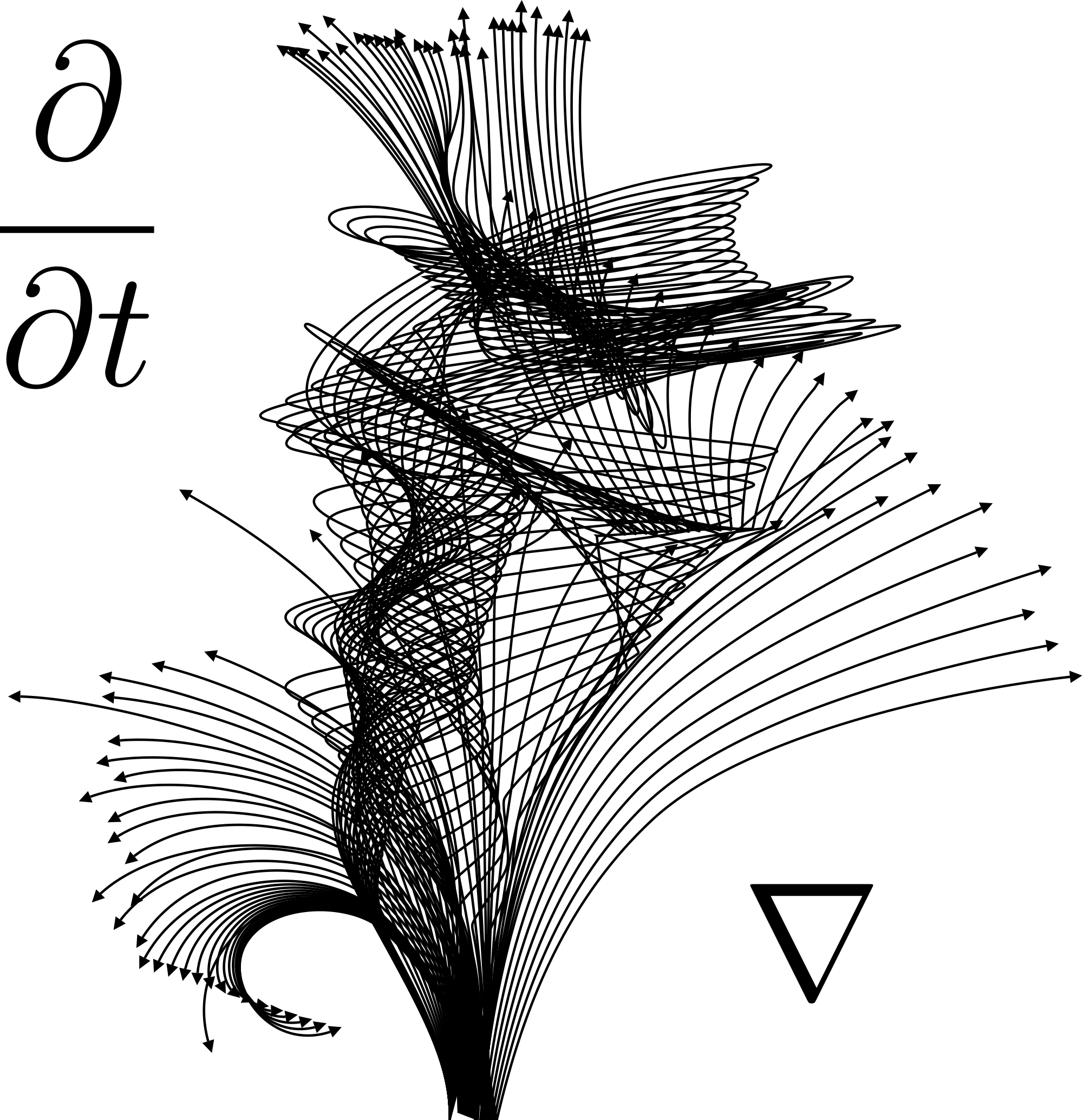
Differential Of A Log - In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. Suppose the argument of the natural log is not just \(x\), but instead is \(g(x)\), a. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the.
Suppose the argument of the natural log is not just \(x\), but instead is \(g(x)\), a. In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the.
In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. Suppose the argument of the natural log is not just \(x\), but instead is \(g(x)\), a. The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule.
Solve the differential equation x dy/dx = y(log y log x +1) Maths
Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the. Suppose the argument of the natural log is not just \(x\), but instead is \(g(x)\), a.
16. The differential coefficient of ( f ( x ) = log ( log x ) ) is
The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the. Suppose the argument of the natural log is not just \(x\), but instead is \(g(x)\), a. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation.
Logtransformed differential absorbance spectra of normalized
In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. Suppose the argument of the natural log is not just \(x\), but instead is \(g(x)\), a. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the.
Log differential intrusion of concrete at 180 d. Download Scientific
The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. Suppose the argument of the natural log is not just \(x\), but instead is \(g(x)\), a. In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation.
16. The differential coefficient of ( f ( x ) = log ( log x ) ) is
The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the. Suppose the argument of the natural log is not just \(x\), but instead is \(g(x)\), a. In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule.
Differential Equations (Definition, Types, Order, Degree, Examples)
Suppose the argument of the natural log is not just \(x\), but instead is \(g(x)\), a. The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation.
Differential Logratio spectra (Log (Io/Is)/Smooth (Log (Io/Is)) and NO
The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the. In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. Suppose the argument of the natural log is not just \(x\), but instead is \(g(x)\), a.
Fillable Online Differential Log Sheet Fax Email Print pdfFiller
Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. Suppose the argument of the natural log is not just \(x\), but instead is \(g(x)\), a. The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the. In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation.
16. The differential coefficient of ( f ( x ) = log ( log x ) ) is
Suppose the argument of the natural log is not just \(x\), but instead is \(g(x)\), a. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the.
The loglog plot of the Differential Configurational Complexity versus
In this section we will discuss logarithmic differentiation. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule. Suppose the argument of the natural log is not just \(x\), but instead is \(g(x)\), a. The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the.
In This Section We Will Discuss Logarithmic Differentiation.
The derivative of log x is 1/(x ln 10) and the derivative of log x with base a is 1/(x ln a) and the. Suppose the argument of the natural log is not just \(x\), but instead is \(g(x)\), a. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule.