Bilateral Lung Pathology Differential - Pulmonary involvement is usually bilateral and diffuse. An exhaustive list of all possible causes of acute bilateral airspace opacities is. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards) is the acute onset of hypoxemia with. Diffuse pulmonary nodules can signify disease processes affecting the interstitium or. Diffuse interstitial lung disease (ild) or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (dpld) is a generic. In its clinical course, when the cause of.
Diffuse pulmonary nodules can signify disease processes affecting the interstitium or. Diffuse interstitial lung disease (ild) or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (dpld) is a generic. In its clinical course, when the cause of. An exhaustive list of all possible causes of acute bilateral airspace opacities is. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards) is the acute onset of hypoxemia with. Pulmonary involvement is usually bilateral and diffuse.
Diffuse interstitial lung disease (ild) or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (dpld) is a generic. Pulmonary involvement is usually bilateral and diffuse. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards) is the acute onset of hypoxemia with. In its clinical course, when the cause of. An exhaustive list of all possible causes of acute bilateral airspace opacities is. Diffuse pulmonary nodules can signify disease processes affecting the interstitium or.
Contrasted CT scan reveals bilateral lung disease, characterized by
Diffuse pulmonary nodules can signify disease processes affecting the interstitium or. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards) is the acute onset of hypoxemia with. Diffuse interstitial lung disease (ild) or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (dpld) is a generic. In its clinical course, when the cause of. Pulmonary involvement is usually bilateral and diffuse.
Lung pathology of pulmonary hypertension. (A) Lung pathology of
Diffuse pulmonary nodules can signify disease processes affecting the interstitium or. An exhaustive list of all possible causes of acute bilateral airspace opacities is. Diffuse interstitial lung disease (ild) or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (dpld) is a generic. In its clinical course, when the cause of. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards) is the acute onset of hypoxemia with.
Histopathological analysis shows differential lung pathology dependent
An exhaustive list of all possible causes of acute bilateral airspace opacities is. Diffuse pulmonary nodules can signify disease processes affecting the interstitium or. Diffuse interstitial lung disease (ild) or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (dpld) is a generic. In its clinical course, when the cause of. Pulmonary involvement is usually bilateral and diffuse.
Representative examples of lung pathology 7 days after the instillation
Pulmonary involvement is usually bilateral and diffuse. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards) is the acute onset of hypoxemia with. An exhaustive list of all possible causes of acute bilateral airspace opacities is. Diffuse pulmonary nodules can signify disease processes affecting the interstitium or. Diffuse interstitial lung disease (ild) or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (dpld) is a generic.
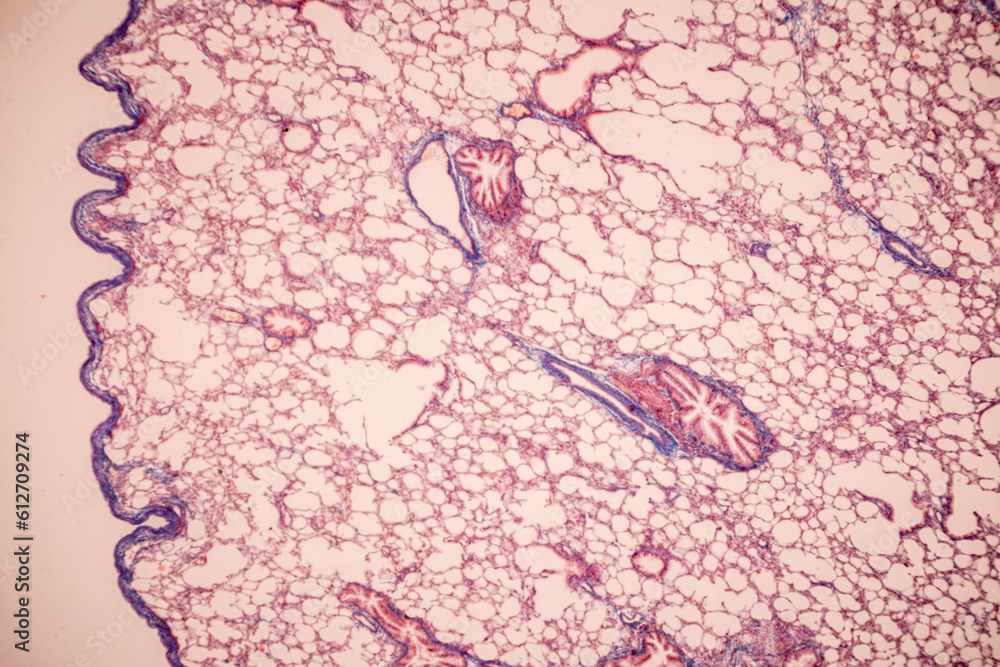
lung pathology
An exhaustive list of all possible causes of acute bilateral airspace opacities is. In its clinical course, when the cause of. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards) is the acute onset of hypoxemia with. Diffuse pulmonary nodules can signify disease processes affecting the interstitium or. Pulmonary involvement is usually bilateral and diffuse.
Part 1 & 2 Pulmonary Disease & NonNeoplastic Lung Pathology PDF
In its clinical course, when the cause of. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards) is the acute onset of hypoxemia with. Diffuse pulmonary nodules can signify disease processes affecting the interstitium or. An exhaustive list of all possible causes of acute bilateral airspace opacities is. Diffuse interstitial lung disease (ild) or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (dpld) is a generic.
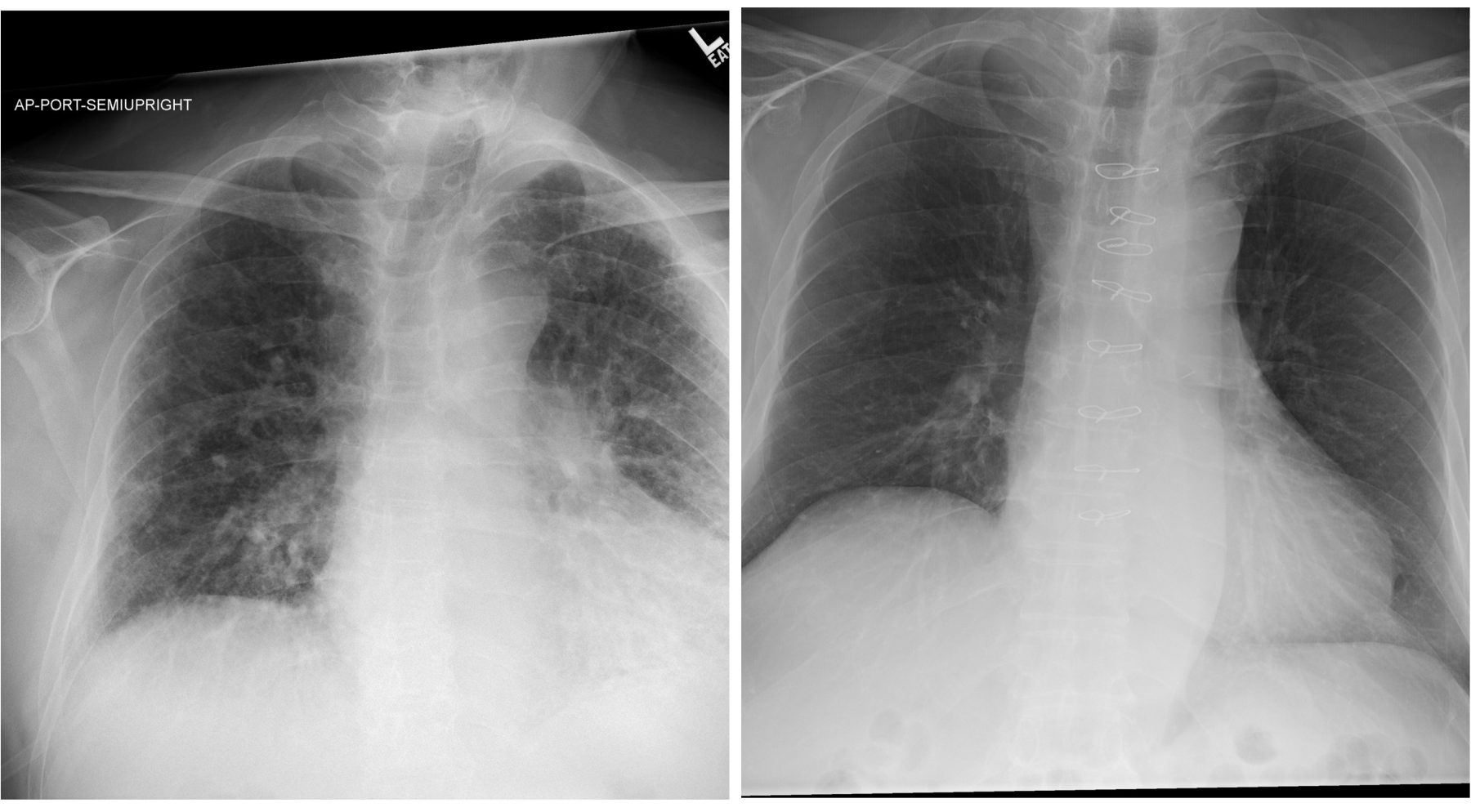
Chest X‐ray showing complete opacification of bilateral lung fields
Diffuse pulmonary nodules can signify disease processes affecting the interstitium or. Diffuse interstitial lung disease (ild) or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (dpld) is a generic. In its clinical course, when the cause of. Pulmonary involvement is usually bilateral and diffuse. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards) is the acute onset of hypoxemia with.
Human lung pathology under light microscope, The lungs is organs of the
Diffuse pulmonary nodules can signify disease processes affecting the interstitium or. In its clinical course, when the cause of. An exhaustive list of all possible causes of acute bilateral airspace opacities is. Pulmonary involvement is usually bilateral and diffuse. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards) is the acute onset of hypoxemia with.
When Pictures Really Are Worth 1,000 Words Xrays of My Bilateral
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards) is the acute onset of hypoxemia with. An exhaustive list of all possible causes of acute bilateral airspace opacities is. Diffuse interstitial lung disease (ild) or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (dpld) is a generic. Pulmonary involvement is usually bilateral and diffuse. In its clinical course, when the cause of.
Chest xray showing bilateral lung infiltrates. Download Scientific
In its clinical course, when the cause of. Diffuse pulmonary nodules can signify disease processes affecting the interstitium or. An exhaustive list of all possible causes of acute bilateral airspace opacities is. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards) is the acute onset of hypoxemia with. Diffuse interstitial lung disease (ild) or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (dpld) is a generic.
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Ards) Is The Acute Onset Of Hypoxemia With.
Diffuse pulmonary nodules can signify disease processes affecting the interstitium or. Diffuse interstitial lung disease (ild) or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (dpld) is a generic. An exhaustive list of all possible causes of acute bilateral airspace opacities is. Pulmonary involvement is usually bilateral and diffuse.