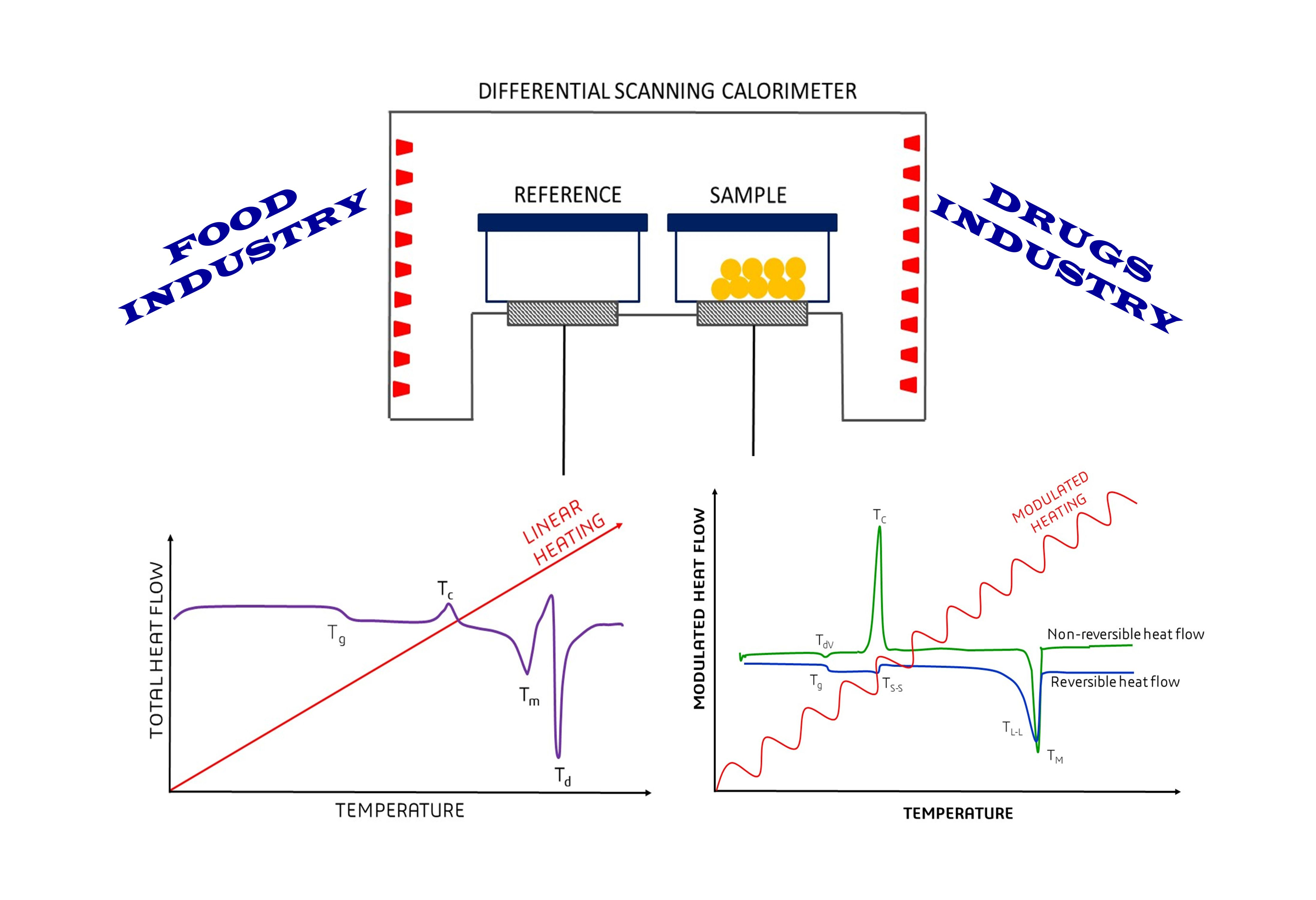
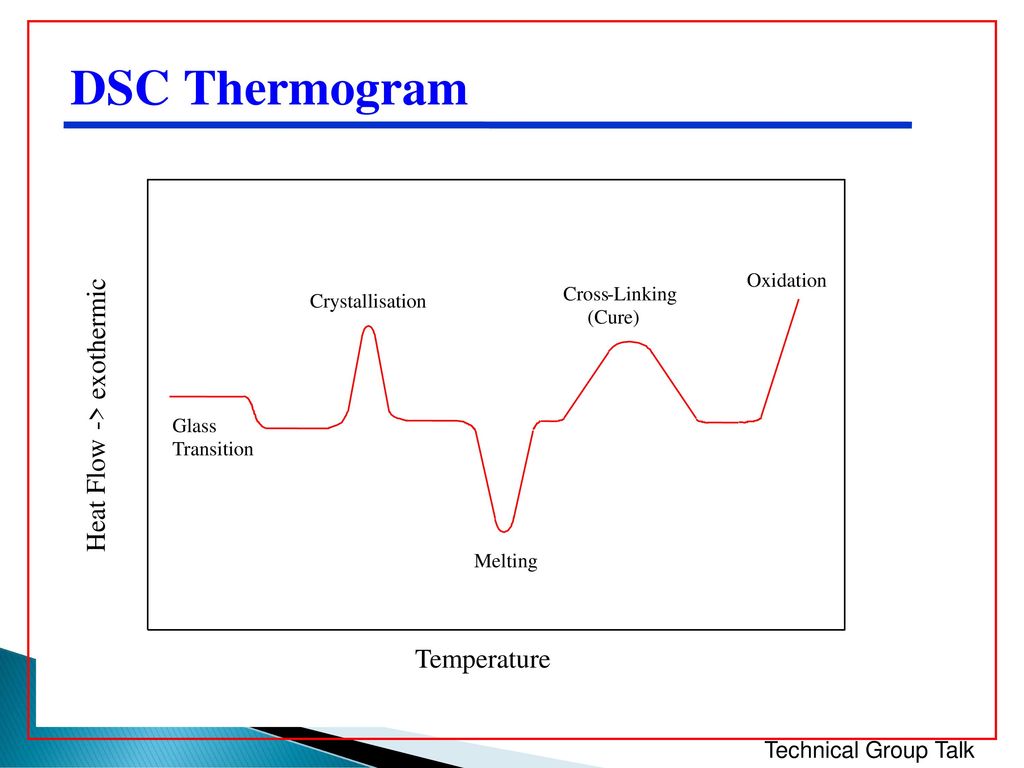
Differential Scanning Calorimetry - Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample specimen as well as enthalpy changes as a function of. In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is. Differential scanning calorimetry is a specific type of calorimetry including both a sample substance and a reference substance, residing in separate chambers. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique.
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample specimen as well as enthalpy changes as a function of. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a. Differential scanning calorimetry is a specific type of calorimetry including both a sample substance and a reference substance, residing in separate chambers.
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample specimen as well as enthalpy changes as a function of. In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a. Differential scanning calorimetry is a specific type of calorimetry including both a sample substance and a reference substance, residing in separate chambers. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is.
SOLUTION Differential scanning calorimetry dsc Studypool
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is. Differential scanning calorimetry is a specific type of calorimetry including both a sample substance and a reference substance, residing in separate chambers. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Janna Maranas Research Group
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample specimen as well as enthalpy changes as a function of. Differential scanning calorimetry is a specific type of calorimetry including both a sample substance and a reference substance, residing in separate chambers. In this technique, the sample and the.
SOLUTION Differential scanning calorimetry Studypool
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample specimen as well as enthalpy changes as a function of. Differential scanning calorimetry.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Automated Calorimetry Facility
In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample specimen as well as enthalpy changes as a function of. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. Differential scanning calorimetry.
An overview of Differential Scanning Calorimetry SETARAM
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is. Differential scanning calorimetry is a specific type of calorimetry including both a sample substance and a reference substance, residing.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Covalent Metrology Material
In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample specimen as well as enthalpy changes as a function of. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. Differential scanning calorimetry.
28 Schematic diagram of Differential scanning calorimetry. Download
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample specimen as well as enthalpy changes as a function of. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a. Differential scanning calorimetry.
differential scanning calorimetry principle Shauna Asbury
Differential scanning calorimetry is a specific type of calorimetry including both a sample substance and a reference substance, residing in separate chambers. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is. In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Avishtech
In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. Differential scanning calorimetry is a specific type of calorimetry including both a sample substance and a reference substance, residing in separate chambers. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Chemistry LibreTexts, 44 OFF
Differential scanning calorimetry is a specific type of calorimetry including both a sample substance and a reference substance, residing in separate chambers. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a direct analytical experimental technique that measures the heat flux ∂q/∂t to or from a sample specimen as well as.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (Dsc) Is A Direct Analytical Experimental Technique That Measures The Heat Flux ∂Q/∂T To Or From A Sample Specimen As Well As Enthalpy Changes As A Function Of.
Differential scanning calorimetry is a specific type of calorimetry including both a sample substance and a reference substance, residing in separate chambers. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is. In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique.