Differential Diagnosis Calf Pain - (1) there is a well localised hypoechoic collection (c). The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular. One of the common symptoms of pad is intermittent claudication, which patients will complain of pain. Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion. Serial longitudinal images of the calf:
Serial longitudinal images of the calf: Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion. One of the common symptoms of pad is intermittent claudication, which patients will complain of pain. (1) there is a well localised hypoechoic collection (c). The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular.
One of the common symptoms of pad is intermittent claudication, which patients will complain of pain. The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular. Serial longitudinal images of the calf: (1) there is a well localised hypoechoic collection (c). Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion.
Cervical Spine Differential Diagnosis Handbook Clinical Physio
Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion. (1) there is a well localised hypoechoic collection (c). Serial longitudinal images of the calf: The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular. One of the common symptoms of pad is intermittent claudication, which patients will complain of pain.
Calf Pain Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment The Healthy
One of the common symptoms of pad is intermittent claudication, which patients will complain of pain. Serial longitudinal images of the calf: The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular. (1) there is a well localised hypoechoic collection (c). Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion.
Adaptació / Adaptation Differential Diagnosis of Calf pain in athletes
The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular. One of the common symptoms of pad is intermittent claudication, which patients will complain of pain. Serial longitudinal images of the calf: Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion. (1) there is a well localised hypoechoic collection (c).
Clinical Edge Infographic Differential diagnosis of calf pain with
Serial longitudinal images of the calf: One of the common symptoms of pad is intermittent claudication, which patients will complain of pain. The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular. Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion. (1) there is a well localised hypoechoic collection (c).
Calf Pain Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment The Healthy
The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular. Serial longitudinal images of the calf: (1) there is a well localised hypoechoic collection (c). One of the common symptoms of pad is intermittent claudication, which patients will complain of pain. Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion.
Figure 1 from Differential Diagnosis of Acute Calf Pain and Swelling
The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular. (1) there is a well localised hypoechoic collection (c). One of the common symptoms of pad is intermittent claudication, which patients will complain of pain. Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion. Serial longitudinal images of the calf:
Lower Leg Pain Differential Diagnosis for Clinicians Therapy Insights
(1) there is a well localised hypoechoic collection (c). One of the common symptoms of pad is intermittent claudication, which patients will complain of pain. Serial longitudinal images of the calf: The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular. Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion.
Stream Physio Edge 065 Differential diagnosis of calf pain in runners
Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion. Serial longitudinal images of the calf: (1) there is a well localised hypoechoic collection (c). The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular. One of the common symptoms of pad is intermittent claudication, which patients will complain of pain.
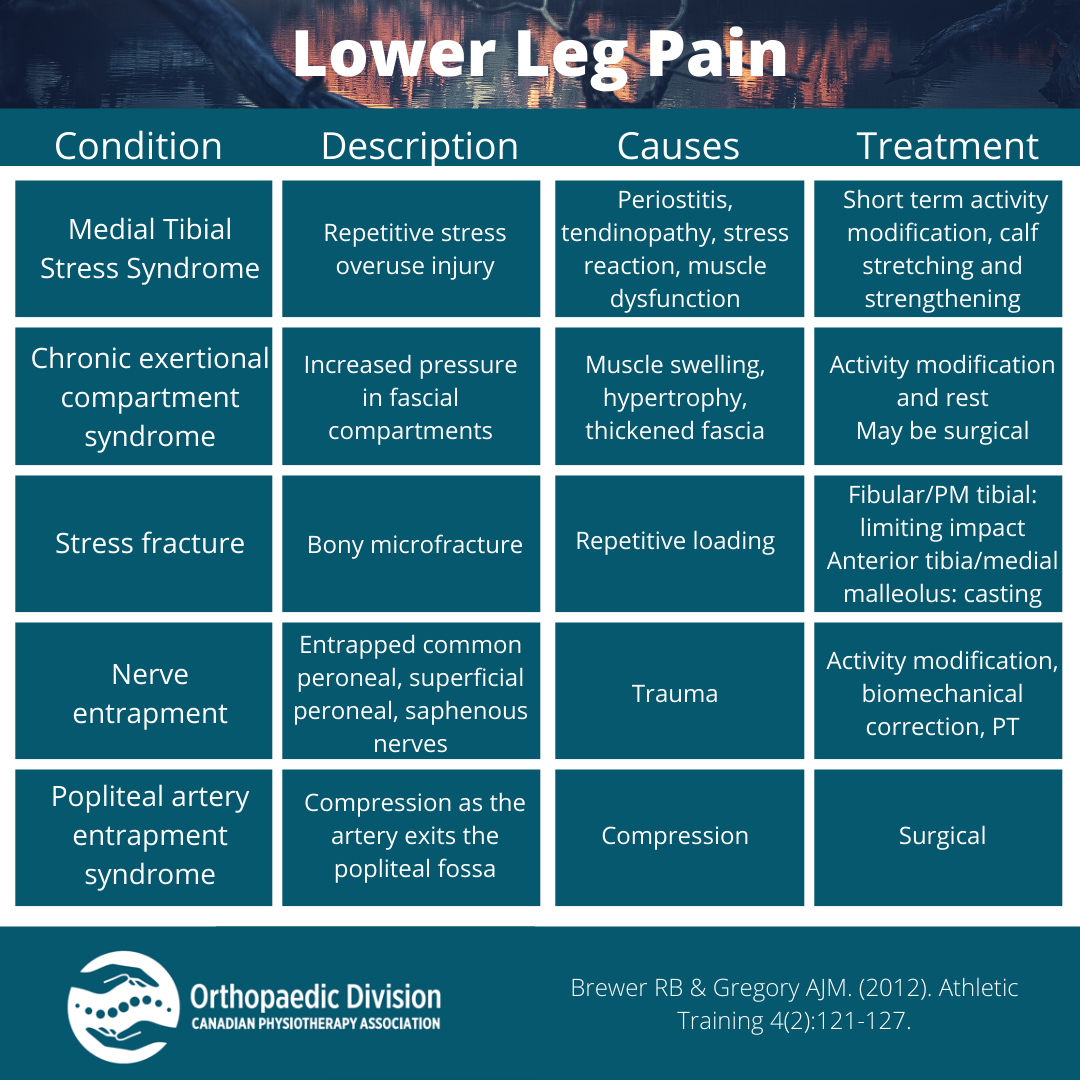
Differential Diagnosis of Lower Leg Pain National Orthopaedic
Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion. The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular. Serial longitudinal images of the calf: One of the common symptoms of pad is intermittent claudication, which patients will complain of pain. (1) there is a well localised hypoechoic collection (c).
(PDF) Differential diagnosis of calf pain by ultrasonography Marcelo
(1) there is a well localised hypoechoic collection (c). Serial longitudinal images of the calf: The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular. Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion. One of the common symptoms of pad is intermittent claudication, which patients will complain of pain.
Serial Longitudinal Images Of The Calf:
The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular. One of the common symptoms of pad is intermittent claudication, which patients will complain of pain. (1) there is a well localised hypoechoic collection (c). Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion.