋅ sec2x ⋅ secx ⋅ tanx. What is the derivative of y = sec3(x)? Differentiate the right side of the equation.
Ex 5.2, 4 Differentiate sec (tan (root x)) Class 12 Finding deri
What is the derivative of y = sec3(x)? Differentiate both sides of the equation. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = sec(x) f (x) = sec (x). The solution is, for problems like these, y.
Differentiate Using The Chain Rule, Which States That D Dx [F (G(X))] D D X [F (G (X))] Is F '(G(X))G'(X) F ′ (G (X)) G ′ (X) Where F (X) = Sec(X) F (X) = Sec (X).
The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′. Secx is equal to 1 cosx. Differentiate the right side of the equation. What is the derivative of y = sec3(x)?
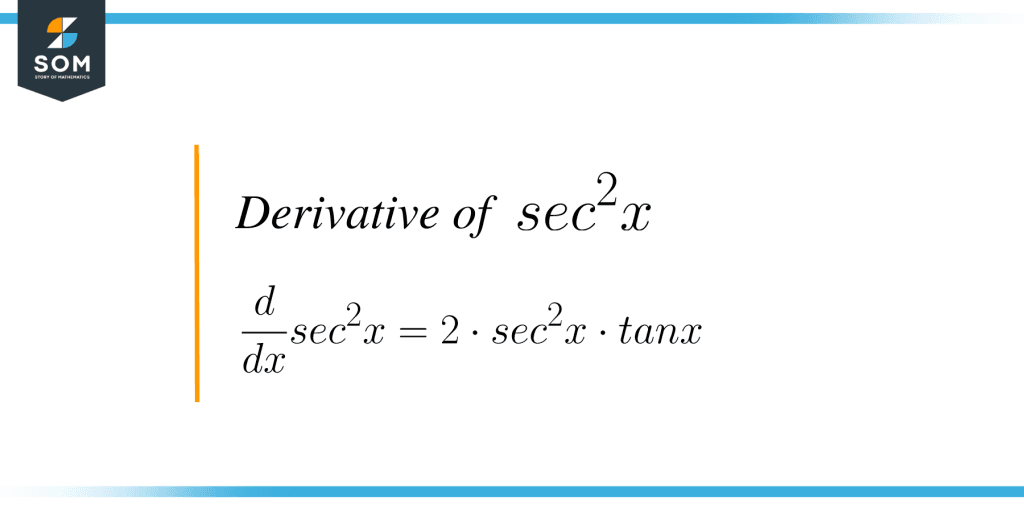
Y' = 3 ⋅ Sec2X ⋅ Secx ⋅ Tanx.
The differentiation formula for the secant trigonometry ratio is given by \[\dfrac{d}{{dx}}(\sec (x)) = \sec (x).\tan (x)\],. Differentiate both sides of the equation. The solution is, for problems like these, y = f. What is the derivative of y = sec3(x)?