Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Differential Diagnosis - Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Type 2 diabetes mellitus consists of an array of dysfunctions characterized by. What is the differential diagnosis of diabetes? How would you frame the differential? Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include:
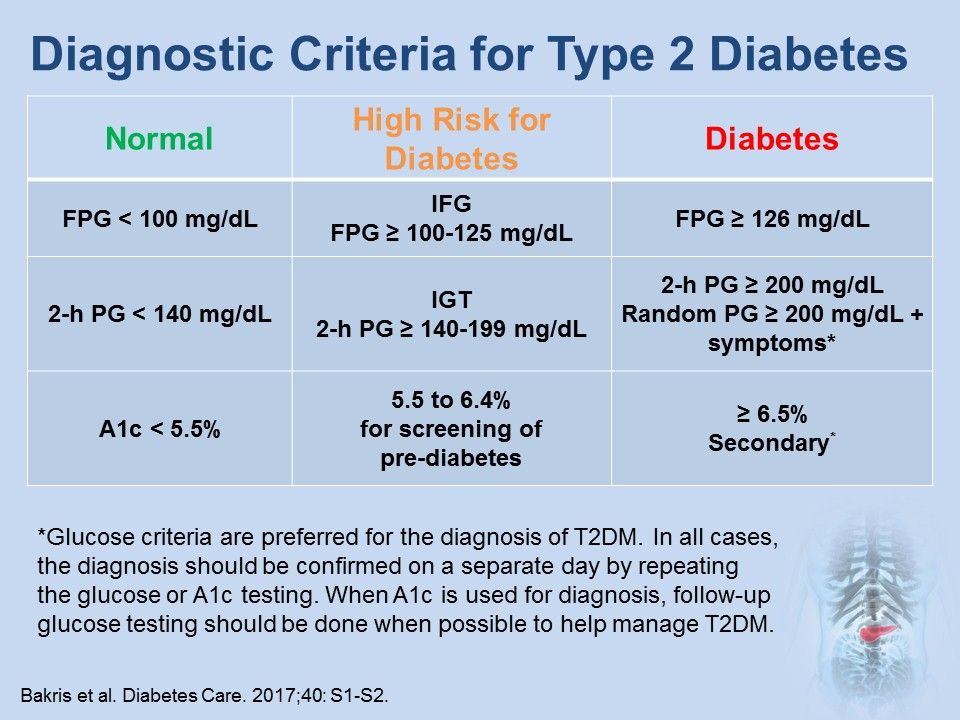
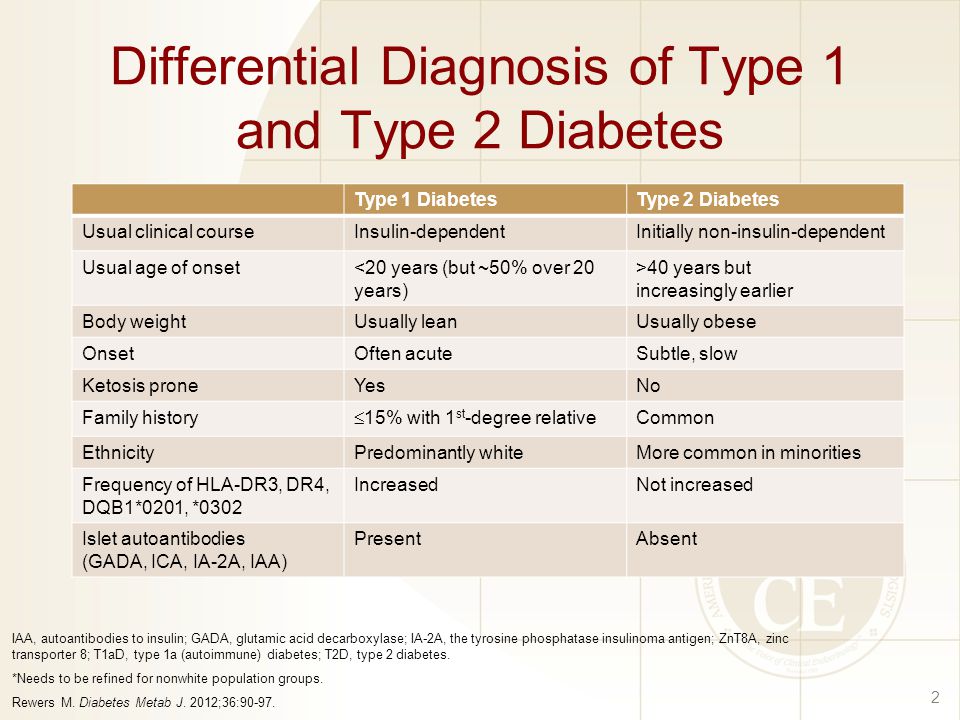
Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: How would you frame the differential? Type 2 diabetes mellitus consists of an array of dysfunctions characterized by. Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. What is the differential diagnosis of diabetes?
Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; What is the differential diagnosis of diabetes? Type 2 diabetes mellitus consists of an array of dysfunctions characterized by. How would you frame the differential? Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications:
(PDF) The question of differential diagnosis of anemia in diabetes mellitus
How would you frame the differential? Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Type 2 diabetes mellitus consists of an array of dysfunctions characterized by. Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. What is the differential diagnosis of diabetes?
Type 2 Diabetes Clinical Suspicion and Diagnosis Patient Care Online
Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: What is the differential diagnosis of diabetes? Type 2 diabetes mellitus consists of an array of dysfunctions characterized by. Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include:
Diagnosis Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 in the Medical Form Stock Image
Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: Type 2 diabetes mellitus consists of an array of dysfunctions characterized by. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%];
Differential Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus PDF Diabetes Autoimmunity
Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: How would you frame the differential? Type 2 diabetes mellitus consists of an array of dysfunctions characterized by. Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: What is the differential diagnosis of diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus (Type 2) Clinical sciences Osmosis Video Library
Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; How would you frame the differential? Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific.
Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
How would you frame the differential? Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: What is the differential diagnosis of diabetes? Type 2 diabetes mellitus consists of an array of dysfunctions characterized by. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%];
Differential Diagnosis For Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 DiabetesWalls
Type 2 diabetes mellitus consists of an array of dysfunctions characterized by. Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. How would you frame the differential? Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include:
Diabetes Mellitus Differential Diagnosis Hot Sex Picture
How would you frame the differential? Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: Type 2 diabetes mellitus consists of an array of dysfunctions characterized by. Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%];
Differential Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus Nursing CE Central
Type 2 diabetes mellitus consists of an array of dysfunctions characterized by. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: How would you frame the differential? Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific.
Blood Sugar Guide Complete diabetes mellitus diagnosis treatment
What is the differential diagnosis of diabetes? Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; How would you frame the differential? Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. Type 2 diabetes mellitus consists of an array of dysfunctions characterized by.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Consists Of An Array Of Dysfunctions Characterized By.
Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; What is the differential diagnosis of diabetes? Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications:
How Would You Frame The Differential?
Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: