Differentiate Integral - Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. We integrate over x and are left with something that depends only on t, not x. The derivative of an integral of a function is. T) dx is a function of t, so we can ask about its t. For an integral of the form $$\tag{1}\int_a^{g(x)} f(t)\,dt,$$ you would find the derivative using the chain rule. The conclusion of the fundamental theorem of calculus can be loosely expressed in words as: Under fairly loose conditions on the. In mathematics, the problem of differentiation of integrals is that of determining under what circumstances the mean value integral of a. As stated above, the basic.
For an integral of the form $$\tag{1}\int_a^{g(x)} f(t)\,dt,$$ you would find the derivative using the chain rule. Under fairly loose conditions on the. The conclusion of the fundamental theorem of calculus can be loosely expressed in words as: T) dx is a function of t, so we can ask about its t. As stated above, the basic. We integrate over x and are left with something that depends only on t, not x. In mathematics, the problem of differentiation of integrals is that of determining under what circumstances the mean value integral of a. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. The derivative of an integral of a function is.
The derivative of an integral of a function is. As stated above, the basic. We integrate over x and are left with something that depends only on t, not x. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. The conclusion of the fundamental theorem of calculus can be loosely expressed in words as: Under fairly loose conditions on the. In mathematics, the problem of differentiation of integrals is that of determining under what circumstances the mean value integral of a. T) dx is a function of t, so we can ask about its t. For an integral of the form $$\tag{1}\int_a^{g(x)} f(t)\,dt,$$ you would find the derivative using the chain rule.
Differential and Integral Calculus Differentiate with Respect to
The conclusion of the fundamental theorem of calculus can be loosely expressed in words as: As stated above, the basic. For an integral of the form $$\tag{1}\int_a^{g(x)} f(t)\,dt,$$ you would find the derivative using the chain rule. We integrate over x and are left with something that depends only on t, not x. Differentiation under the integral sign is an.
real analysis Proof of Differentiate under the integral Mathematics
As stated above, the basic. The conclusion of the fundamental theorem of calculus can be loosely expressed in words as: Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. T) dx is a function of t, so we can ask about its t. For an integral of the form $$\tag{1}\int_a^{g(x)} f(t)\,dt,$$ you would find.
Download Difference, Differentiate, Delimitation. RoyaltyFree Stock
As stated above, the basic. For an integral of the form $$\tag{1}\int_a^{g(x)} f(t)\,dt,$$ you would find the derivative using the chain rule. The derivative of an integral of a function is. The conclusion of the fundamental theorem of calculus can be loosely expressed in words as: Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain.
SOLUTION Differentiate integral Studypool
Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. For an integral of the form $$\tag{1}\int_a^{g(x)} f(t)\,dt,$$ you would find the derivative using the chain rule. The conclusion of the fundamental theorem of calculus can be loosely expressed in words as: The derivative of an integral of a function is. T) dx is a.
How to differentiate (wrt r) an integral whose integration bound is
In mathematics, the problem of differentiation of integrals is that of determining under what circumstances the mean value integral of a. Under fairly loose conditions on the. For an integral of the form $$\tag{1}\int_a^{g(x)} f(t)\,dt,$$ you would find the derivative using the chain rule. As stated above, the basic. Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used.
Differential and Integral Calculus Differentiate with Respect to
As stated above, the basic. We integrate over x and are left with something that depends only on t, not x. The conclusion of the fundamental theorem of calculus can be loosely expressed in words as: In mathematics, the problem of differentiation of integrals is that of determining under what circumstances the mean value integral of a. Under fairly loose.
Solved Differentiate the function. F(x) = integral^x^2_2x
For an integral of the form $$\tag{1}\int_a^{g(x)} f(t)\,dt,$$ you would find the derivative using the chain rule. The conclusion of the fundamental theorem of calculus can be loosely expressed in words as: The derivative of an integral of a function is. As stated above, the basic. We integrate over x and are left with something that depends only on t,.
SOLUTION Indefinite integral Studypool Worksheets Library
T) dx is a function of t, so we can ask about its t. The derivative of an integral of a function is. We integrate over x and are left with something that depends only on t, not x. Under fairly loose conditions on the. As stated above, the basic.
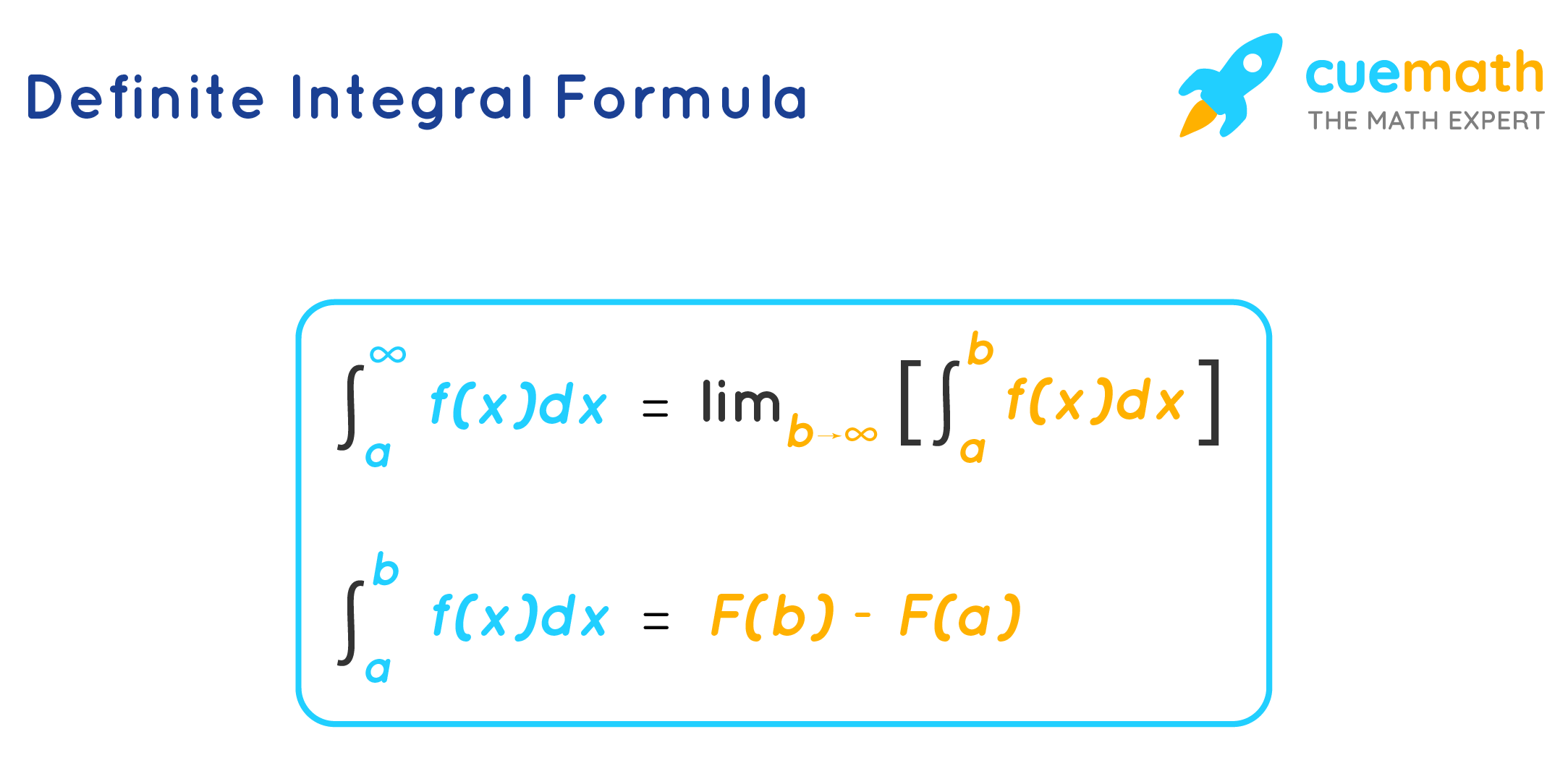
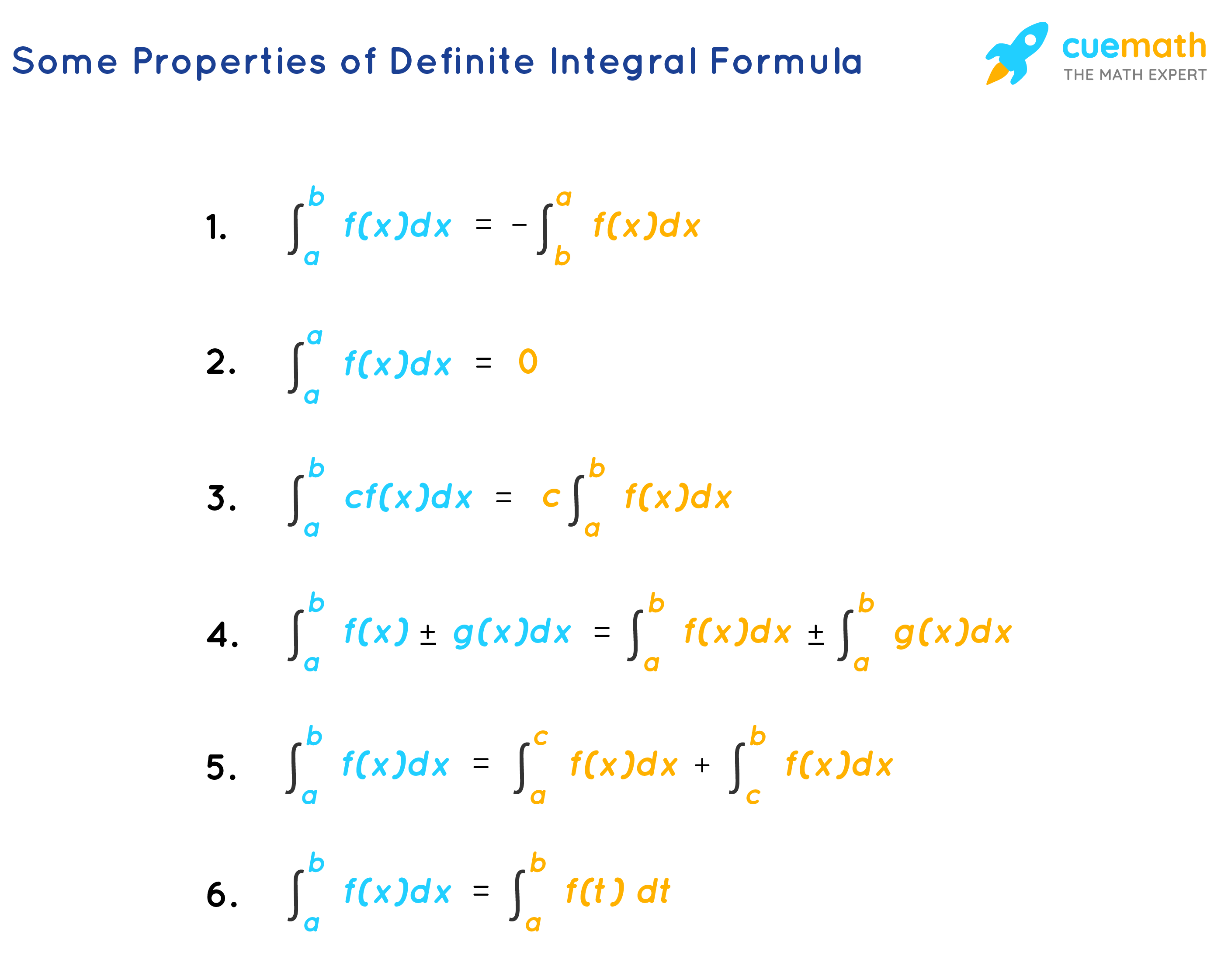
Definite Integral Formula Learn Formula to Calculate Definite Integral
We integrate over x and are left with something that depends only on t, not x. The derivative of an integral of a function is. The conclusion of the fundamental theorem of calculus can be loosely expressed in words as: As stated above, the basic. For an integral of the form $$\tag{1}\int_a^{g(x)} f(t)\,dt,$$ you would find the derivative using the.
Definite Integral Formula Learn Formula to Calculate Definite Integral
Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. In mathematics, the problem of differentiation of integrals is that of determining under what circumstances the mean value integral of a. T) dx is a function of t, so we can ask about its t. Under fairly loose conditions on the. We integrate over x.
Under Fairly Loose Conditions On The.
Differentiation under the integral sign is an operation in calculus used to evaluate certain integrals. We integrate over x and are left with something that depends only on t, not x. The conclusion of the fundamental theorem of calculus can be loosely expressed in words as: The derivative of an integral of a function is.
T) Dx Is A Function Of T, So We Can Ask About Its T.
As stated above, the basic. For an integral of the form $$\tag{1}\int_a^{g(x)} f(t)\,dt,$$ you would find the derivative using the chain rule. In mathematics, the problem of differentiation of integrals is that of determining under what circumstances the mean value integral of a.