Bernoulli's Equation Differential Equation - Bernoulli differential equation is one of the topics that fall under calculus and differential equations. It is a nonlinear differential equation of a specific kind that can be. In this section we are going to take a look at differential equations in the form, where p(x) p (x) and q(x) q (x) are continuous functions on the interval we’re working on and n n is a. When n = 1 the. How to solve this special first order differential equation. When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation. A bernoulli equation has this form: Dy dx +p(x)y = q(x)yn, where n 6= 1 (the equation is thus nonlinear). To find the solution, change the dependent variable. A bernoulli differential equation can be written in the following standard form:
A bernoulli differential equation can be written in the following standard form: When n = 1 the. To find the solution, change the dependent variable. A bernoulli equation has this form: Bernoulli differential equation is one of the topics that fall under calculus and differential equations. When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation. Dy dx +p(x)y = q(x)yn, where n 6= 1 (the equation is thus nonlinear). It is a nonlinear differential equation of a specific kind that can be. In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is called a bernoulli differential equation if it is of the form y ′ + p ( x ) y = q ( x ) y n , {\displaystyle y'+p(x)y=q(x)y^{n},} where n {\displaystyle n} is. In this section we are going to take a look at differential equations in the form, where p(x) p (x) and q(x) q (x) are continuous functions on the interval we’re working on and n n is a.
When n = 1 the. When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation. A bernoulli differential equation can be written in the following standard form: Bernoulli differential equation is one of the topics that fall under calculus and differential equations. To find the solution, change the dependent variable. A bernoulli equation has this form: How to solve this special first order differential equation. In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is called a bernoulli differential equation if it is of the form y ′ + p ( x ) y = q ( x ) y n , {\displaystyle y'+p(x)y=q(x)y^{n},} where n {\displaystyle n} is. In this section we are going to take a look at differential equations in the form, where p(x) p (x) and q(x) q (x) are continuous functions on the interval we’re working on and n n is a. It is a nonlinear differential equation of a specific kind that can be.
Bernoulli’s differential equation Yawin
When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation. It is a nonlinear differential equation of a specific kind that can be. In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is called a bernoulli differential equation if it is of the form y ′ + p ( x ) y = q ( x ).
What is Bernoulli's Equation Bernoulli's Principle Definition
A bernoulli equation has this form: In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is called a bernoulli differential equation if it is of the form y ′ + p ( x ) y = q ( x ) y n , {\displaystyle y'+p(x)y=q(x)y^{n},} where n {\displaystyle n} is. When n = 1 the. In this section we are going to take.
Differential Equation Calculator
How to solve this special first order differential equation. In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is called a bernoulli differential equation if it is of the form y ′ + p ( x ) y = q ( x ) y n , {\displaystyle y'+p(x)y=q(x)y^{n},} where n {\displaystyle n} is. In this section we are going to take a look.
SOLUTION Differential equation the bernoulli equation Studypool
Dy dx +p(x)y = q(x)yn, where n 6= 1 (the equation is thus nonlinear). Bernoulli differential equation is one of the topics that fall under calculus and differential equations. A bernoulli differential equation can be written in the following standard form: In this section we are going to take a look at differential equations in the form, where p(x) p.
SOLUTION Differential equation bernoulli s equations with solved
In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is called a bernoulli differential equation if it is of the form y ′ + p ( x ) y = q ( x ) y n , {\displaystyle y'+p(x)y=q(x)y^{n},} where n {\displaystyle n} is. When n = 1 the. When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear.
Differential Equation Calculator
A bernoulli differential equation can be written in the following standard form: A bernoulli equation has this form: Dy dx +p(x)y = q(x)yn, where n 6= 1 (the equation is thus nonlinear). In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is called a bernoulli differential equation if it is of the form y ′ + p ( x ) y = q.
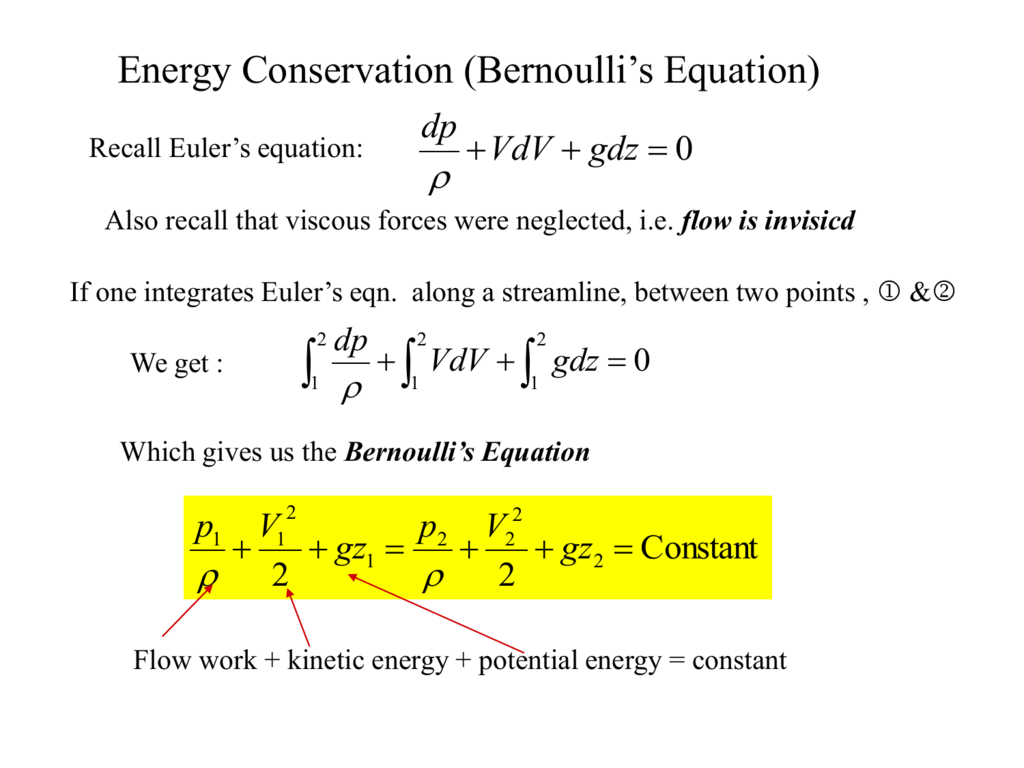
Energy Conservation (Bernoulli's Equation)
When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation. In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is called a bernoulli differential equation if it is of the form y ′ + p ( x ) y = q ( x ) y n , {\displaystyle y'+p(x)y=q(x)y^{n},} where n {\displaystyle n} is. It is a.
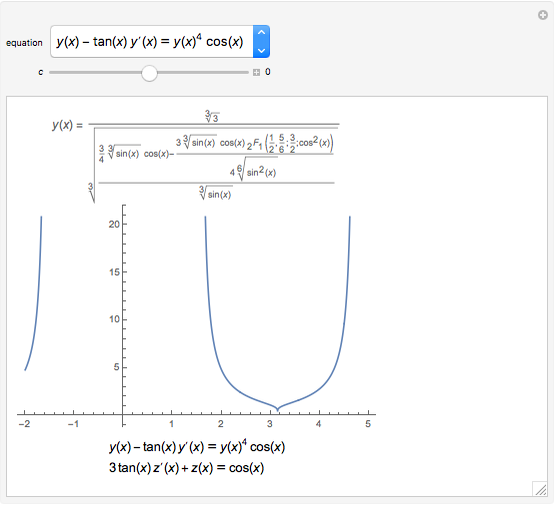
Bernoulli's Differential Equation Wolfram Demonstrations Project
In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is called a bernoulli differential equation if it is of the form y ′ + p ( x ) y = q ( x ) y n , {\displaystyle y'+p(x)y=q(x)y^{n},} where n {\displaystyle n} is. When n = 1 the. Bernoulli differential equation is one of the topics that fall under calculus and differential.
The Bernoulli's Equation in Different Conditions Download Scientific
In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is called a bernoulli differential equation if it is of the form y ′ + p ( x ) y = q ( x ) y n , {\displaystyle y'+p(x)y=q(x)y^{n},} where n {\displaystyle n} is. A bernoulli differential equation can be written in the following standard form: Dy dx +p(x)y = q(x)yn, where n.
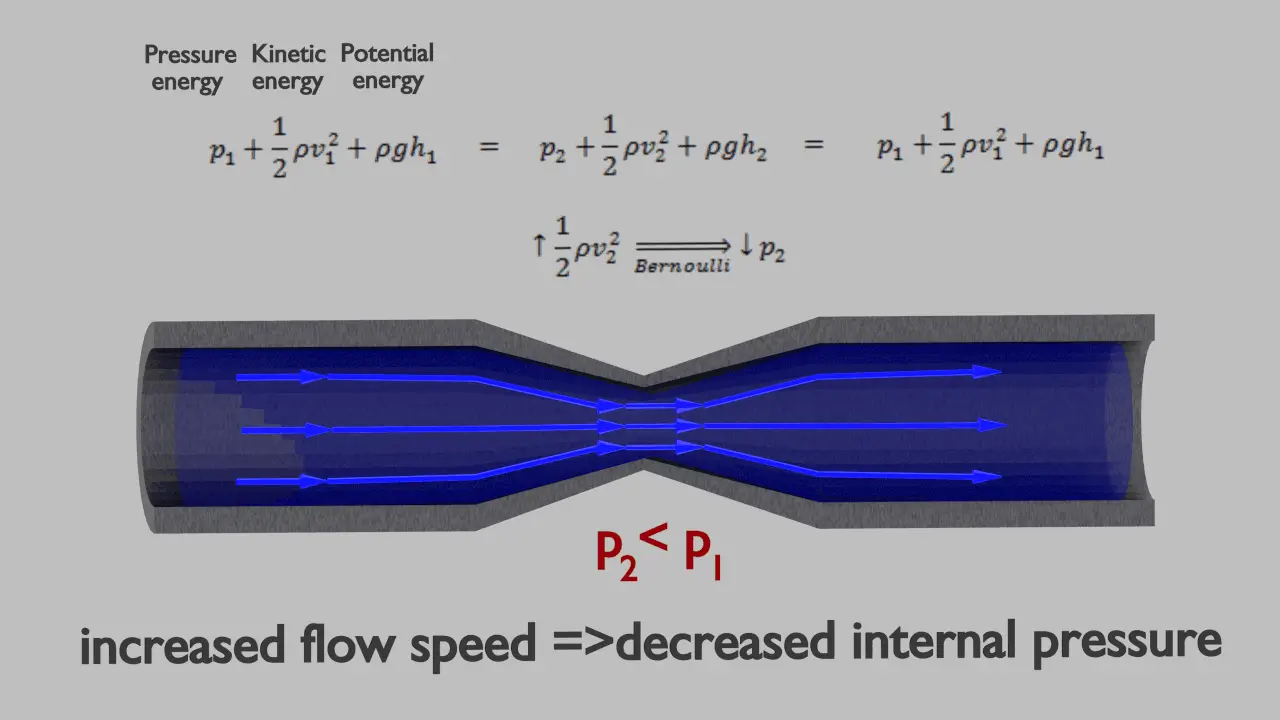
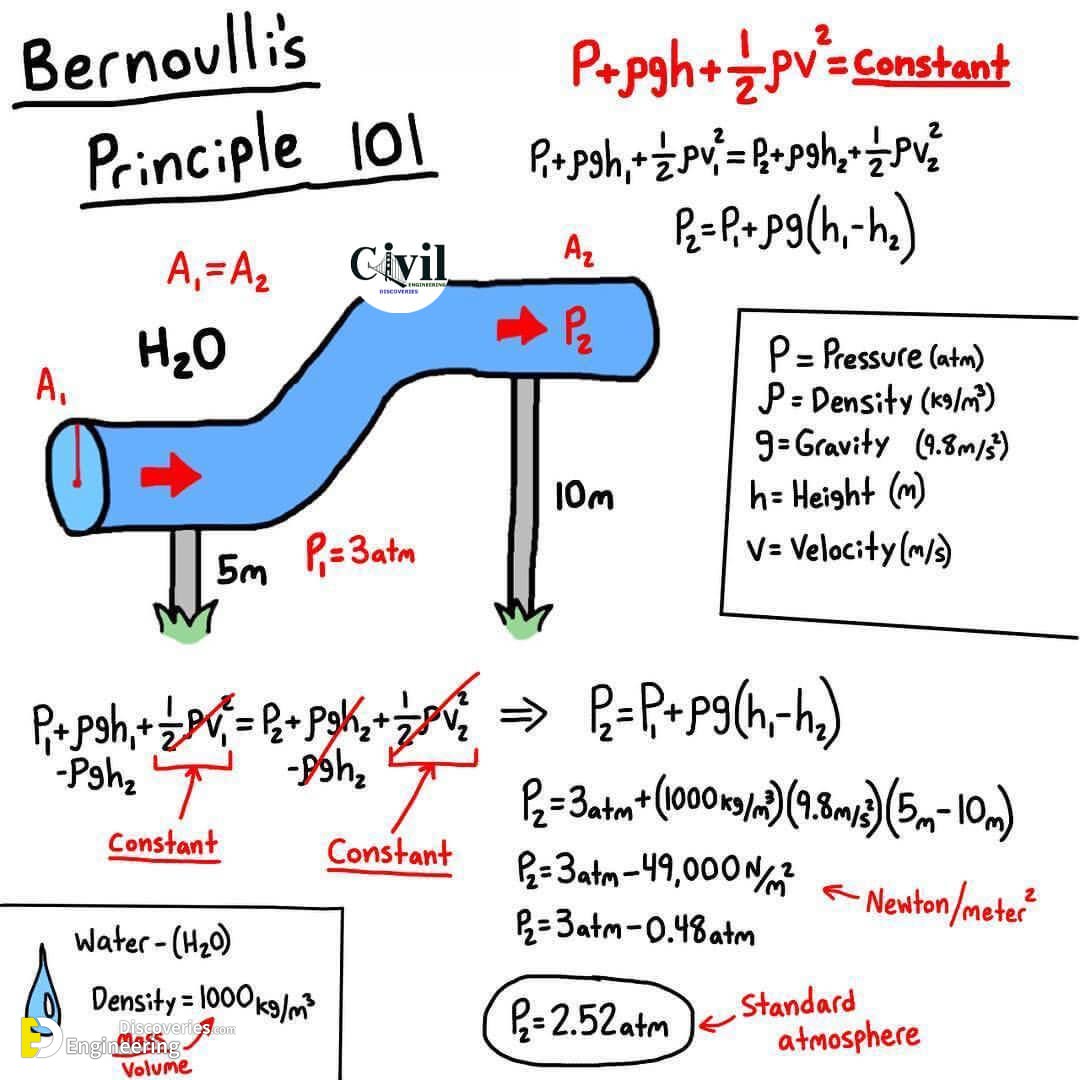
Understanding Bernoulli's Equation Engineering Discoveries
When n = 1 the. A bernoulli differential equation can be written in the following standard form: In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is called a bernoulli differential equation if it is of the form y ′ + p ( x ) y = q ( x ) y n , {\displaystyle y'+p(x)y=q(x)y^{n},} where n {\displaystyle n} is. To find.
When N = 0 The Equation Can Be Solved As A First Order Linear Differential Equation.
Bernoulli differential equation is one of the topics that fall under calculus and differential equations. Dy dx +p(x)y = q(x)yn, where n 6= 1 (the equation is thus nonlinear). A bernoulli equation has this form: A bernoulli differential equation can be written in the following standard form:
It Is A Nonlinear Differential Equation Of A Specific Kind That Can Be.
When n = 1 the. In this section we are going to take a look at differential equations in the form, where p(x) p (x) and q(x) q (x) are continuous functions on the interval we’re working on and n n is a. How to solve this special first order differential equation. In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is called a bernoulli differential equation if it is of the form y ′ + p ( x ) y = q ( x ) y n , {\displaystyle y'+p(x)y=q(x)y^{n},} where n {\displaystyle n} is.