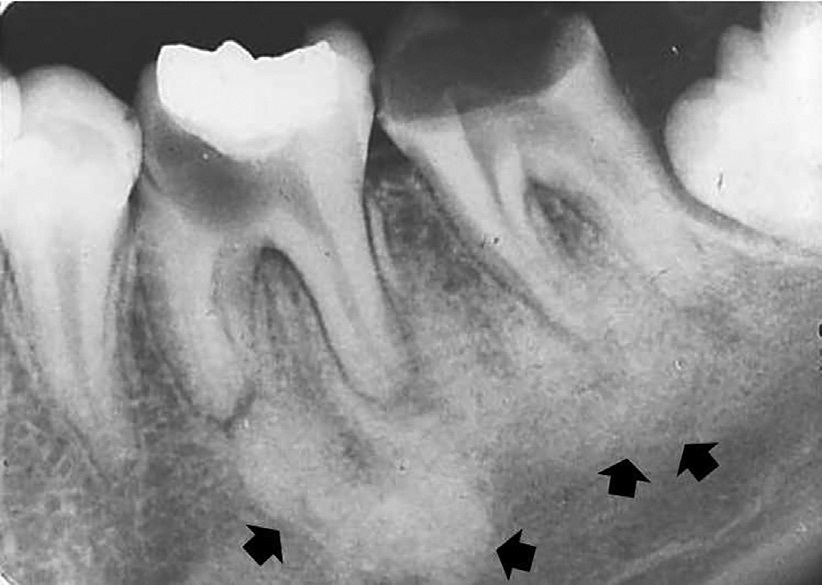
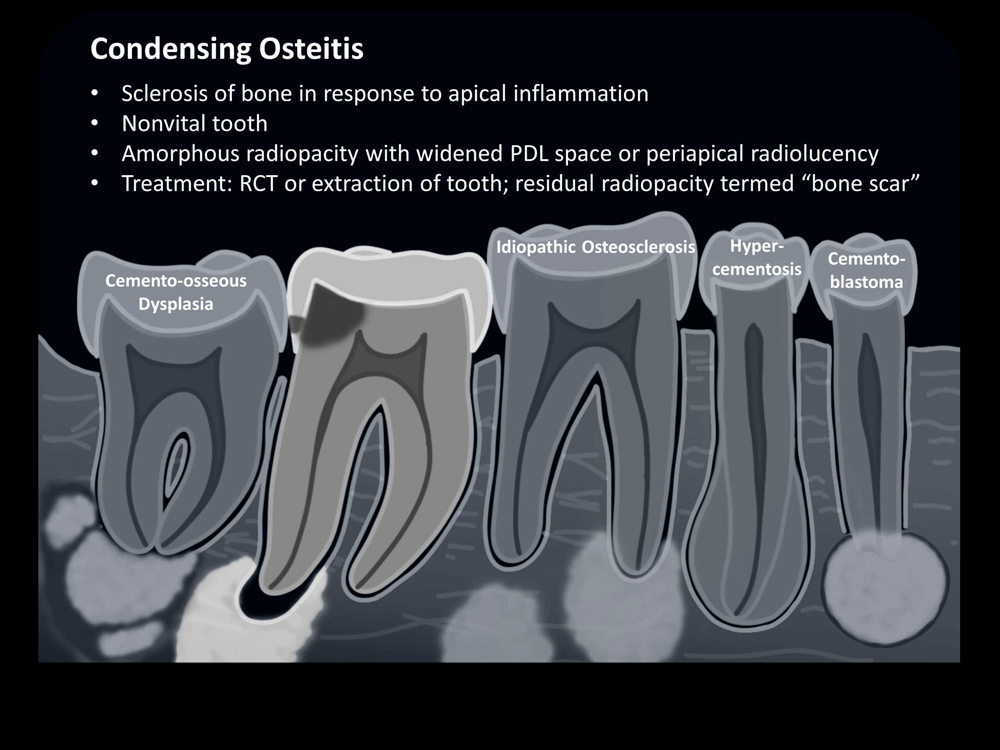
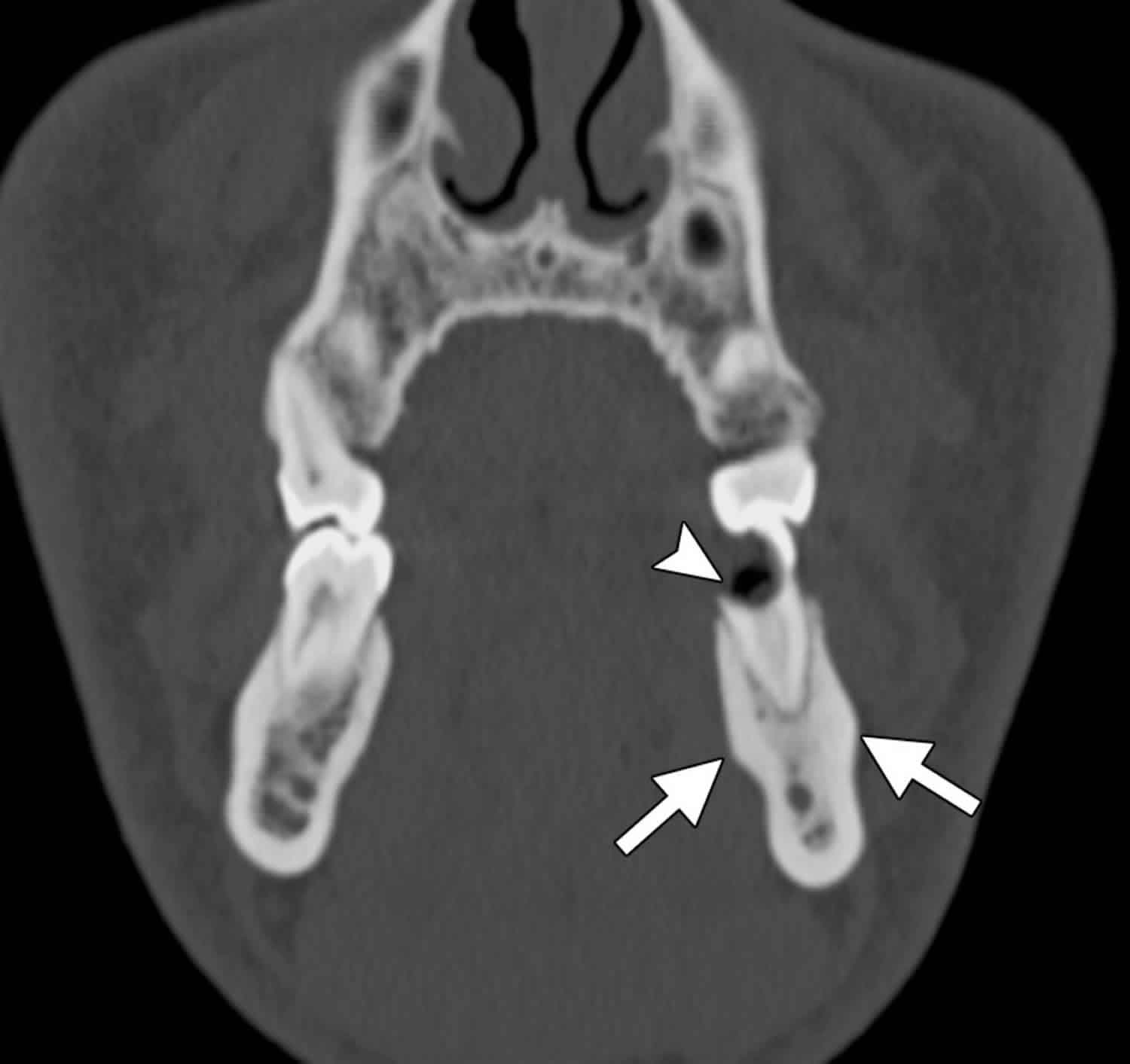
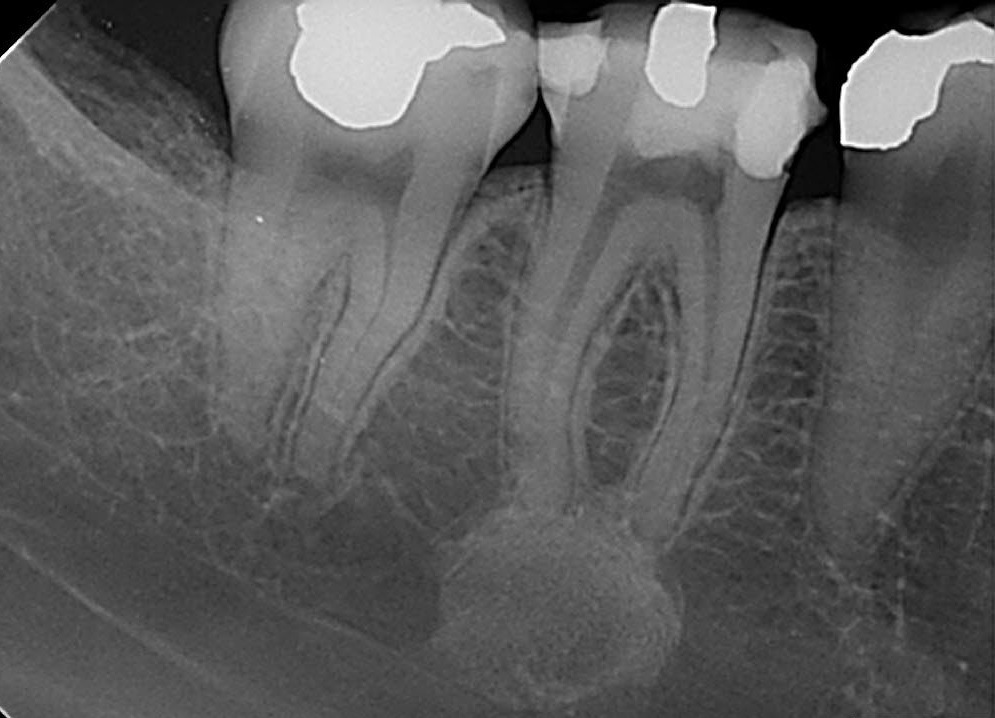
Condensing Osteitis Differential Diagnosis - Condensing osteitis is most often seen on panoramic xray as a radiopaque lesion. Aetiological treatment of pulp inflammation or occlusal trauma is recommended. Mandibular left molar pa radiograph showing condensing osteitis in relation to both. Condensing osteitis is a diffuse radiopaque lesion representing a localized bony reaction to a low. Diagnosis typically involves a clinical examination by a dentist or endodontist, complemented by.
Mandibular left molar pa radiograph showing condensing osteitis in relation to both. Diagnosis typically involves a clinical examination by a dentist or endodontist, complemented by. Condensing osteitis is most often seen on panoramic xray as a radiopaque lesion. Condensing osteitis is a diffuse radiopaque lesion representing a localized bony reaction to a low. Aetiological treatment of pulp inflammation or occlusal trauma is recommended.
Aetiological treatment of pulp inflammation or occlusal trauma is recommended. Diagnosis typically involves a clinical examination by a dentist or endodontist, complemented by. Condensing osteitis is a diffuse radiopaque lesion representing a localized bony reaction to a low. Condensing osteitis is most often seen on panoramic xray as a radiopaque lesion. Mandibular left molar pa radiograph showing condensing osteitis in relation to both.
Condensing osteitis News Dentagama
Condensing osteitis is most often seen on panoramic xray as a radiopaque lesion. Diagnosis typically involves a clinical examination by a dentist or endodontist, complemented by. Aetiological treatment of pulp inflammation or occlusal trauma is recommended. Mandibular left molar pa radiograph showing condensing osteitis in relation to both. Condensing osteitis is a diffuse radiopaque lesion representing a localized bony reaction.
Condensing Osteitis The Condition of Extra Bone Growth
Diagnosis typically involves a clinical examination by a dentist or endodontist, complemented by. Condensing osteitis is a diffuse radiopaque lesion representing a localized bony reaction to a low. Condensing osteitis is most often seen on panoramic xray as a radiopaque lesion. Mandibular left molar pa radiograph showing condensing osteitis in relation to both. Aetiological treatment of pulp inflammation or occlusal.
Condensing osteitis wikidoc
Condensing osteitis is most often seen on panoramic xray as a radiopaque lesion. Aetiological treatment of pulp inflammation or occlusal trauma is recommended. Condensing osteitis is a diffuse radiopaque lesion representing a localized bony reaction to a low. Diagnosis typically involves a clinical examination by a dentist or endodontist, complemented by. Mandibular left molar pa radiograph showing condensing osteitis in.
Condensing Osteitis Symptoms, Diagnosis and Management Oris Dental
Aetiological treatment of pulp inflammation or occlusal trauma is recommended. Condensing osteitis is most often seen on panoramic xray as a radiopaque lesion. Diagnosis typically involves a clinical examination by a dentist or endodontist, complemented by. Condensing osteitis is a diffuse radiopaque lesion representing a localized bony reaction to a low. Mandibular left molar pa radiograph showing condensing osteitis in.
Condensing Osteitis Teeth at Vanessa Welborn blog
Condensing osteitis is most often seen on panoramic xray as a radiopaque lesion. Mandibular left molar pa radiograph showing condensing osteitis in relation to both. Aetiological treatment of pulp inflammation or occlusal trauma is recommended. Diagnosis typically involves a clinical examination by a dentist or endodontist, complemented by. Condensing osteitis is a diffuse radiopaque lesion representing a localized bony reaction.
Condensing osteitis definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis & treatment
Mandibular left molar pa radiograph showing condensing osteitis in relation to both. Aetiological treatment of pulp inflammation or occlusal trauma is recommended. Condensing osteitis is a diffuse radiopaque lesion representing a localized bony reaction to a low. Condensing osteitis is most often seen on panoramic xray as a radiopaque lesion. Diagnosis typically involves a clinical examination by a dentist or.
Condensing Osteitis Teeth at Vanessa Welborn blog
Diagnosis typically involves a clinical examination by a dentist or endodontist, complemented by. Condensing osteitis is most often seen on panoramic xray as a radiopaque lesion. Mandibular left molar pa radiograph showing condensing osteitis in relation to both. Condensing osteitis is a diffuse radiopaque lesion representing a localized bony reaction to a low. Aetiological treatment of pulp inflammation or occlusal.
Condensing osteitis definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis & treatment
Diagnosis typically involves a clinical examination by a dentist or endodontist, complemented by. Aetiological treatment of pulp inflammation or occlusal trauma is recommended. Condensing osteitis is a diffuse radiopaque lesion representing a localized bony reaction to a low. Mandibular left molar pa radiograph showing condensing osteitis in relation to both. Condensing osteitis is most often seen on panoramic xray as.
Condensing osteitis News Dentagama
Aetiological treatment of pulp inflammation or occlusal trauma is recommended. Condensing osteitis is most often seen on panoramic xray as a radiopaque lesion. Diagnosis typically involves a clinical examination by a dentist or endodontist, complemented by. Condensing osteitis is a diffuse radiopaque lesion representing a localized bony reaction to a low. Mandibular left molar pa radiograph showing condensing osteitis in.
(PDF) Bilateral condensing osteitis of clavicles differential
Mandibular left molar pa radiograph showing condensing osteitis in relation to both. Condensing osteitis is most often seen on panoramic xray as a radiopaque lesion. Aetiological treatment of pulp inflammation or occlusal trauma is recommended. Diagnosis typically involves a clinical examination by a dentist or endodontist, complemented by. Condensing osteitis is a diffuse radiopaque lesion representing a localized bony reaction.
Condensing Osteitis Is Most Often Seen On Panoramic Xray As A Radiopaque Lesion.
Diagnosis typically involves a clinical examination by a dentist or endodontist, complemented by. Mandibular left molar pa radiograph showing condensing osteitis in relation to both. Condensing osteitis is a diffuse radiopaque lesion representing a localized bony reaction to a low. Aetiological treatment of pulp inflammation or occlusal trauma is recommended.