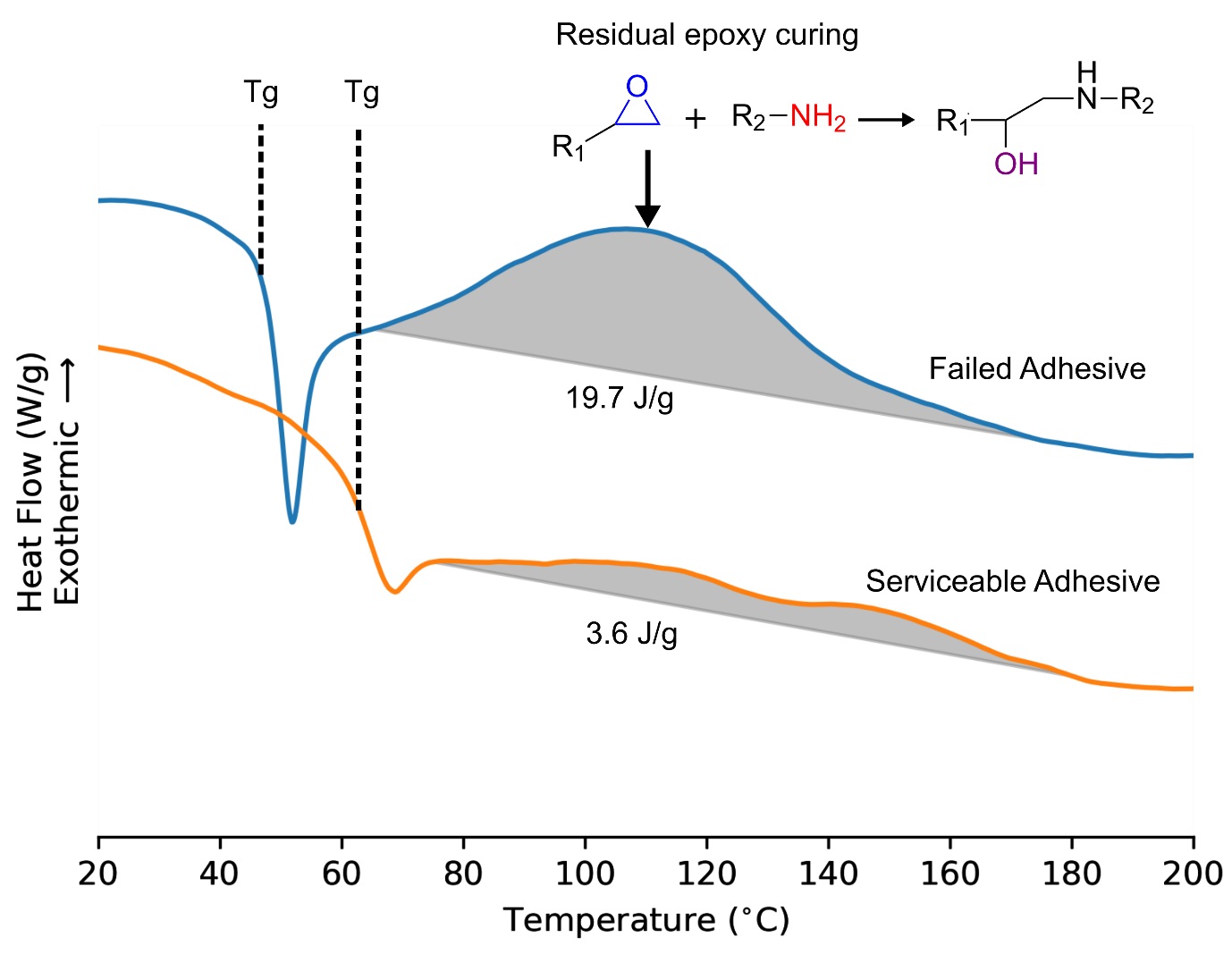
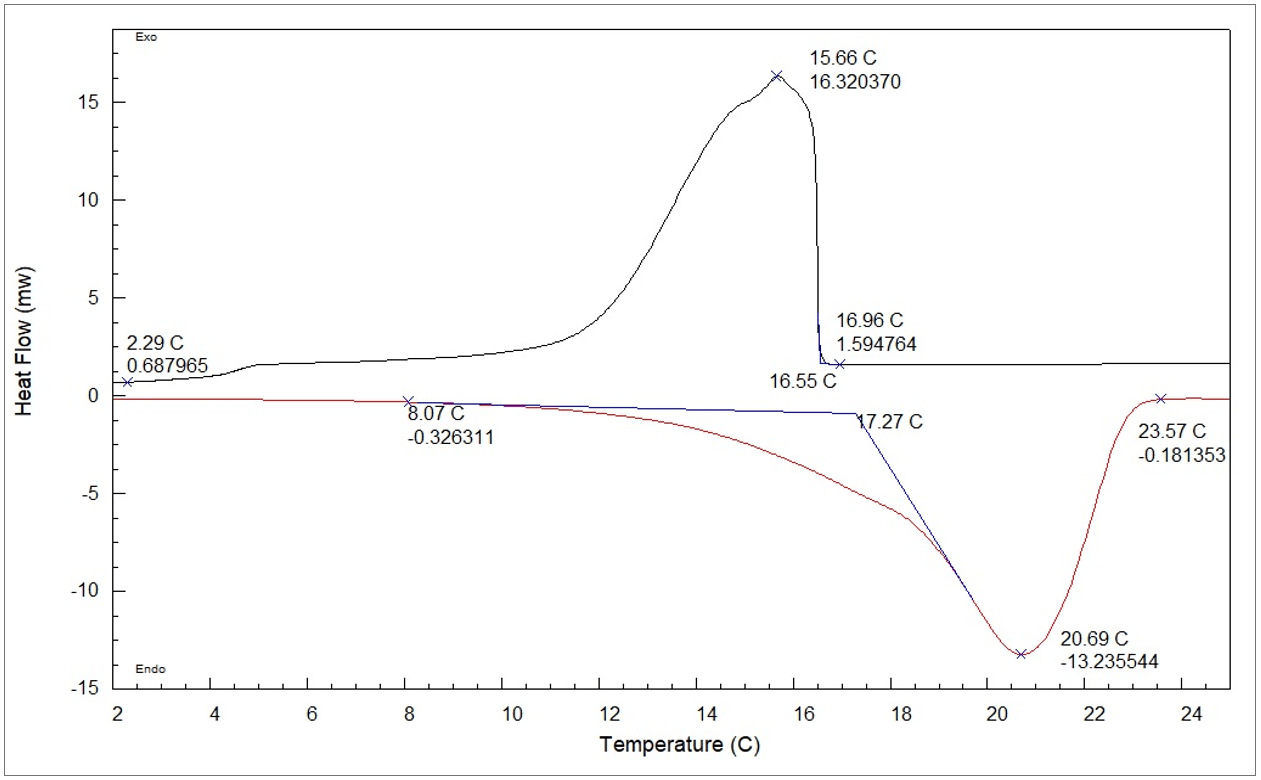
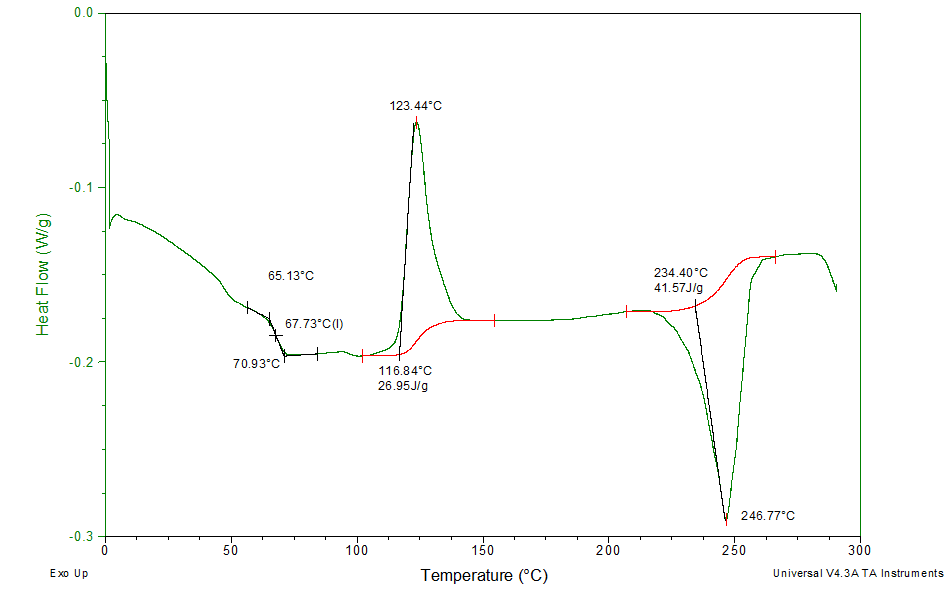
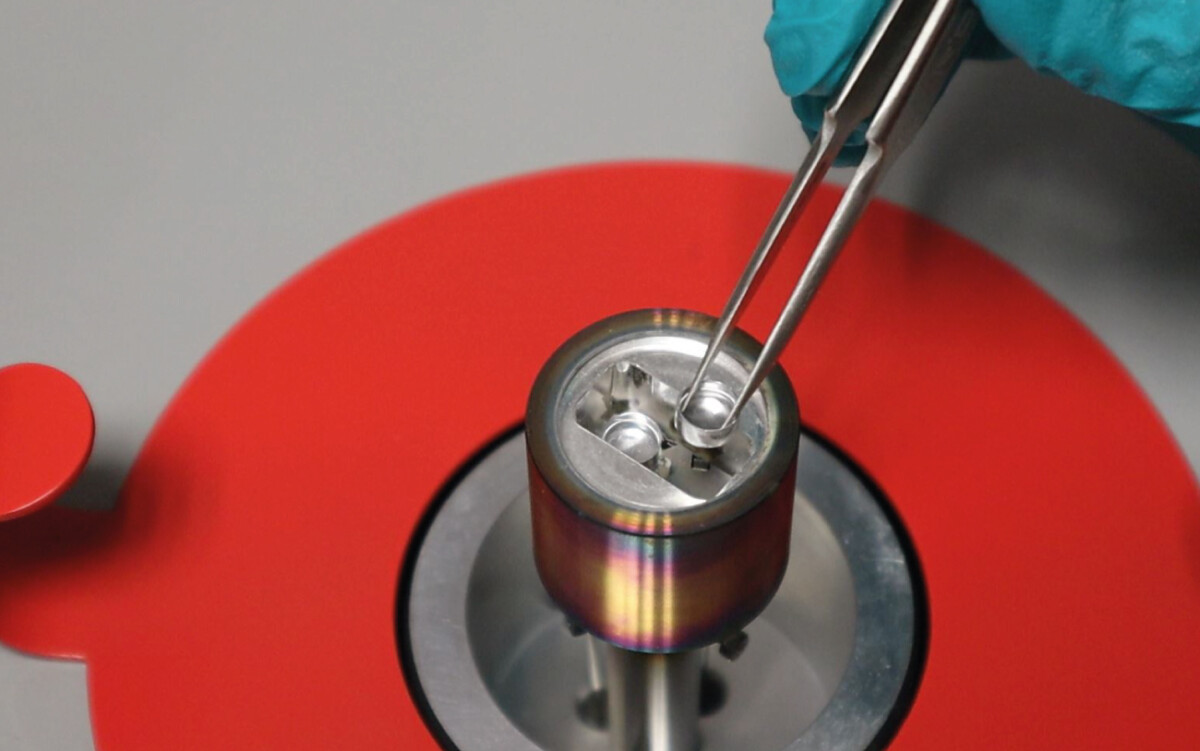
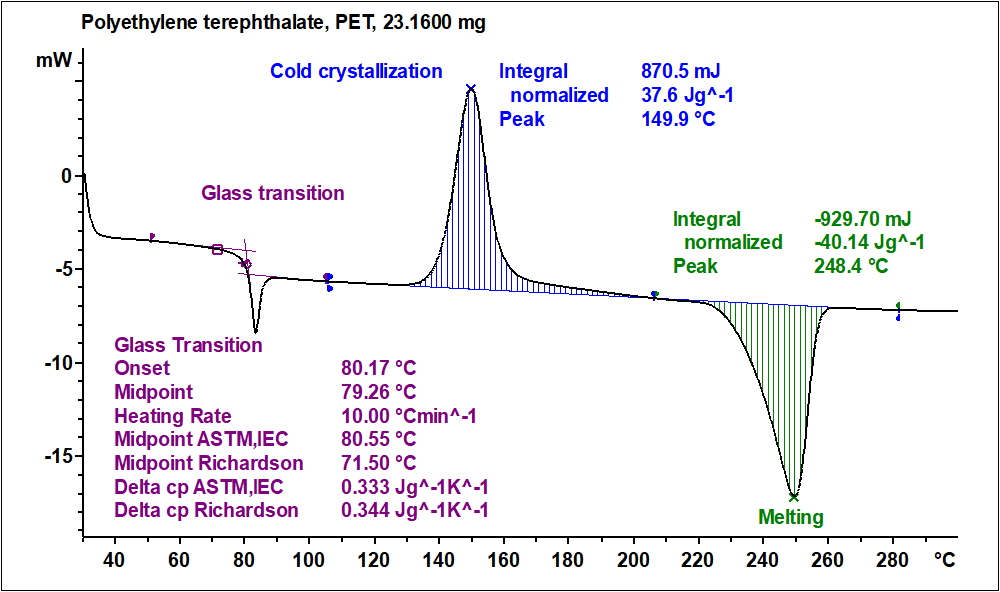
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc - In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. The pans are placed on. In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a precisely. In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum pans with crimped tops. Furthermore, the chemical reaction such as thermal curing, heat history, specific.
In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a precisely. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. Furthermore, the chemical reaction such as thermal curing, heat history, specific. In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum pans with crimped tops. The pans are placed on. In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a.
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. Furthermore, the chemical reaction such as thermal curing, heat history, specific. The pans are placed on. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is. In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum pans with crimped tops. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a precisely. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a.
Interpretation Of Dsc Curve Differential Scanning Calorimetry Hot Sex
In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a precisely. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is. In this technique,.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Experiments At Different
Furthermore, the chemical reaction such as thermal curing, heat history, specific. In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum pans with crimped tops. In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a. The pans are placed on. In this technique, the sample.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Experiments At Different
In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a precisely. In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a. Furthermore, the chemical reaction such as thermal curing, heat history, specific. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in.
Adhesive Cure Troubleshooting with Differential Scanning Calorimetry
The pans are placed on. In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum pans with crimped tops. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is. Furthermore,.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Shiv Nadar University
In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a precisely. In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum pans with crimped tops. Furthermore, the chemical reaction such as thermal curing, heat history, specific. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) As An Analytical, 49 OFF
In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. Dsc enables the measurements of the.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Experiments At Different
In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a precisely. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum pans with crimped tops. In this technique, the sample.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Covalent Metrology
In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum pans with crimped tops. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. The pans are placed on. In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a precisely..
An overview of Differential Scanning Calorimetry SETARAM
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is. The pans are placed on. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Surface Science Western
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a precisely. In this technique, the sample.
The Pans Are Placed On.
Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum pans with crimped tops. Furthermore, the chemical reaction such as thermal curing, heat history, specific. In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a precisely.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (Dsc) Has Become The Most Widely Used Thermal Analysis Technique.
In this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization.