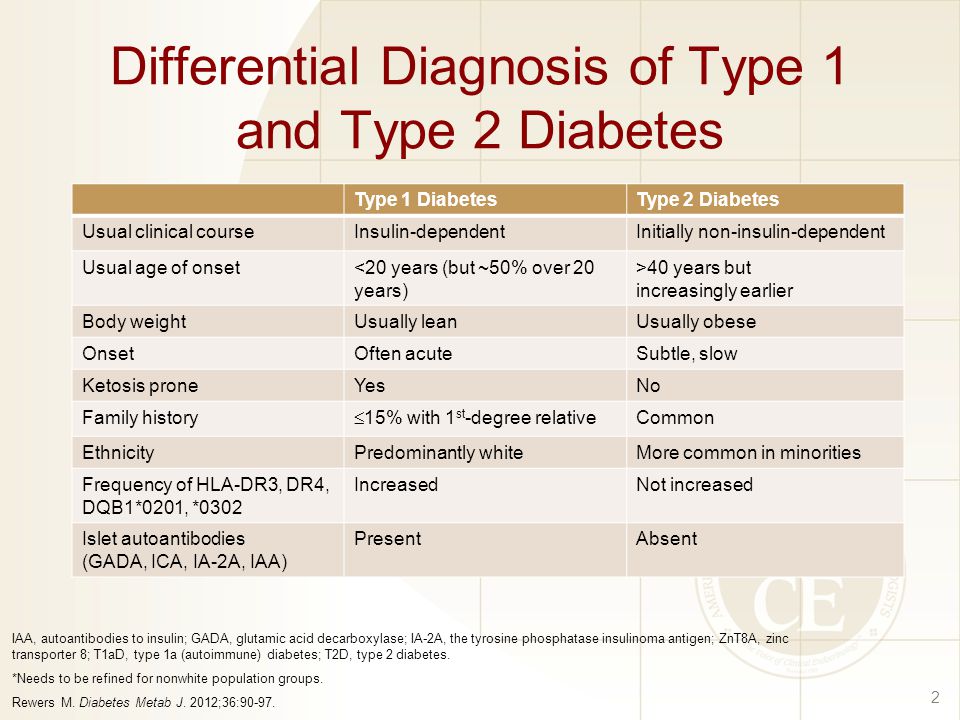
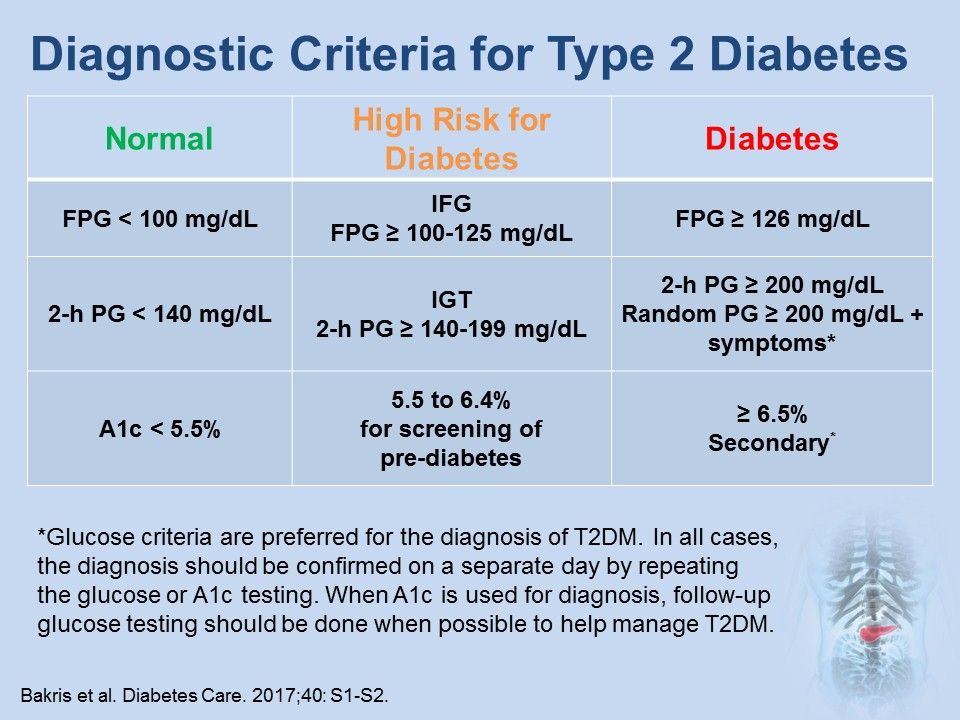
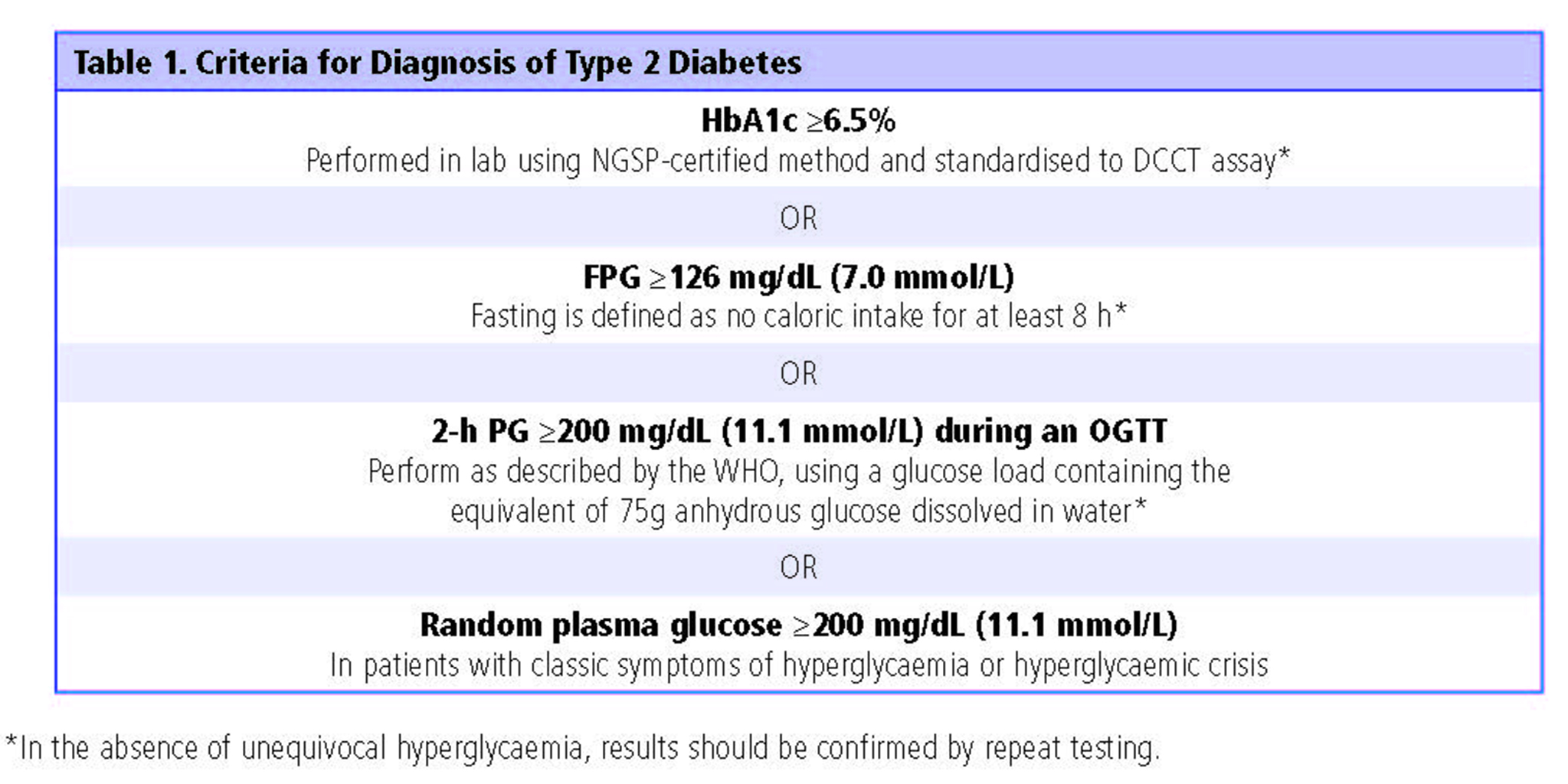
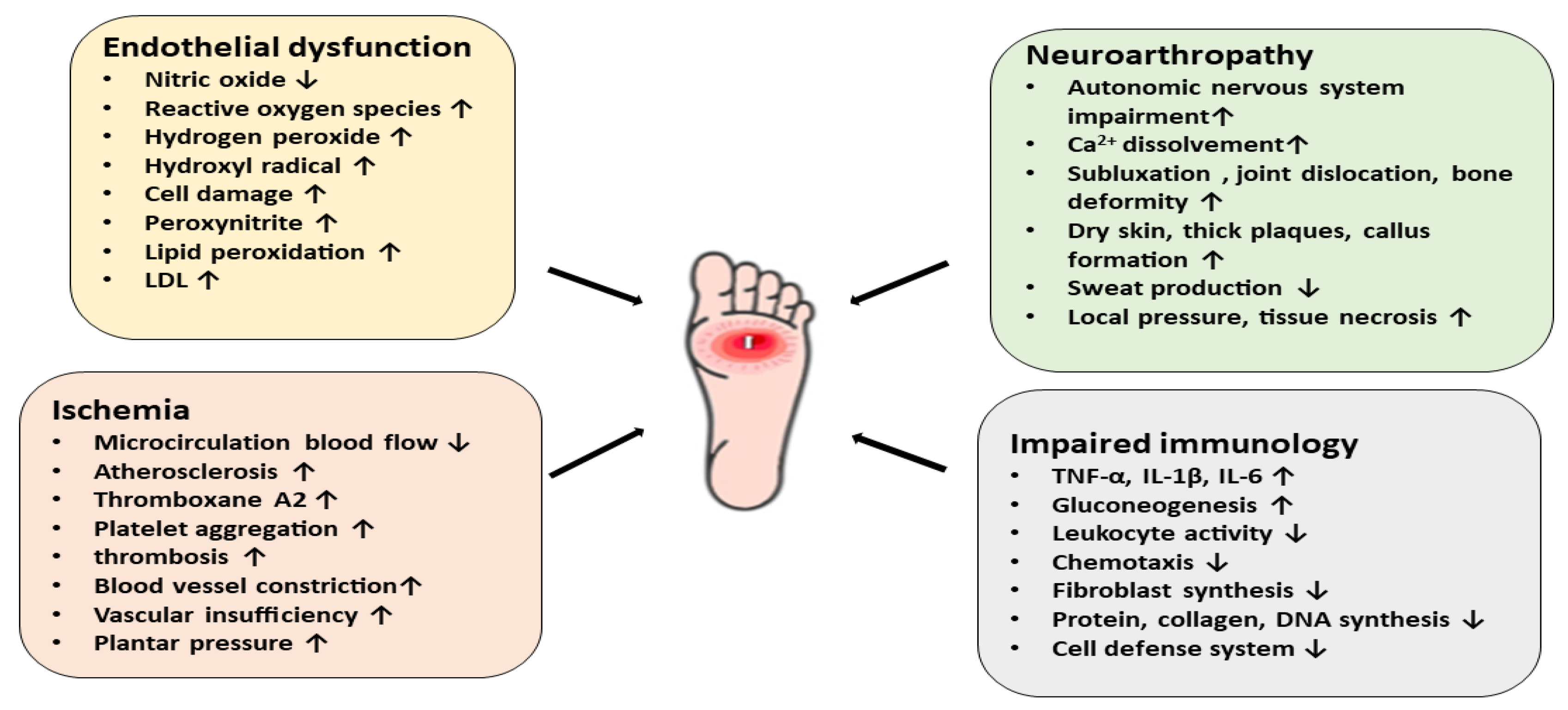
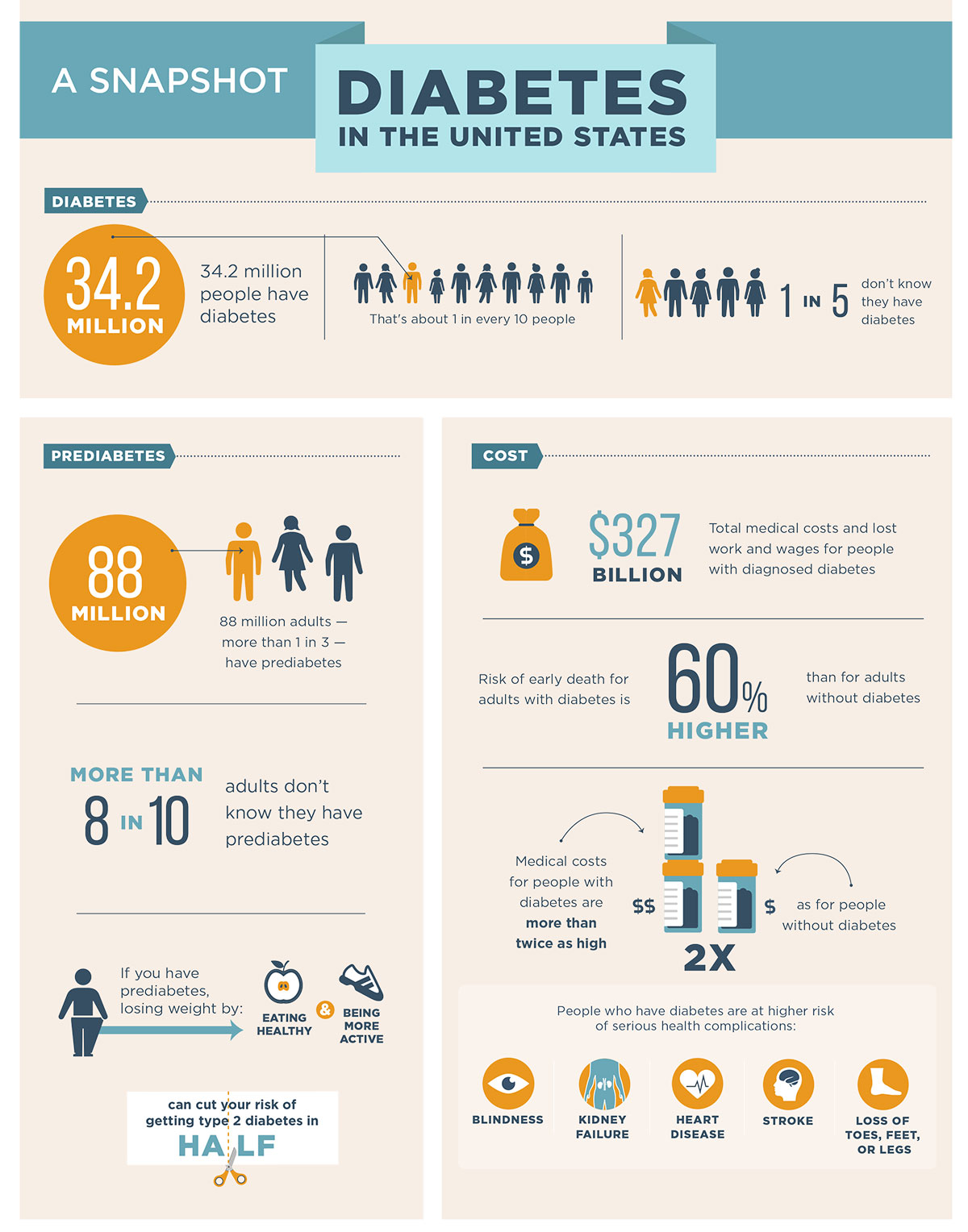
Differential Diagnosis For Type 2 Diabetes - Learn how to distinguish between diabetes mellitus type 2 and diabetes insipidus. As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%];
In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Learn how to distinguish between diabetes mellitus type 2 and diabetes insipidus. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be.
Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. Learn how to distinguish between diabetes mellitus type 2 and diabetes insipidus. As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications:
Differential Diagnosis For Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 DiabetesWalls
Learn how to distinguish between diabetes mellitus type 2 and diabetes insipidus. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical.
Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosis
Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Learn how to distinguish between diabetes mellitus type 2 and diabetes insipidus. In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%];
Type 2 Diabetes Clinical Suspicion and Diagnosis Patient Care Online
Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. Learn how to distinguish between diabetes mellitus type 2 and diabetes insipidus. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be.
6 Quick and Accurate Test for Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosis Drlogy
Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Learn how to distinguish between diabetes mellitus type 2 and diabetes insipidus. As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be.
Diagnosis Diagnosis Type 2 Diabetes
Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Learn how to distinguish between diabetes mellitus type 2 and diabetes insipidus. In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical.
Diabetes Mellitus Differential Diagnosis Hot Sex Picture
In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Learn how to distinguish between diabetes mellitus type 2 and diabetes insipidus. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%];
Differential Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus PDF Diabetes Autoimmunity
As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. Learn how to distinguish between diabetes mellitus type 2 and diabetes insipidus.
Diagnosis CARES Diabetes
As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Learn how to distinguish between diabetes mellitus type 2 and diabetes insipidus. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical.
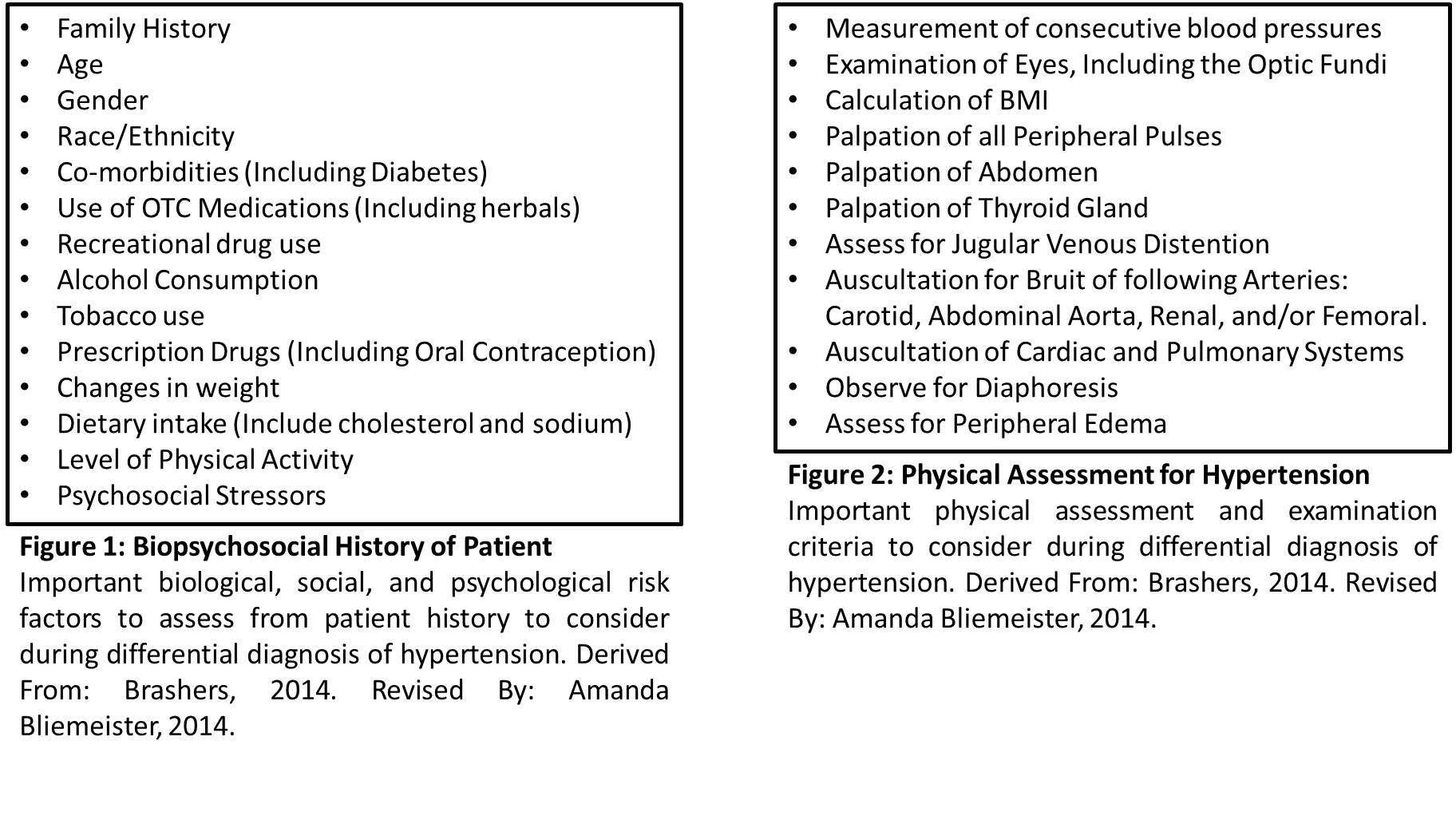
Differential Diagnoses Hypertension Case Study
Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Learn how to distinguish between diabetes mellitus type 2 and diabetes insipidus. In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications:
Type 2 Diabetes Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan
In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Learn how to distinguish between diabetes mellitus type 2 and diabetes insipidus. As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be.
Ndh Is Defined As Raised Blood Glucose Levels (Hba1C 42 To 47 Mmol/Mol [6.0% To 6.4%];
As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. Learn how to distinguish between diabetes mellitus type 2 and diabetes insipidus.