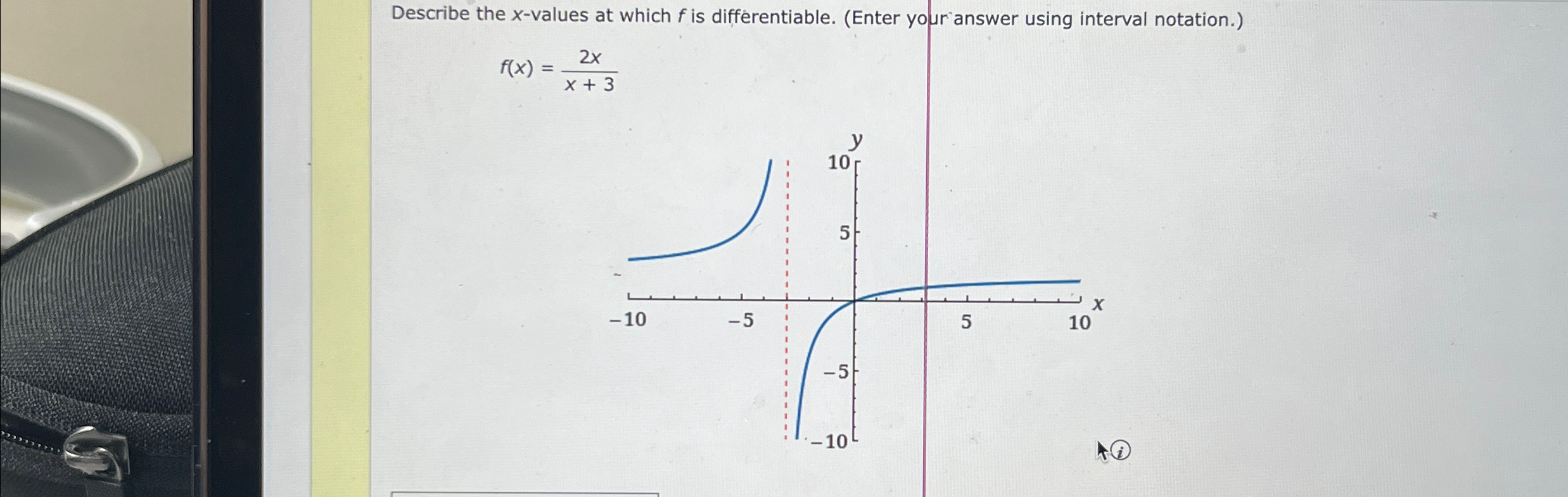
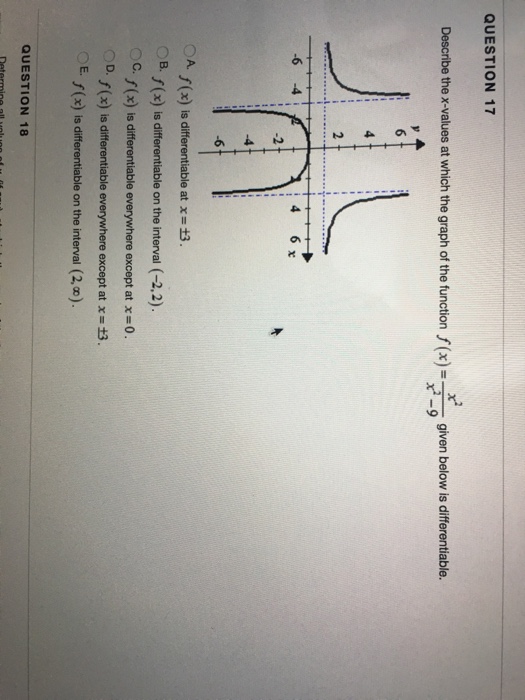
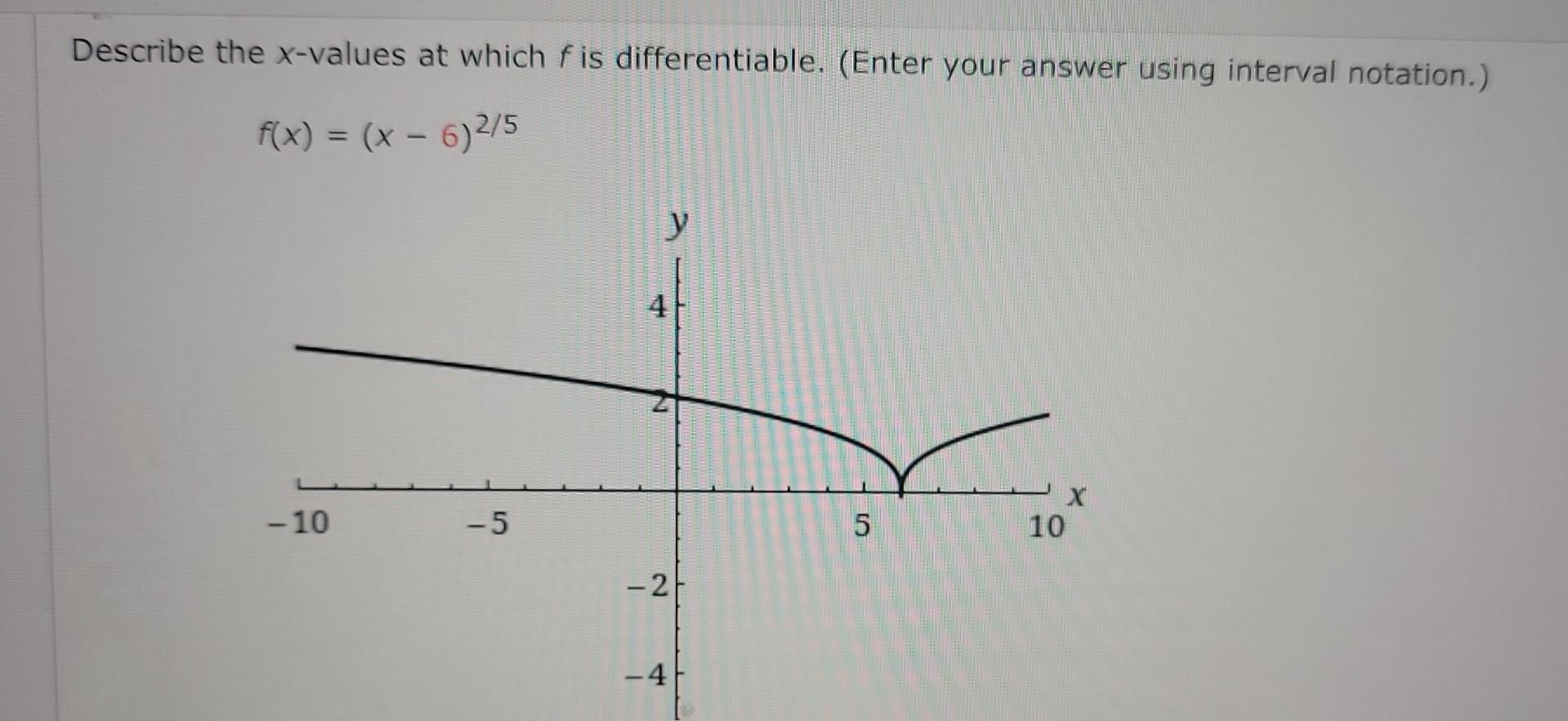
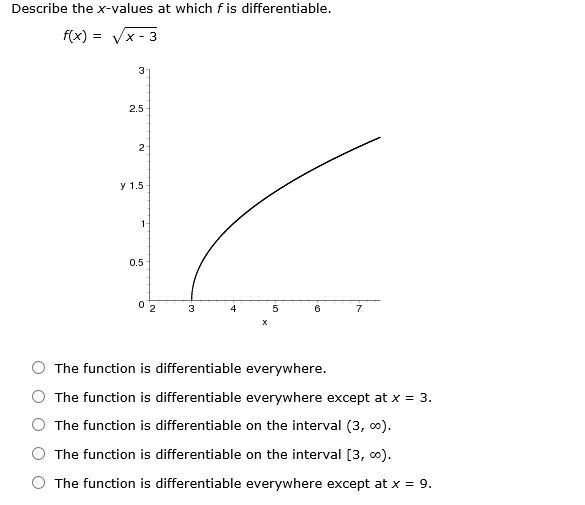
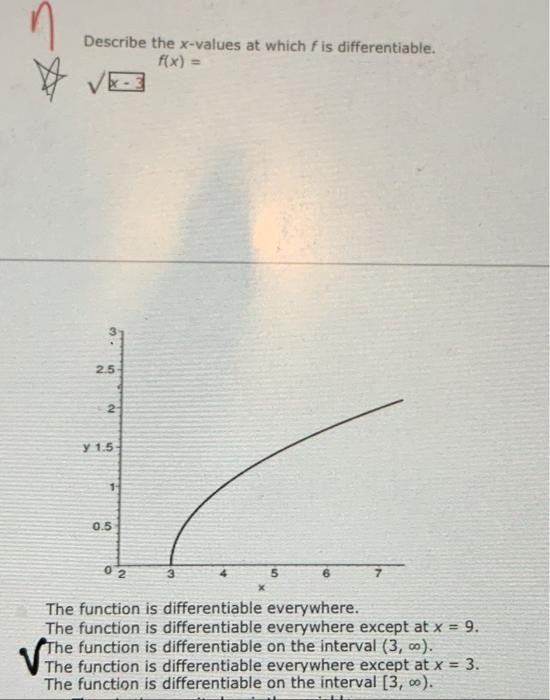
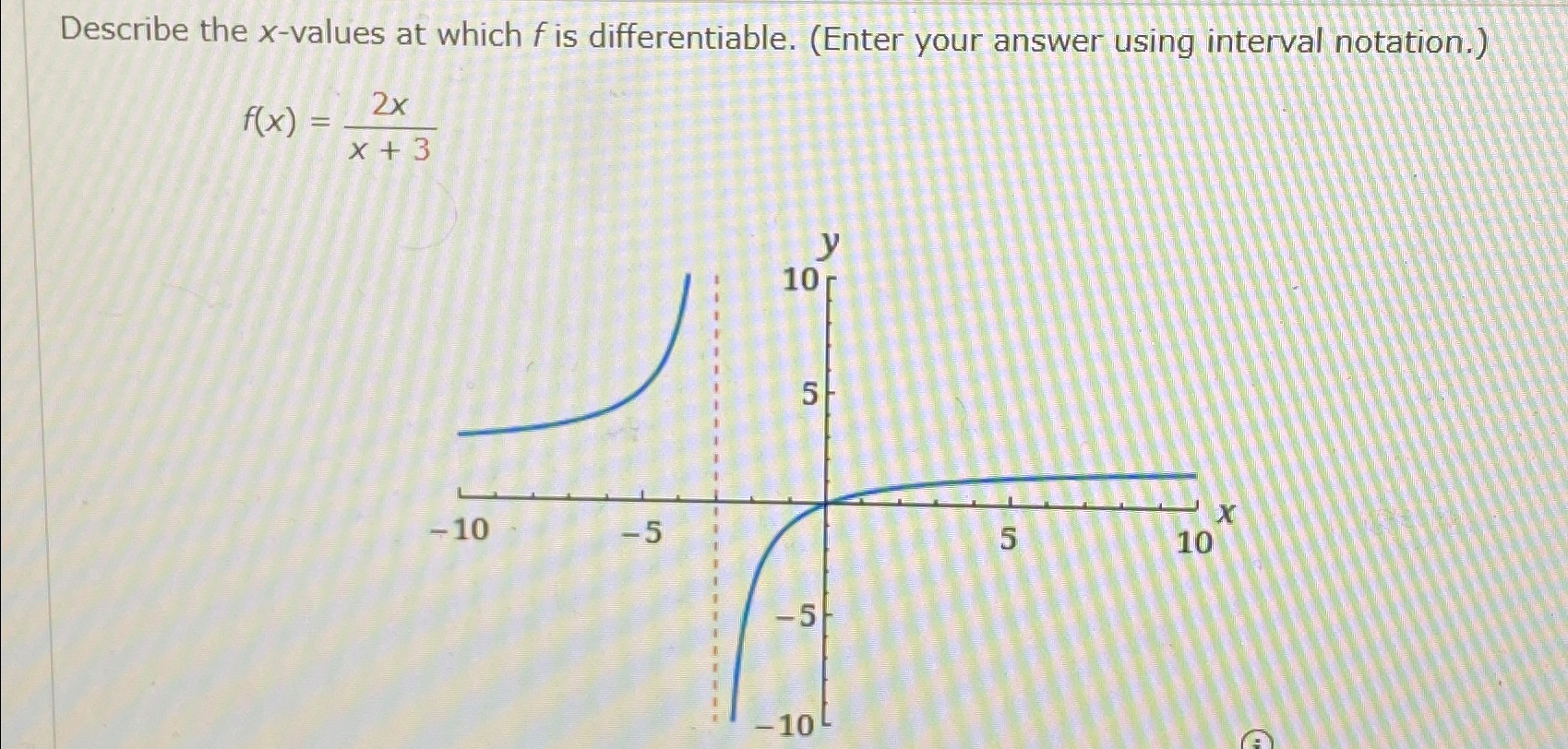
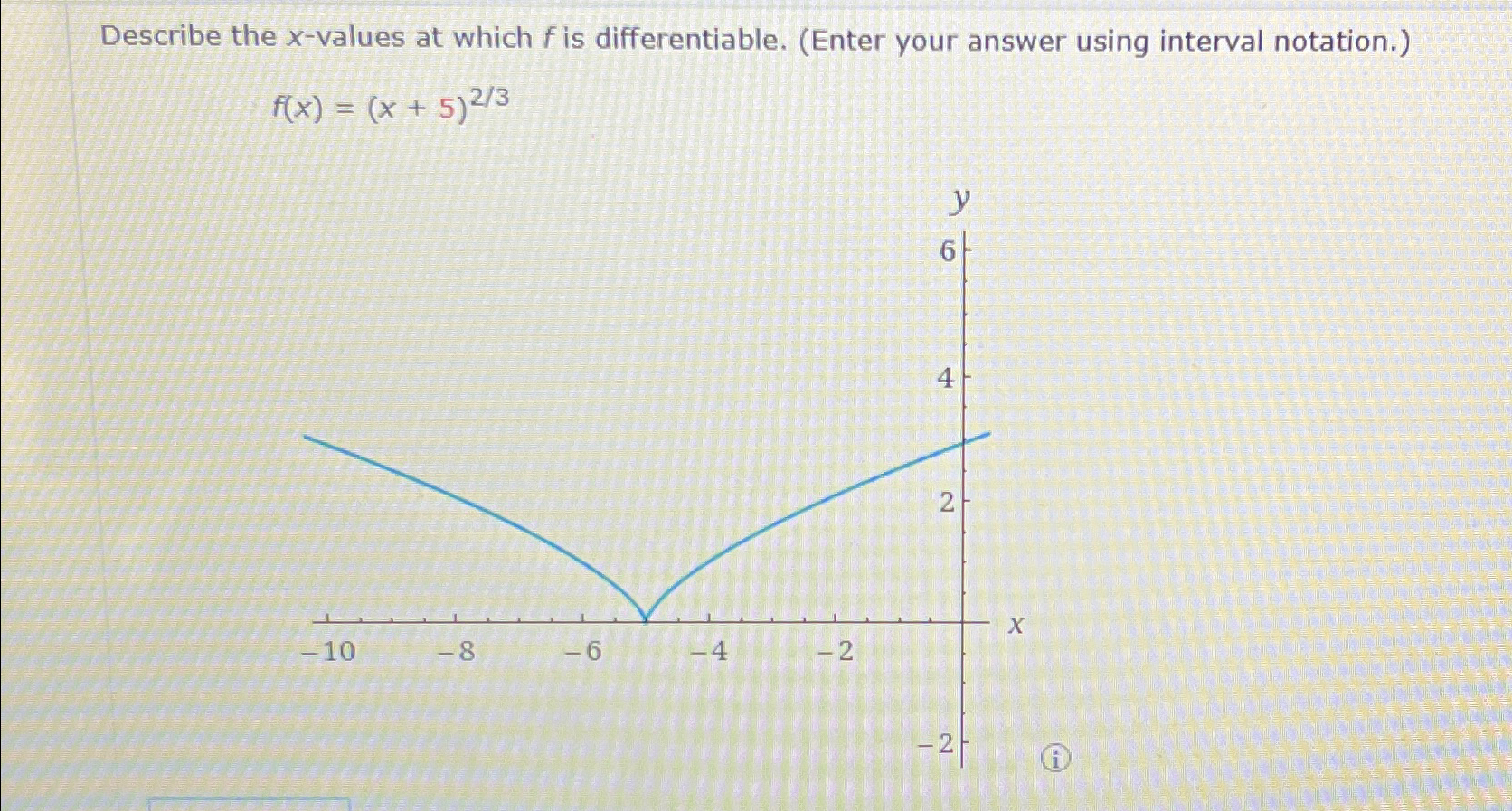
Describe The X Values At Which F Is Differentiable - Here, derivative does not exist. To see where f is differentiable, we have to take the derivative of the function. Since the derivative (x − 3) − 1 / 3 is defined for all real values of x, therefore the given function f (x).
To see where f is differentiable, we have to take the derivative of the function. Since the derivative (x − 3) − 1 / 3 is defined for all real values of x, therefore the given function f (x). Here, derivative does not exist.
Here, derivative does not exist. Since the derivative (x − 3) − 1 / 3 is defined for all real values of x, therefore the given function f (x). To see where f is differentiable, we have to take the derivative of the function.
Solved Describe the xvalues at which f is differentiable.
To see where f is differentiable, we have to take the derivative of the function. Since the derivative (x − 3) − 1 / 3 is defined for all real values of x, therefore the given function f (x). Here, derivative does not exist.
Solved Describe the xvalues at which the graph of the
To see where f is differentiable, we have to take the derivative of the function. Here, derivative does not exist. Since the derivative (x − 3) − 1 / 3 is defined for all real values of x, therefore the given function f (x).
Solved Describe the xvalues at which f is differentiable.
To see where f is differentiable, we have to take the derivative of the function. Here, derivative does not exist. Since the derivative (x − 3) − 1 / 3 is defined for all real values of x, therefore the given function f (x).
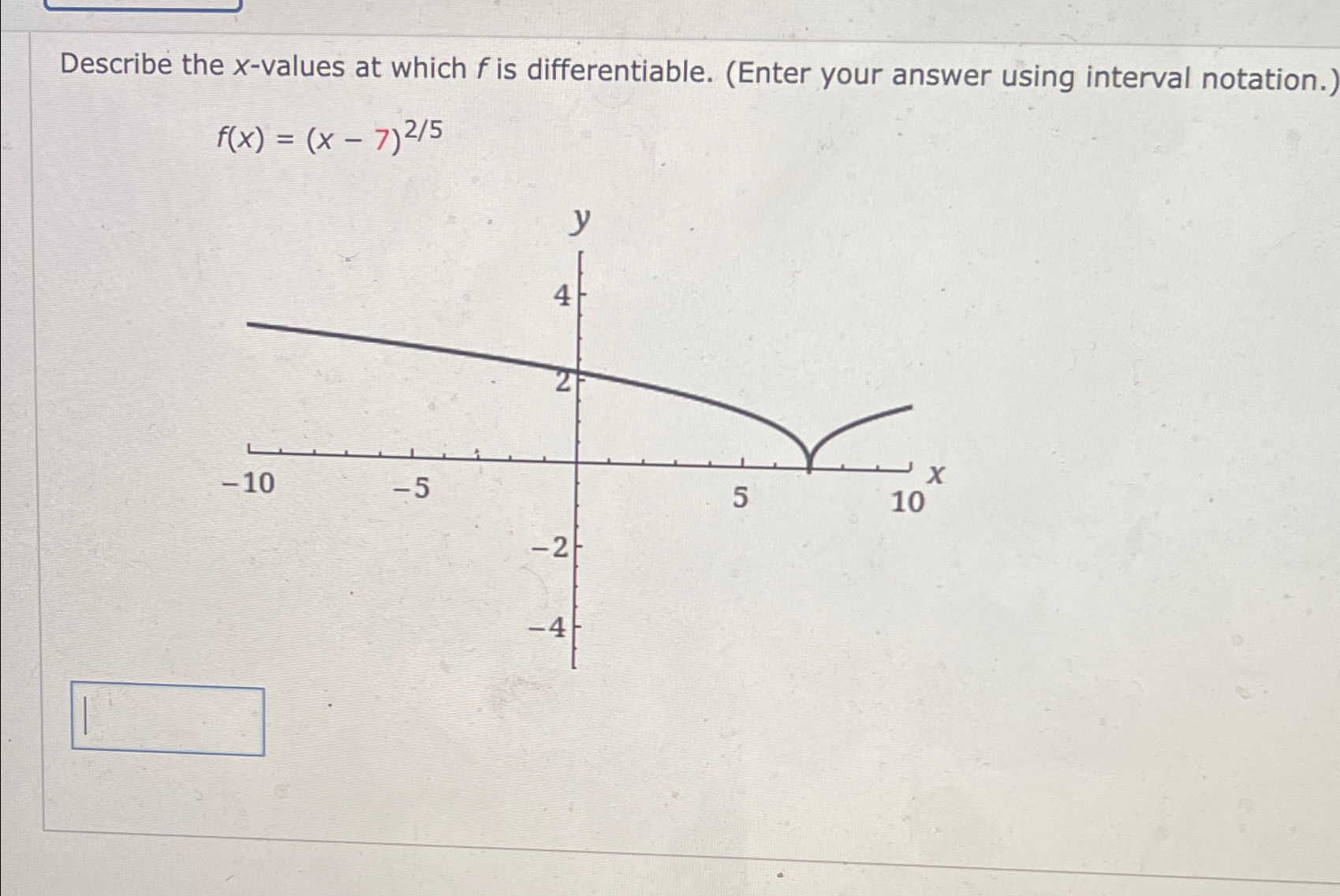
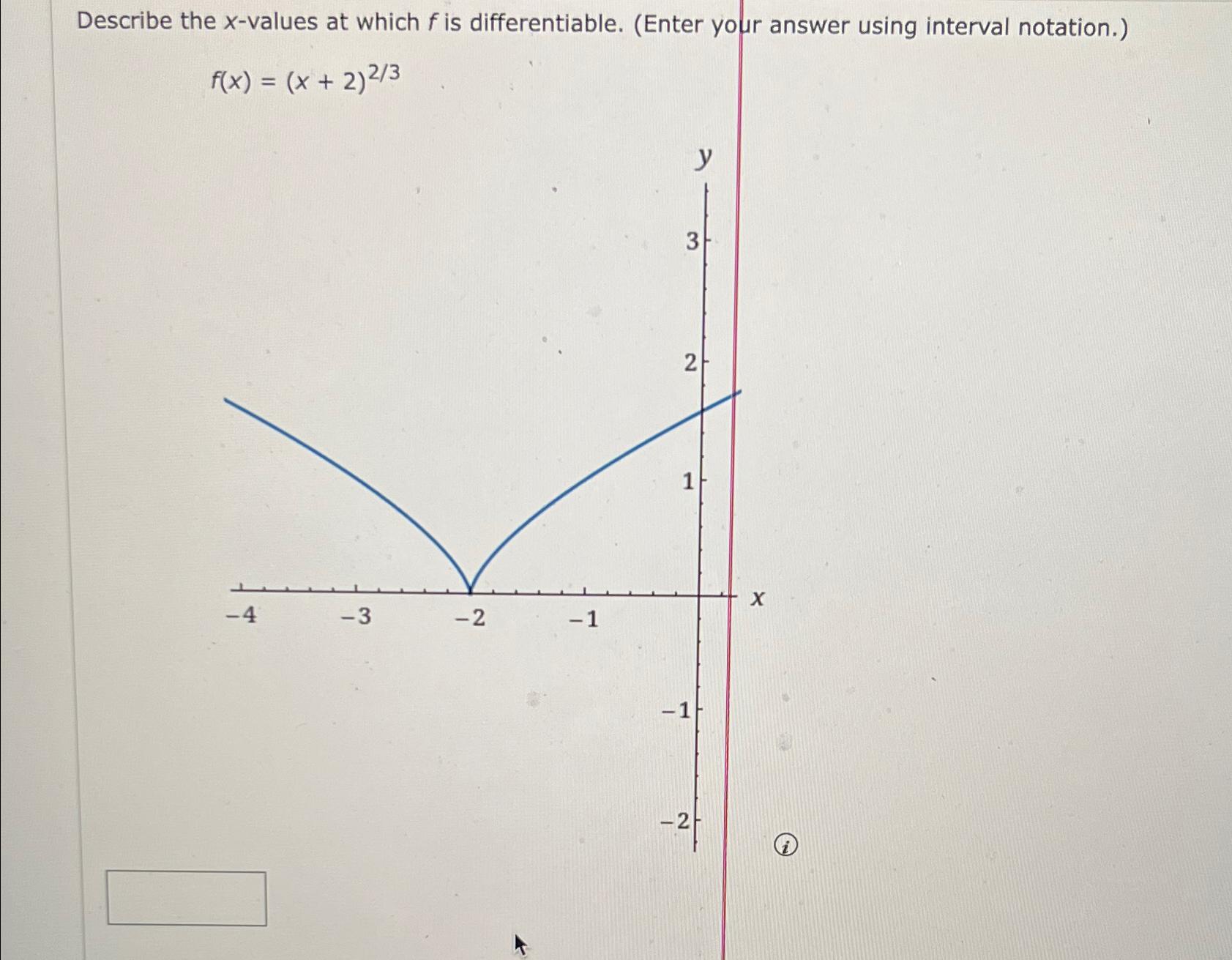
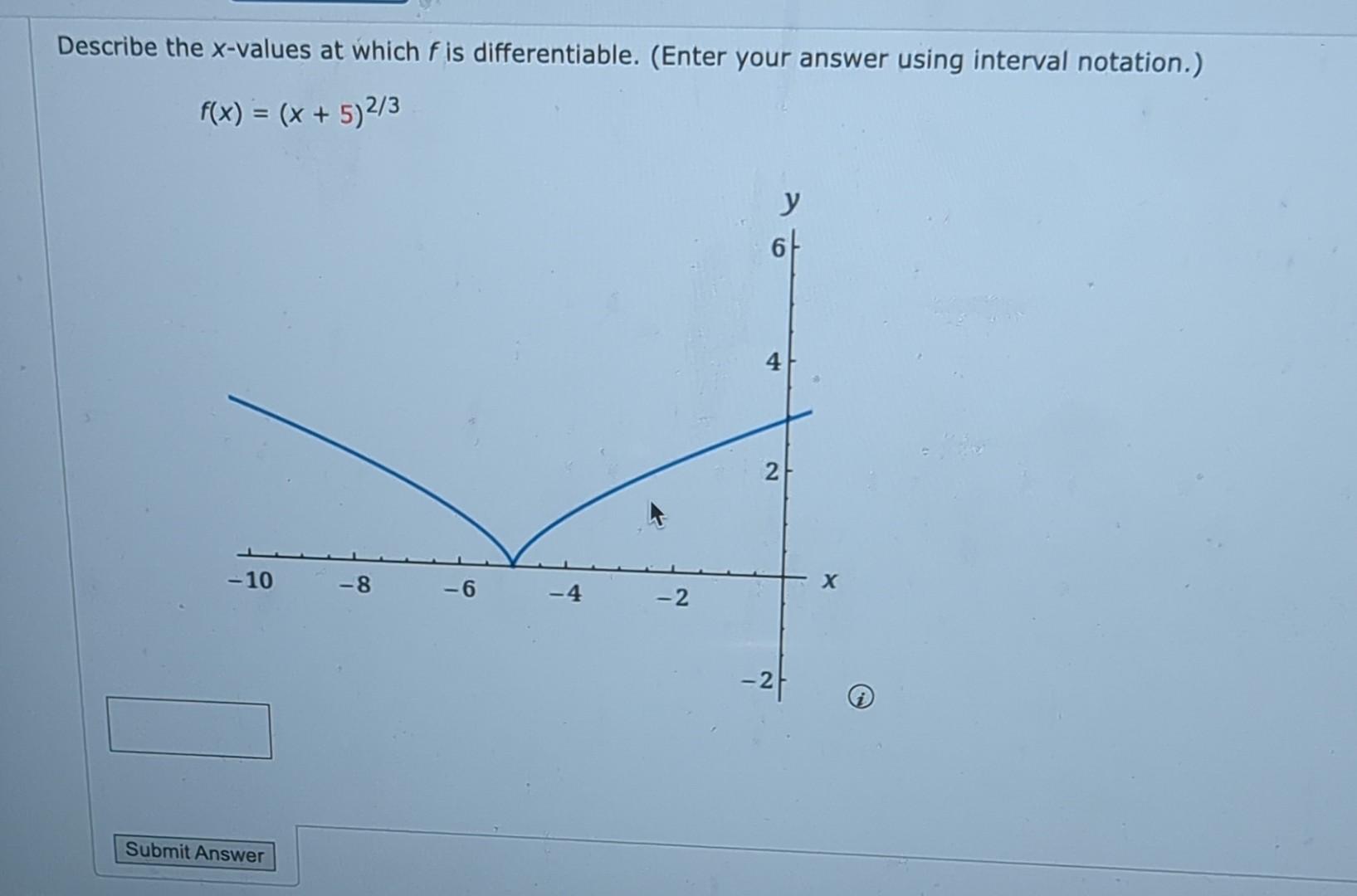
Solved Describe the xvalues at which f is differentiable.
To see where f is differentiable, we have to take the derivative of the function. Since the derivative (x − 3) − 1 / 3 is defined for all real values of x, therefore the given function f (x). Here, derivative does not exist.
Solved Describe the xvalues at which f is differentiable.
To see where f is differentiable, we have to take the derivative of the function. Here, derivative does not exist. Since the derivative (x − 3) − 1 / 3 is defined for all real values of x, therefore the given function f (x).
Solved Describe the xvalues at which f is differentiable.
Since the derivative (x − 3) − 1 / 3 is defined for all real values of x, therefore the given function f (x). To see where f is differentiable, we have to take the derivative of the function. Here, derivative does not exist.
Solved Describe the xvalues at which f is differentiable.
Since the derivative (x − 3) − 1 / 3 is defined for all real values of x, therefore the given function f (x). Here, derivative does not exist. To see where f is differentiable, we have to take the derivative of the function.
Solved Describe the xvalues at which f is differentiable.
Here, derivative does not exist. Since the derivative (x − 3) − 1 / 3 is defined for all real values of x, therefore the given function f (x). To see where f is differentiable, we have to take the derivative of the function.
Solved Describe the xvalues at which f is differentiable.
Here, derivative does not exist. To see where f is differentiable, we have to take the derivative of the function. Since the derivative (x − 3) − 1 / 3 is defined for all real values of x, therefore the given function f (x).
Here, Derivative Does Not Exist.
To see where f is differentiable, we have to take the derivative of the function. Since the derivative (x − 3) − 1 / 3 is defined for all real values of x, therefore the given function f (x).