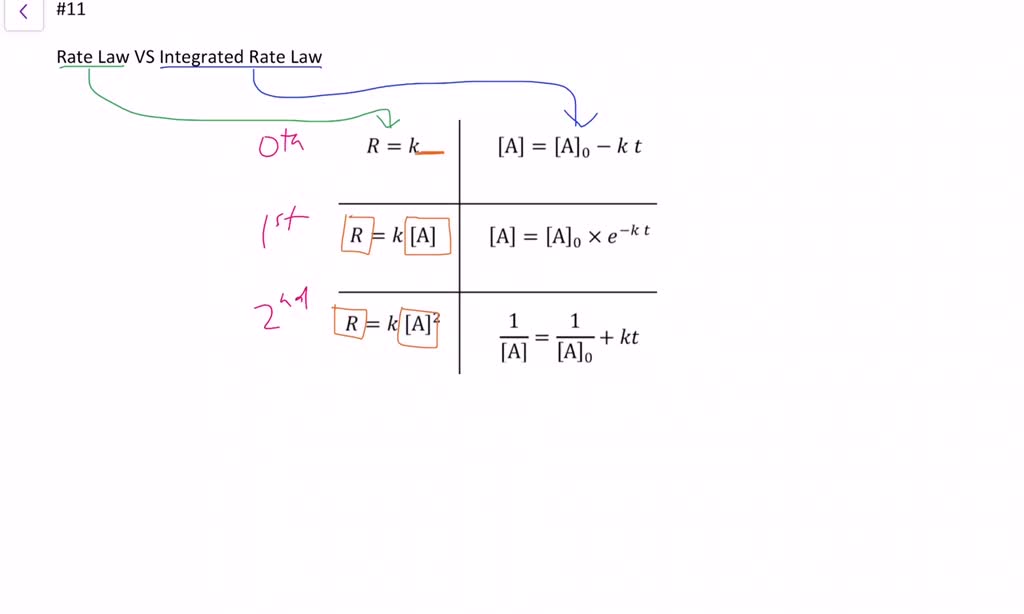
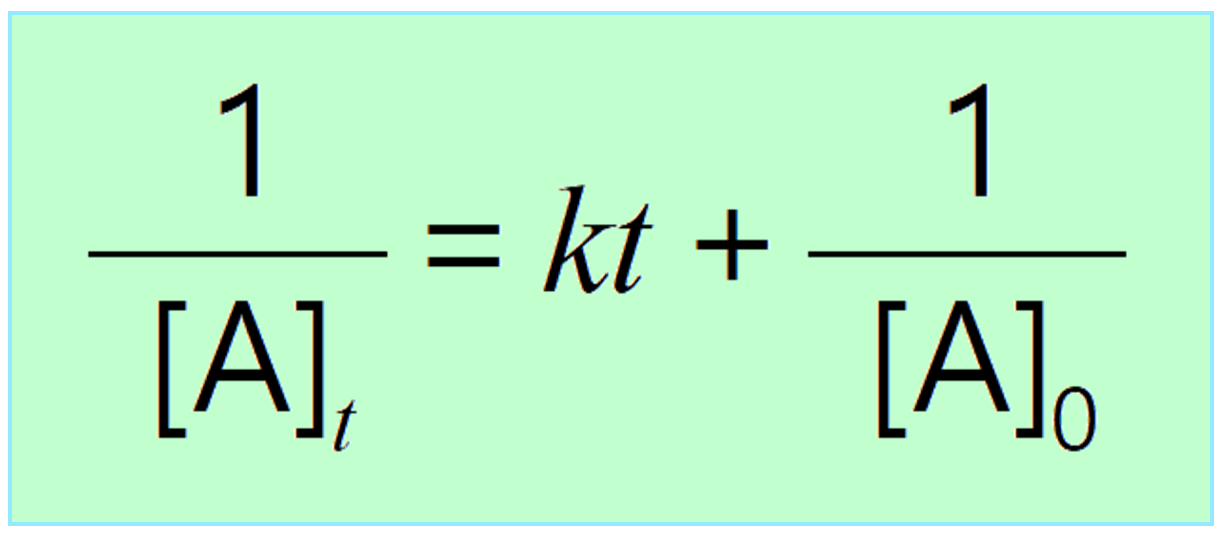Differential Rate Law - In other words, if we have a reaction of the type: Rate = k[a]m[b]n[c]p… in which [a], [b], and [c] represent the molar concentrations of. A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or more reactants (δ[r]) over a specific time interval (δt). They are used to describe what is. Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one or more reactants over a particular period of time; Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration of reactants (d [r]) over a small interval of time (dt). In general, a rate law (or differential rate law, as it is sometimes called) takes this form: The differential rate law can be.
Rate = k[a]m[b]n[c]p… in which [a], [b], and [c] represent the molar concentrations of. Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one or more reactants over a particular period of time; Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration of reactants (d [r]) over a small interval of time (dt). In other words, if we have a reaction of the type: In general, a rate law (or differential rate law, as it is sometimes called) takes this form: They are used to describe what is. A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or more reactants (δ[r]) over a specific time interval (δt). The differential rate law can be.
In other words, if we have a reaction of the type: Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration of reactants (d [r]) over a small interval of time (dt). Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one or more reactants over a particular period of time; In general, a rate law (or differential rate law, as it is sometimes called) takes this form: The differential rate law can be. Rate = k[a]m[b]n[c]p… in which [a], [b], and [c] represent the molar concentrations of. A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or more reactants (δ[r]) over a specific time interval (δt). They are used to describe what is.
The type of rate law for a reaction, either the d…
A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or more reactants (δ[r]) over a specific time interval (δt). Rate = k[a]m[b]n[c]p… in which [a], [b], and [c] represent the molar concentrations of. In general, a rate law (or differential rate law, as it is sometimes called) takes this form: The differential.
Differential Rate Law Equation Method… Chemistry in Hindi
The differential rate law can be. Rate = k[a]m[b]n[c]p… in which [a], [b], and [c] represent the molar concentrations of. A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or more reactants (δ[r]) over a specific time interval (δt). Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in.
Rate Law and Integrated Rate Law Diagram Quizlet
In other words, if we have a reaction of the type: Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration of reactants (d [r]) over a small interval of time (dt). In general, a rate law (or differential rate law, as it is sometimes called) takes this form: The differential.
Integrated Rate Law Chemistry Steps
Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one or more reactants over a particular period of time; Rate = k[a]m[b]n[c]p… in which [a], [b], and [c] represent the molar concentrations of. In general, a rate law (or differential rate law, as it is sometimes called) takes this form: Differential.
Solved From the differential rate law for a secondorder
Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration of reactants (d [r]) over a small interval of time (dt). In other words, if we have a reaction of the type: A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or more.
Solved (5pts) 15. Provide the differential rate law and
In other words, if we have a reaction of the type: In general, a rate law (or differential rate law, as it is sometimes called) takes this form: Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration of reactants (d [r]) over a small interval of time (dt). The differential.
Integrated Rate Law Chemistry Steps
The differential rate law can be. In general, a rate law (or differential rate law, as it is sometimes called) takes this form: Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration of reactants (d [r]) over a small interval of time (dt). A differential rate law expresses the reaction.
Differential Rate Equation
The differential rate law can be. Rate = k[a]m[b]n[c]p… in which [a], [b], and [c] represent the molar concentrations of. They are used to describe what is. Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one or more reactants over a particular period of time; In other words, if we.
Solved 2. Differential rate law relates instantaneous
Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration of reactants (d [r]) over a small interval of time (dt). They are used to describe what is. In general, a rate law (or differential rate law, as it is sometimes called) takes this form: The differential rate law can be..
Differential and Integrated Rate Equation
A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or more reactants (δ[r]) over a specific time interval (δt). Rate = k[a]m[b]n[c]p… in which [a], [b], and [c] represent the molar concentrations of. They are used to describe what is. Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction.
In General, A Rate Law (Or Differential Rate Law, As It Is Sometimes Called) Takes This Form:
In other words, if we have a reaction of the type: Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration of reactants (d [r]) over a small interval of time (dt). Rate = k[a]m[b]n[c]p… in which [a], [b], and [c] represent the molar concentrations of. They are used to describe what is.
Differential Rate Laws Express The Rate Of Reaction As A Function Of A Change In The Concentration Of One Or More Reactants Over A Particular Period Of Time;
A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or more reactants (δ[r]) over a specific time interval (δt). The differential rate law can be.