Constant Coefficient Differential Equation - Learn how to solve homogeneous and nonhomogeneous linear differential equations. If a ( x), b ( x), and c ( x) are actually constants, a ( x) ≡ a ≠ 0, b ( x) ≡ b, c ( x) ≡ c, then the equation. Steinuniversity of connecticut linear differential equations with constant coefficients. The general form for a homogeneous constant coefficient second order linear. We first consider the homogenous equation with constant coefficients: This is a second order linear homogeneous equation with constant. Ay′ ′ + by′ + cy = 0 (3.2.1).
This is a second order linear homogeneous equation with constant. Ay′ ′ + by′ + cy = 0 (3.2.1). The general form for a homogeneous constant coefficient second order linear. Steinuniversity of connecticut linear differential equations with constant coefficients. Learn how to solve homogeneous and nonhomogeneous linear differential equations. If a ( x), b ( x), and c ( x) are actually constants, a ( x) ≡ a ≠ 0, b ( x) ≡ b, c ( x) ≡ c, then the equation. We first consider the homogenous equation with constant coefficients:
This is a second order linear homogeneous equation with constant. We first consider the homogenous equation with constant coefficients: The general form for a homogeneous constant coefficient second order linear. Ay′ ′ + by′ + cy = 0 (3.2.1). Learn how to solve homogeneous and nonhomogeneous linear differential equations. If a ( x), b ( x), and c ( x) are actually constants, a ( x) ≡ a ≠ 0, b ( x) ≡ b, c ( x) ≡ c, then the equation. Steinuniversity of connecticut linear differential equations with constant coefficients.
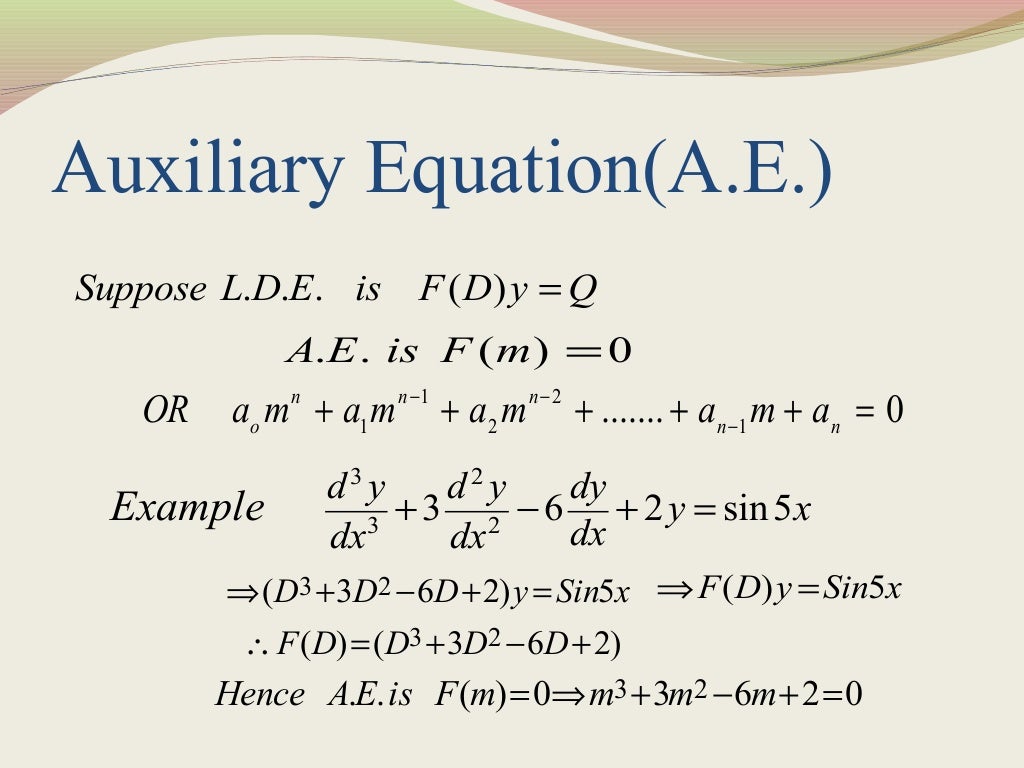
Linear differential equation with constant coefficient
The general form for a homogeneous constant coefficient second order linear. Ay′ ′ + by′ + cy = 0 (3.2.1). Learn how to solve homogeneous and nonhomogeneous linear differential equations. If a ( x), b ( x), and c ( x) are actually constants, a ( x) ≡ a ≠ 0, b ( x) ≡ b, c ( x) ≡.
Linear differential equation with constant coefficient
This is a second order linear homogeneous equation with constant. The general form for a homogeneous constant coefficient second order linear. Steinuniversity of connecticut linear differential equations with constant coefficients. If a ( x), b ( x), and c ( x) are actually constants, a ( x) ≡ a ≠ 0, b ( x) ≡ b, c ( x) ≡.
Solve the following linear differential equation with constant
Learn how to solve homogeneous and nonhomogeneous linear differential equations. The general form for a homogeneous constant coefficient second order linear. Ay′ ′ + by′ + cy = 0 (3.2.1). If a ( x), b ( x), and c ( x) are actually constants, a ( x) ≡ a ≠ 0, b ( x) ≡ b, c ( x) ≡.
SOLUTION Linear differential equation with constant coefficient
Ay′ ′ + by′ + cy = 0 (3.2.1). Learn how to solve homogeneous and nonhomogeneous linear differential equations. This is a second order linear homogeneous equation with constant. Steinuniversity of connecticut linear differential equations with constant coefficients. We first consider the homogenous equation with constant coefficients:
Linear differential equation with constant coefficient
We first consider the homogenous equation with constant coefficients: If a ( x), b ( x), and c ( x) are actually constants, a ( x) ≡ a ≠ 0, b ( x) ≡ b, c ( x) ≡ c, then the equation. This is a second order linear homogeneous equation with constant. The general form for a homogeneous constant.
Linear differential equation with constant coefficient
We first consider the homogenous equation with constant coefficients: Ay′ ′ + by′ + cy = 0 (3.2.1). This is a second order linear homogeneous equation with constant. The general form for a homogeneous constant coefficient second order linear. Steinuniversity of connecticut linear differential equations with constant coefficients.
Linear differential equation with constant coefficient
This is a second order linear homogeneous equation with constant. We first consider the homogenous equation with constant coefficients: The general form for a homogeneous constant coefficient second order linear. Learn how to solve homogeneous and nonhomogeneous linear differential equations. Ay′ ′ + by′ + cy = 0 (3.2.1).
Linear differential equation with constant coefficient
We first consider the homogenous equation with constant coefficients: The general form for a homogeneous constant coefficient second order linear. Steinuniversity of connecticut linear differential equations with constant coefficients. Ay′ ′ + by′ + cy = 0 (3.2.1). Learn how to solve homogeneous and nonhomogeneous linear differential equations.
Linear differential equation with constant coefficient
If a ( x), b ( x), and c ( x) are actually constants, a ( x) ≡ a ≠ 0, b ( x) ≡ b, c ( x) ≡ c, then the equation. The general form for a homogeneous constant coefficient second order linear. Ay′ ′ + by′ + cy = 0 (3.2.1). Steinuniversity of connecticut linear differential equations.
Linear differential equation with constant coefficient
The general form for a homogeneous constant coefficient second order linear. Ay′ ′ + by′ + cy = 0 (3.2.1). We first consider the homogenous equation with constant coefficients: Steinuniversity of connecticut linear differential equations with constant coefficients. If a ( x), b ( x), and c ( x) are actually constants, a ( x) ≡ a ≠ 0, b.
Ay′ ′ + By′ + Cy = 0 (3.2.1).
Steinuniversity of connecticut linear differential equations with constant coefficients. We first consider the homogenous equation with constant coefficients: Learn how to solve homogeneous and nonhomogeneous linear differential equations. The general form for a homogeneous constant coefficient second order linear.
If A ( X), B ( X), And C ( X) Are Actually Constants, A ( X) ≡ A ≠ 0, B ( X) ≡ B, C ( X) ≡ C, Then The Equation.
This is a second order linear homogeneous equation with constant.