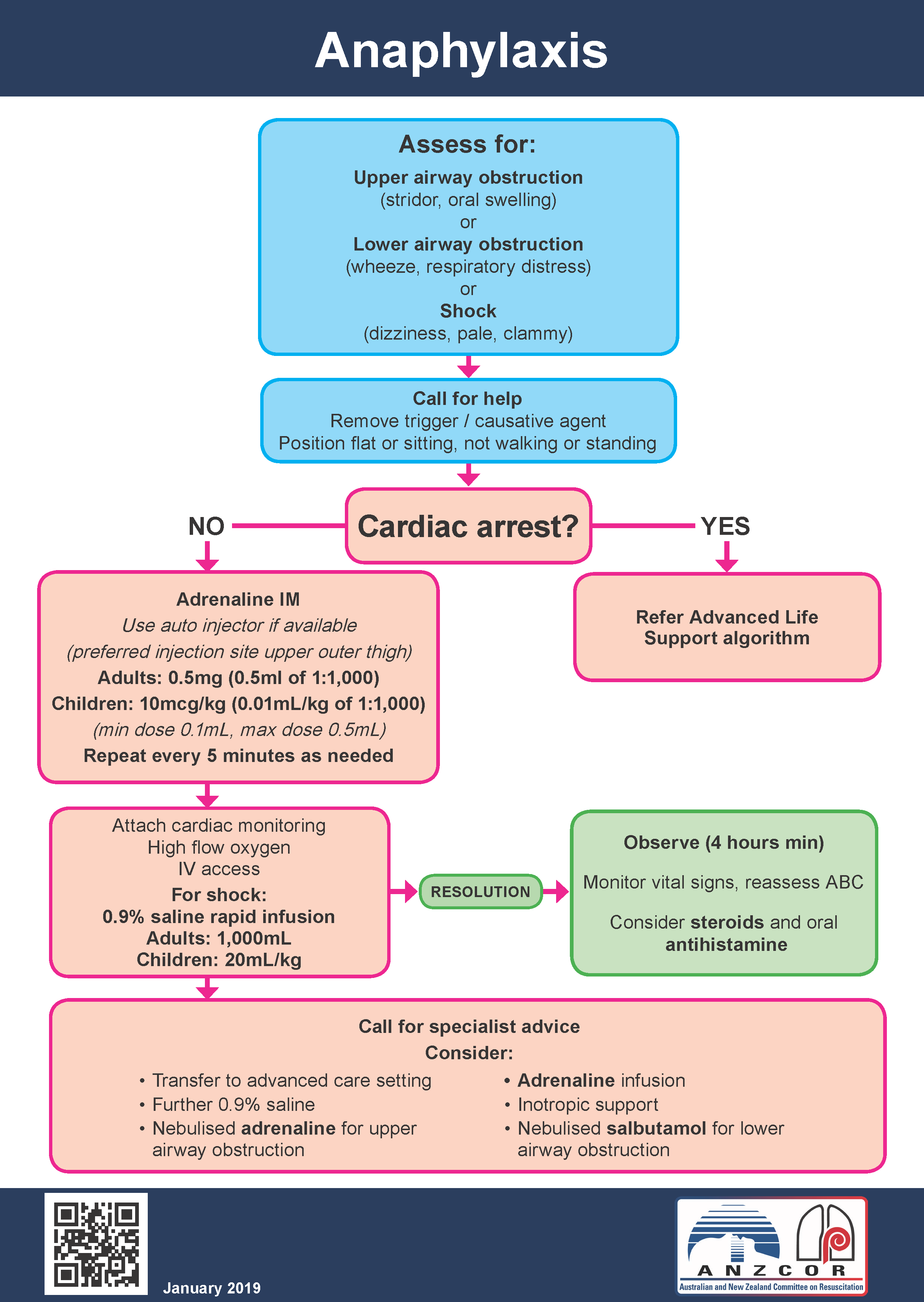
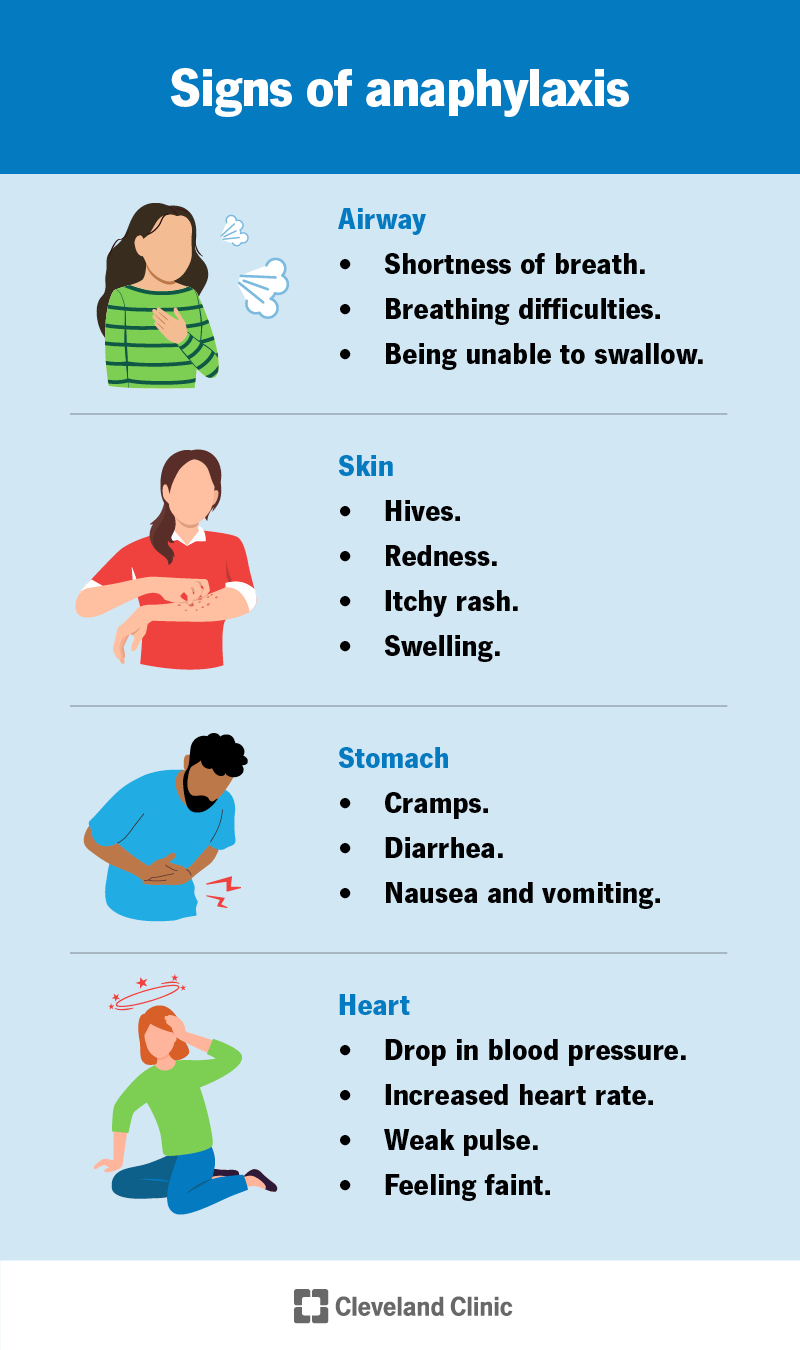
Differential Diagnosis Anaphylaxis - Infection (epiglottitis, croup, abscess), tumour, foreign body, smoke or. Differential diagnosis in practical terms, it is not necessary to differentiate between anaphylactic. The differential diagnosis of anaphylaxis in infants (ie, children under two years of age) and in. Table 4 summarizes some of the most common conditions that mimic anaphylaxis and. The clinical diagnosis of anaphylaxis is based on.
Infection (epiglottitis, croup, abscess), tumour, foreign body, smoke or. The clinical diagnosis of anaphylaxis is based on. Differential diagnosis in practical terms, it is not necessary to differentiate between anaphylactic. Table 4 summarizes some of the most common conditions that mimic anaphylaxis and. The differential diagnosis of anaphylaxis in infants (ie, children under two years of age) and in.
Table 4 summarizes some of the most common conditions that mimic anaphylaxis and. Differential diagnosis in practical terms, it is not necessary to differentiate between anaphylactic. Infection (epiglottitis, croup, abscess), tumour, foreign body, smoke or. The differential diagnosis of anaphylaxis in infants (ie, children under two years of age) and in. The clinical diagnosis of anaphylaxis is based on.
Differential diagnosis of anaphylaxis 16 Download Table
The differential diagnosis of anaphylaxis in infants (ie, children under two years of age) and in. The clinical diagnosis of anaphylaxis is based on. Differential diagnosis in practical terms, it is not necessary to differentiate between anaphylactic. Table 4 summarizes some of the most common conditions that mimic anaphylaxis and. Infection (epiglottitis, croup, abscess), tumour, foreign body, smoke or.
Differential diagnosis of anaesthesiarelated anaphylaxis Download Table
Infection (epiglottitis, croup, abscess), tumour, foreign body, smoke or. Table 4 summarizes some of the most common conditions that mimic anaphylaxis and. The clinical diagnosis of anaphylaxis is based on. Differential diagnosis in practical terms, it is not necessary to differentiate between anaphylactic. The differential diagnosis of anaphylaxis in infants (ie, children under two years of age) and in.
Anaphylaxis Symptoms Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
The differential diagnosis of anaphylaxis in infants (ie, children under two years of age) and in. The clinical diagnosis of anaphylaxis is based on. Infection (epiglottitis, croup, abscess), tumour, foreign body, smoke or. Table 4 summarizes some of the most common conditions that mimic anaphylaxis and. Differential diagnosis in practical terms, it is not necessary to differentiate between anaphylactic.
Anaphylaxis.pdf
Table 4 summarizes some of the most common conditions that mimic anaphylaxis and. The differential diagnosis of anaphylaxis in infants (ie, children under two years of age) and in. Differential diagnosis in practical terms, it is not necessary to differentiate between anaphylactic. The clinical diagnosis of anaphylaxis is based on. Infection (epiglottitis, croup, abscess), tumour, foreign body, smoke or.
Differential Diagnosis of Anaphylaxis Download Table
Infection (epiglottitis, croup, abscess), tumour, foreign body, smoke or. Differential diagnosis in practical terms, it is not necessary to differentiate between anaphylactic. Table 4 summarizes some of the most common conditions that mimic anaphylaxis and. The clinical diagnosis of anaphylaxis is based on. The differential diagnosis of anaphylaxis in infants (ie, children under two years of age) and in.
Anaphylaxis
Table 4 summarizes some of the most common conditions that mimic anaphylaxis and. The clinical diagnosis of anaphylaxis is based on. Differential diagnosis in practical terms, it is not necessary to differentiate between anaphylactic. Infection (epiglottitis, croup, abscess), tumour, foreign body, smoke or. The differential diagnosis of anaphylaxis in infants (ie, children under two years of age) and in.
Differential diagnosis of anaphylaxis 16 Download Table
The differential diagnosis of anaphylaxis in infants (ie, children under two years of age) and in. Table 4 summarizes some of the most common conditions that mimic anaphylaxis and. The clinical diagnosis of anaphylaxis is based on. Differential diagnosis in practical terms, it is not necessary to differentiate between anaphylactic. Infection (epiglottitis, croup, abscess), tumour, foreign body, smoke or.
Anaphylaxisb Allergy Medik
Differential diagnosis in practical terms, it is not necessary to differentiate between anaphylactic. The clinical diagnosis of anaphylaxis is based on. Table 4 summarizes some of the most common conditions that mimic anaphylaxis and. Infection (epiglottitis, croup, abscess), tumour, foreign body, smoke or. The differential diagnosis of anaphylaxis in infants (ie, children under two years of age) and in.
(PDF) Algorithm of differential diagnosis for anaphylaxis
The clinical diagnosis of anaphylaxis is based on. Infection (epiglottitis, croup, abscess), tumour, foreign body, smoke or. Differential diagnosis in practical terms, it is not necessary to differentiate between anaphylactic. Table 4 summarizes some of the most common conditions that mimic anaphylaxis and. The differential diagnosis of anaphylaxis in infants (ie, children under two years of age) and in.
Anaphylaxis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis Treatment, 50 OFF
The differential diagnosis of anaphylaxis in infants (ie, children under two years of age) and in. Table 4 summarizes some of the most common conditions that mimic anaphylaxis and. The clinical diagnosis of anaphylaxis is based on. Infection (epiglottitis, croup, abscess), tumour, foreign body, smoke or. Differential diagnosis in practical terms, it is not necessary to differentiate between anaphylactic.
Differential Diagnosis In Practical Terms, It Is Not Necessary To Differentiate Between Anaphylactic.
The differential diagnosis of anaphylaxis in infants (ie, children under two years of age) and in. The clinical diagnosis of anaphylaxis is based on. Table 4 summarizes some of the most common conditions that mimic anaphylaxis and. Infection (epiglottitis, croup, abscess), tumour, foreign body, smoke or.