Define Differential Reproduction - Differential reproduction refers to the process of selective breeding of plants and animals, where. Differential reproductive success consists of a statistical analysis of the outcome. The process in nature by which, according to darwin's theory of evolution, organisms that are. A situation in which some individuals leave more offspring in the next generation than do others,. Since the environment can’t support unlimited population. A general term for a shift in the frequency of a gene’s allelic variants within a population over.
The process in nature by which, according to darwin's theory of evolution, organisms that are. Since the environment can’t support unlimited population. Differential reproduction refers to the process of selective breeding of plants and animals, where. A situation in which some individuals leave more offspring in the next generation than do others,. A general term for a shift in the frequency of a gene’s allelic variants within a population over. Differential reproductive success consists of a statistical analysis of the outcome.
A general term for a shift in the frequency of a gene’s allelic variants within a population over. Since the environment can’t support unlimited population. A situation in which some individuals leave more offspring in the next generation than do others,. Differential reproduction refers to the process of selective breeding of plants and animals, where. The process in nature by which, according to darwin's theory of evolution, organisms that are. Differential reproductive success consists of a statistical analysis of the outcome.
Differential Reproductive Success in the Science of Evolution
Differential reproduction refers to the process of selective breeding of plants and animals, where. Differential reproductive success consists of a statistical analysis of the outcome. A general term for a shift in the frequency of a gene’s allelic variants within a population over. A situation in which some individuals leave more offspring in the next generation than do others,. Since.
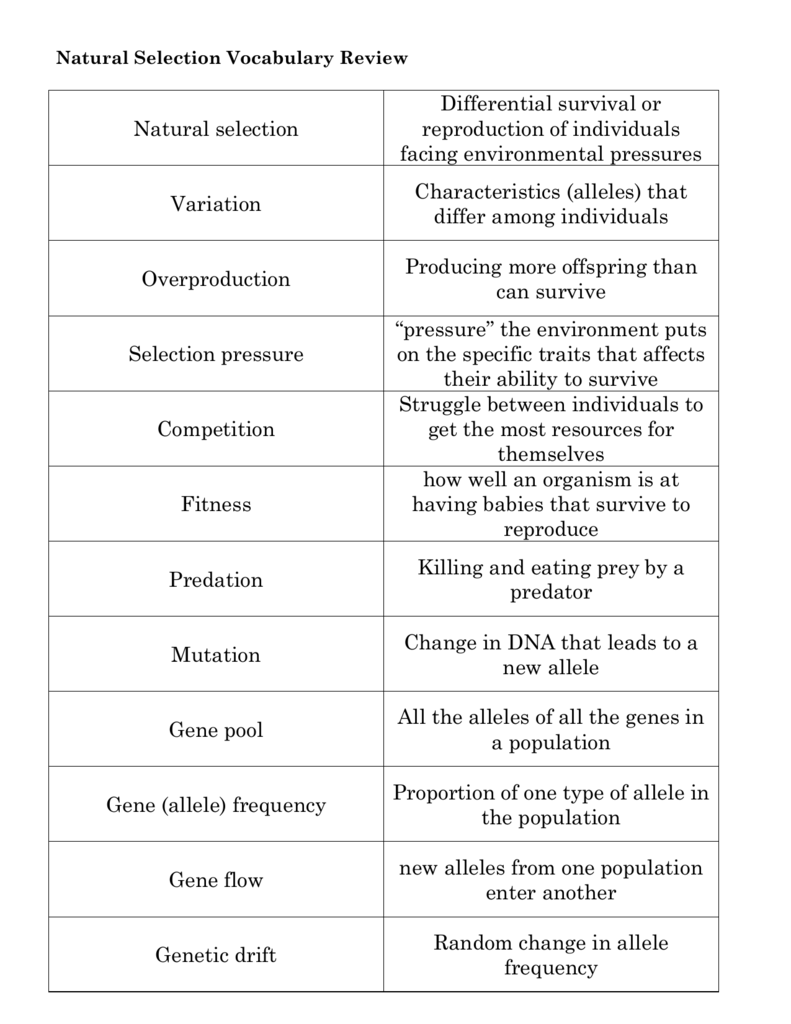
Natural selection Differential survival or reproduction of individuals
A situation in which some individuals leave more offspring in the next generation than do others,. A general term for a shift in the frequency of a gene’s allelic variants within a population over. Since the environment can’t support unlimited population. Differential reproduction refers to the process of selective breeding of plants and animals, where. Differential reproductive success consists of.
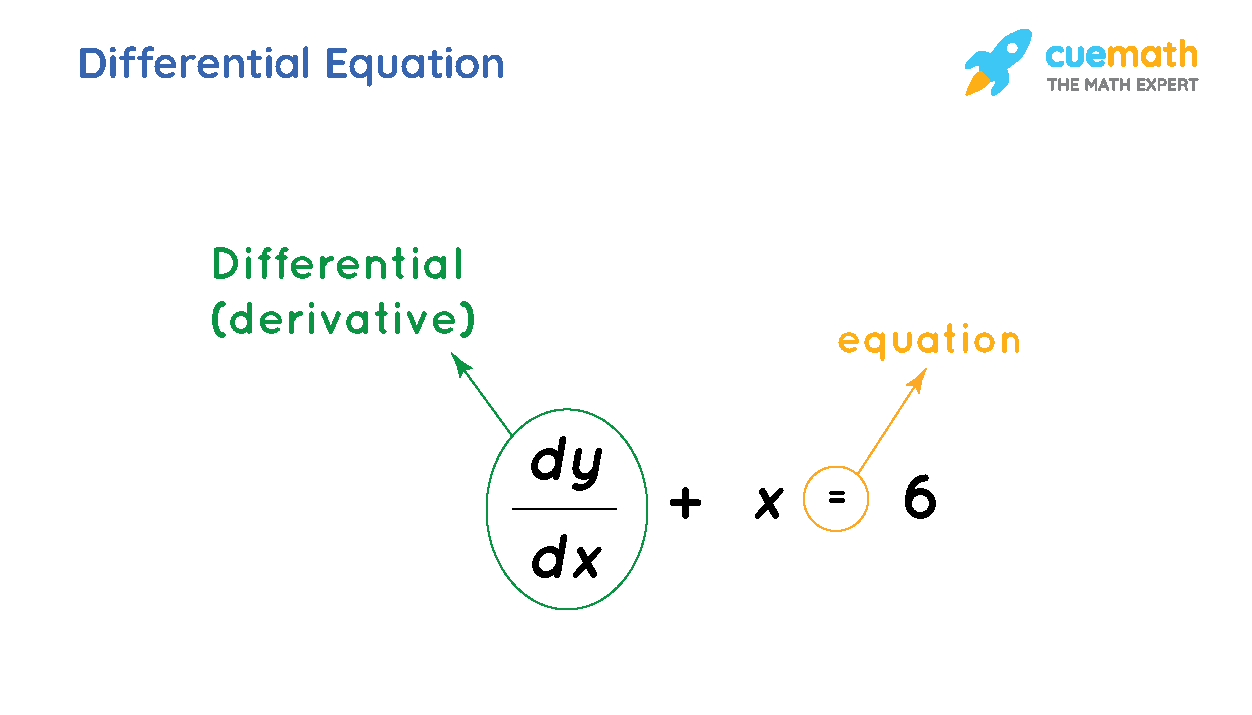
Differential Equations Definition, Types, Order, Examples
The process in nature by which, according to darwin's theory of evolution, organisms that are. Differential reproductive success consists of a statistical analysis of the outcome. Differential reproduction refers to the process of selective breeding of plants and animals, where. A general term for a shift in the frequency of a gene’s allelic variants within a population over. A situation.
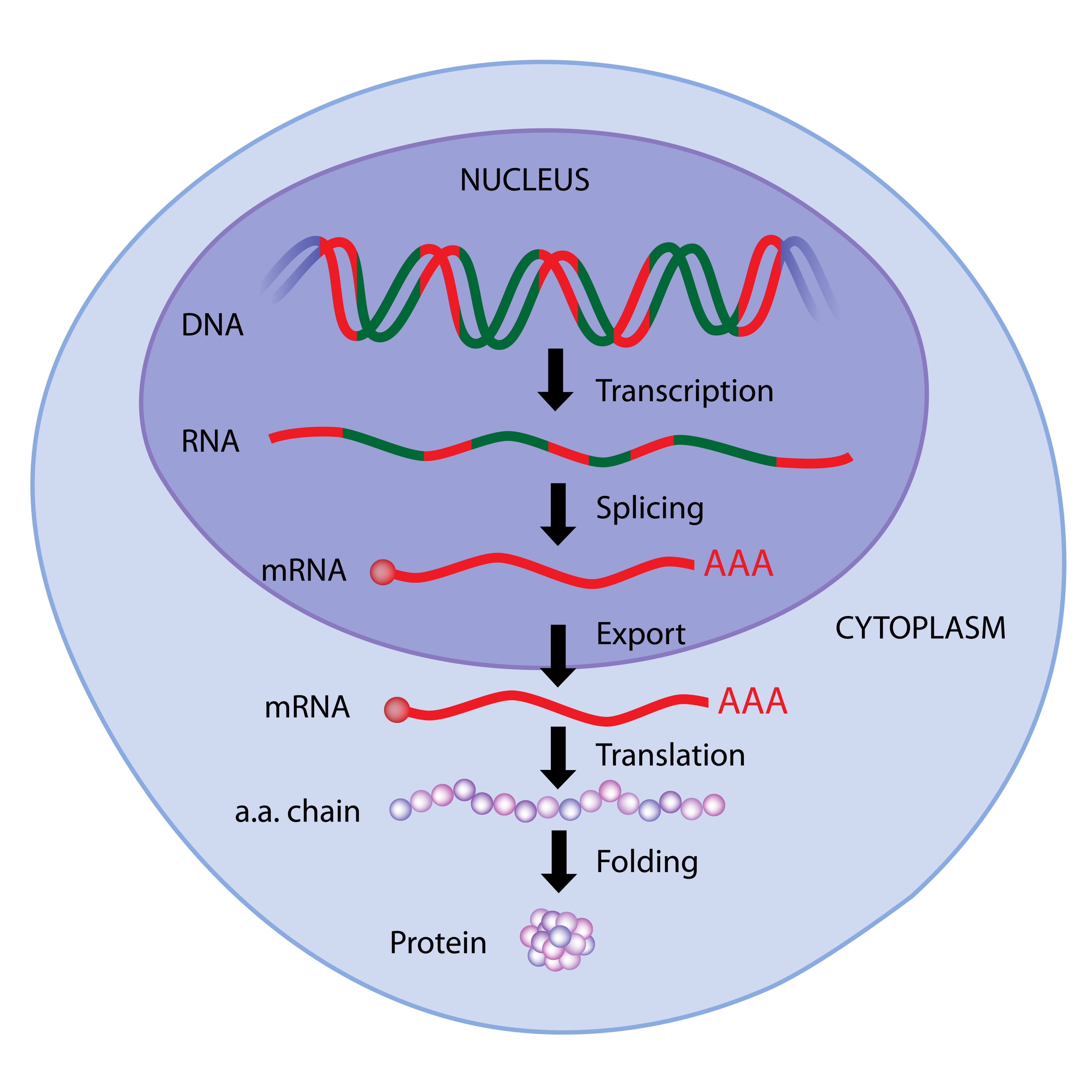
Differential Gene Expression — EducationHQ
A general term for a shift in the frequency of a gene’s allelic variants within a population over. A situation in which some individuals leave more offspring in the next generation than do others,. Since the environment can’t support unlimited population. The process in nature by which, according to darwin's theory of evolution, organisms that are. Differential reproductive success consists.
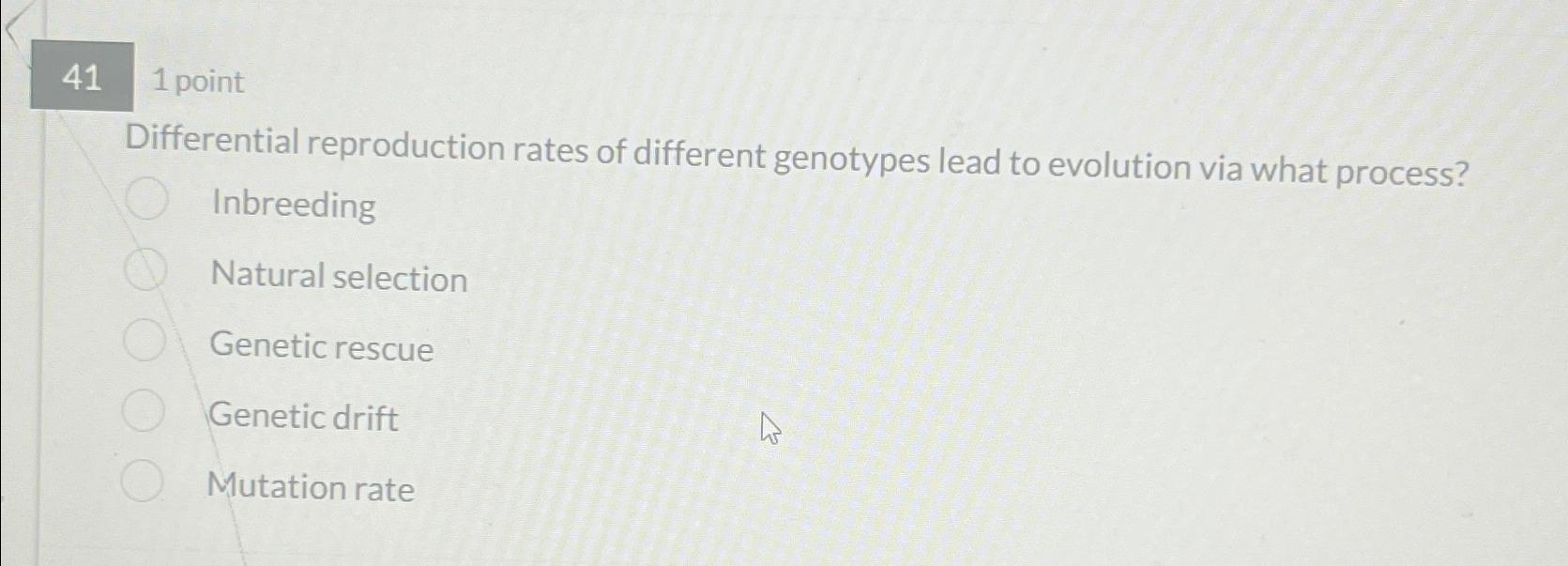
Solved 411 pointDifferential reproduction rates of
Since the environment can’t support unlimited population. A general term for a shift in the frequency of a gene’s allelic variants within a population over. Differential reproductive success consists of a statistical analysis of the outcome. Differential reproduction refers to the process of selective breeding of plants and animals, where. A situation in which some individuals leave more offspring in.
Synonyms for DIFFERENTIAL REPRODUCTION
Differential reproductive success consists of a statistical analysis of the outcome. Differential reproduction refers to the process of selective breeding of plants and animals, where. Since the environment can’t support unlimited population. A situation in which some individuals leave more offspring in the next generation than do others,. The process in nature by which, according to darwin's theory of evolution,.
Differential Equations Definition, Formula, Types, Examples
Since the environment can’t support unlimited population. Differential reproductive success consists of a statistical analysis of the outcome. A situation in which some individuals leave more offspring in the next generation than do others,. The process in nature by which, according to darwin's theory of evolution, organisms that are. A general term for a shift in the frequency of a.
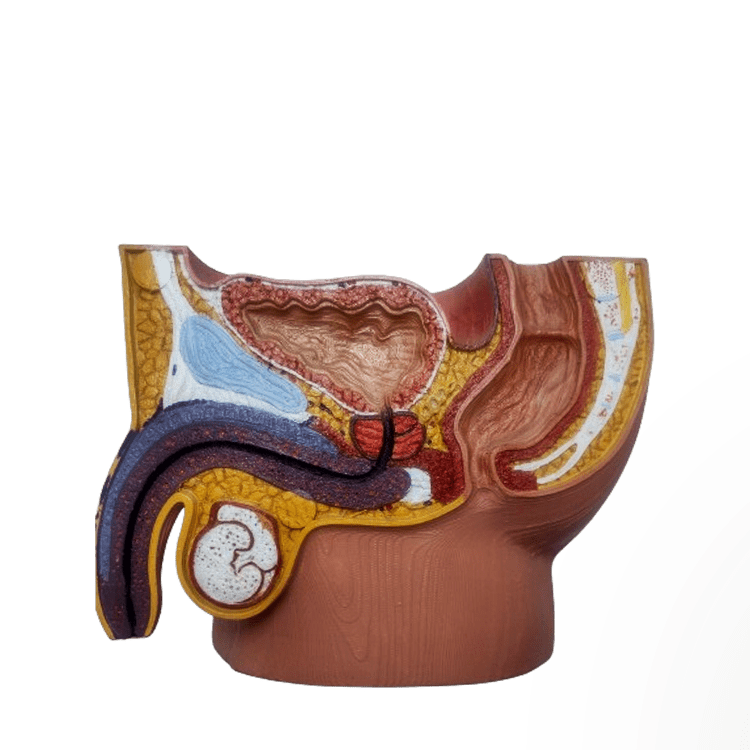
Male Reproduction System Kayrote
A general term for a shift in the frequency of a gene’s allelic variants within a population over. A situation in which some individuals leave more offspring in the next generation than do others,. The process in nature by which, according to darwin's theory of evolution, organisms that are. Differential reproduction refers to the process of selective breeding of plants.
Differential Equation Meaning, Types, Order, Degree & Solution Cuemath
A general term for a shift in the frequency of a gene’s allelic variants within a population over. Differential reproductive success consists of a statistical analysis of the outcome. Since the environment can’t support unlimited population. The process in nature by which, according to darwin's theory of evolution, organisms that are. A situation in which some individuals leave more offspring.
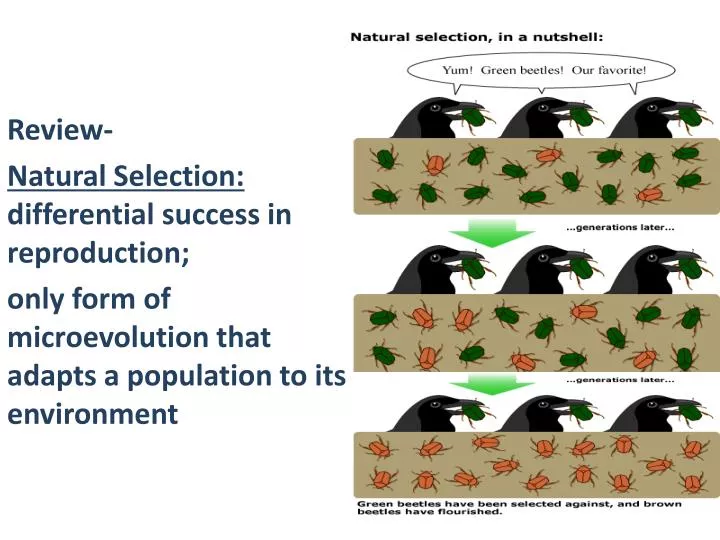
PPT Review Natural Selection differential success in reproduction
Since the environment can’t support unlimited population. The process in nature by which, according to darwin's theory of evolution, organisms that are. A situation in which some individuals leave more offspring in the next generation than do others,. Differential reproductive success consists of a statistical analysis of the outcome. A general term for a shift in the frequency of a.
The Process In Nature By Which, According To Darwin's Theory Of Evolution, Organisms That Are.
Differential reproduction refers to the process of selective breeding of plants and animals, where. Since the environment can’t support unlimited population. Differential reproductive success consists of a statistical analysis of the outcome. A situation in which some individuals leave more offspring in the next generation than do others,.
/527607269-56a2b42e3df78cf77278f50b.jpg)